Features
World Science Day:

A message to Inculcate Scientific Temper in Society
By Prof. Kirthi Tennakone
(ktenna@yahoo.co.uk)
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) has proclaimed 10th November as the day for celebrating science – The World Science Day for Peace and Development. The proclamation aims to promote science in the society creating public awareness to exploit its virtues. The theme this year is “science with and for society “- implying wider participation of citizens in scientific endeavors and strengthening the engagement of science for social advancement, particularly to highlight how science deals with the COVID-19 pandemic
What is science?
To most of us, science means technological gadgetries or happenings like going to the moon. Actually it is much more than a means of providing material comforts and glamorous technological feats.
Science is fathoming principles operating in nature by observation, experiment and reasoning leading to generalizations or theories continuously tested and corrected to explain things and make predictions.
The above thought process or scientific method find equal relevance in gaining knowledge, analysis of existing ideas, planning and innovative design, decision making at all levels and matters of everyday life. The grasping the essence of scientific method, enlighten people to abandon ideologies, occultism and fundamentalism as baseless maleficent trends.
Universality of Science
Unlike other human affairs – science stands unique – not having color, caste or divisions based on geography and inherently secular. We have Western music and Eastern music, Western cooking and Eastern cooking, but not Western Science and Eastern Science. There is no elitism in science or in its practitioners- science sits in harmony with art, literature, ethics and virtuous politics. The intrinsic nature of science make it the mightiest force to unite the world. Unfortunately, for no fault of science, findings of science have been used for destruction, widening differences. Inequalities in access to sciences leads social disparity and geopolitical divisions. Recognizing necessity of addressing these issues, is an aspiration of the World Science Day.
Scientific Temper
The readiness of citizens to adopt scientific method is scientific temper. This quality drives societies towards progress – creating conditions conducive to innovation and wellbeing. The term ‘scientific temper’ was coined by Pandith Jawaharlal Nehru who elaborated the idea in his inspiring statement. “What is needed is the scientific approach, the adventurous and yet the critical temper of science, search for truth and new knowledge, the refusal to accept anything without testing and trial, the capacity to change previous conclusions in the face of new evidence, the reliance on observed facts and not on pre-conceived theory, the hard discipline of the mind – all this is necessary, not merely for application of science but for life itself and solution of its problems”.
Nehru
The Constitution of India adopted the Nehru’s concept of scientific temper in its 42nd amendment declaring “It shall be the duty of every citizen of India to develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform”
Today, inoculation of scientific temper in society and compelling the policy maker to adopt it is an urgency ever than before. The adherence to scientific method in all decisions and actions remain the only option available for us to face the challenge of the COVID pandemic.
Achievements of Science
Apart from being the progenitor of modern technology, science provided answers many puzzles confronting humanity – including ones highlighted below.
The cause of many diseases have determined, enabling design of efficacious remedies. Here, a finding relevant in today’s context is the fundamental understanding how viruses infect human body, which paved way for producing the first successful drug to combat a viral disease. American Chemist Gertrude Elion who showed that the drug named Acyclovir is effective in curing herpes and chickenpox, shared the 1988 Nobel Prize for Physiology. Gertrude work is a solace for humanity- an earnest hope, a cure for COVID-19 will be found.
Elion
 The age-old problem how animals and plants inherit their characters was explained by Watson and Crick in terms of DNA. So-called PCR test for detecting COVID and gene editing – alteration of DNA for advantage are two of the thousands of applications of this discovery. This year chemistry Nobel Prize was awarded to two women scientists, Emmanuelle Charpentier for the latter discovery
The age-old problem how animals and plants inherit their characters was explained by Watson and Crick in terms of DNA. So-called PCR test for detecting COVID and gene editing – alteration of DNA for advantage are two of the thousands of applications of this discovery. This year chemistry Nobel Prize was awarded to two women scientists, Emmanuelle Charpentier for the latter discovery
The Structure of matter up to tinier and tinier bits have been elucidated. Here, the existence of an elementary particle now named Higgs boson was predicted by Peter Higgs and two other physicists. The gigantic machine – Large Hadron Collider built in Geneva at a cost of 5 billion dollars confirmed prediction in 2012 – huge cost but zero-dollar immediate economic return! Why the machine was built at such a huge cost? It proved the correctness of one of the deepest conclusions of human intellect grasped decades earlier – a confidence to use science to face gravest challenges and look forward. The worth of this result and the message it passes to the society far exceeds the monetary cost- a minuscule compared to the costs of weapons development.
Likewise, the universe in excessively large expanses of space and time has been explored, revealing perplexing mysteries – pointing to the conclusion that space, time and matter originated 14 billion years ago as an explosion.
Science facilitates understanding, provokes curiosity and endless exploration – raises questions seeking answers- identify the potentialities of innovations and tells how to implement them. Hidden secrets and problems are there for future generations to explore and solve. Science tells how we should proceed in solving problems.
Evidently, recommendations or remedies coming from sources other than science – rituals or quackery will not mitigate the COVID-19 pandemic
Technology
Technology means making things to ease living or gain more knowledge. Ancients knew how to make tools and build civil engineering structures- this is empherical technology acquired by experience and trial and error improvement. Advent of science transformed ancient technology. Scientific concepts opened the door for designing and planning – delivering superior products far more quickly compared to empherical methods.
All modern technological achievements are outcomes of science progressing in different directions. For example, the techniques behind your smartphone is a consequence of a paradigm shift in science – birth of the quantum theory in early nineteen hundreds. It is extremely unlikely that someone to have invented a smartphone previously.
The most significant cause for revolutionary advancement in both science and technology has been use of technology purely for propose of gaining new knowledge. Galileo made telescopes and turned them to sky – beginning of observational astronomy. Since then the state-of –art technologies has been used make more powerful telescopes to unravel secrets of the cosmos. The Dutch lens maker and scientist Antoine Leeuwenhoek was first to see microbes by magnification. The subsequent adoption of newer technologies to design microscopes to see smaller entities; transformed medicine, biology and science of materials.
Science in developing nations
A major cause of weaknesses in developing countries owes much to the comparative deficiency of the scientific temper or readiness to grasp scientific method and adopt it freely and wisely.
Developing nations apparently support science considering it an essentiality for technological advancement and maintain a workforce of technicians and specialists. They pay less attention to educational, research and knowledge dissemination activities that engender scientific temper into the society. Generally a blind overemphasize of technological aspects of science expecting immediate economic returns – a counterproductive policy generally advocated by mediocrity among scientific community who misguide the politician.
Pandith Nehru, delivering a speech at the foundation ceremony of the Tata Institute of Fundamental Studies in 1954 has said “Lot of people may not know, why an emphasis is being put on science. Why so much money is spent? The big countries have more power while our country has remained poor. If we wish to empower our country, which is now independent, we have to create a strong base- so we can learn the basics. This may not show immediate results but finally result in uplift of the country”.
The present status of science and technology in India speaks volumes of the well-foundedness of Nehru’s prophecy
A primary reason why the nations continuing to be poor and failing to reap fruits of science is neglect of basics and essential foundations of technology. They entertain any fashion ending with the term ‘technology’- biotechnology, nanotechnology, communication technology etc., forgetting to cure deficiencies in older but essential disciplines. Sri Lanka is weak in chemical industry – raw materials exported without value addition. Yet there is a tendency to believe that nanotechnology would be the biggest hope for our industry. Science is a prerequisite to technology and establishing older a technology, is a prerequisite to newer technologies.
Example of Rwanda
Until late 1900s Rwanda was one of the most unfortunate nations in the world. Civil war killed nearly one million people, destroying the entire infrastructure. As Rwanda owes not much natural resources, the new government realized that the only path to wake-up would be to exploit science and technology. Rwandan President Paul Kagame invited the mathematical physicist Professor Romain Murenzi, a national of his country working in United States to serve as the Minister of Science. Murenzi drew up the policy on science, technology and innovation emphasizing both basic and applied aspects and the necessity of evidence based decision making in all affairs. Although Rwanda didn’t inherit a grandeur of an ancient culture to boast, the effectives of right policies are now visible – earning the credential “Africa’s Science and Tech Powerhouse “in a timeline of just two decades.
Useful and useless disciplines
All over the world, especially in developing countries there is a tendency to demarcate academic discipline into two categories – useful and useless. Arts, humanities and fundamental science in the latter category and technological and business studies in the former. Amanda Ruggeri an editor of BBC, in her essay titled “.Why worthless humanities degree may set you for life? ” state , education policies echoed around the world implicate – forget the liberal arts – non vocational degrees that include natural and social sciences, mathematics and humanities, such as history, philosophy and languages”. Science and arts enrich each other, they are not contrasting and every nation need takers of both and everybody benefits from acquaintance and appreciation these two cultures.
Science Curricula and Teaching: A Prevalent Trend
Today science curricula and teaching emphasize learning techniques, neglecting explanations as to how the techniques came to being. Syllabi are revised omitting thought provoking basics to accommodate technological stuff- believing these lead to technical competence necessary for generating innovations. It is pointless to introduce workings of an electron microscope into a school science curriculum without providing cheap ordinary optical microscopes to rural schools. Sometimes the optical microscope available in schools are locked-up in a cupboards. Rather than introducing complicated intricacies into a syllabus a child should be provided with an opportunity to see a bacterium through an ordinary microscope. Such an activity would turn him or her to a productive scientist or an innovator.
Diverting science towards technology is absolutely important. However every country needs to have universities and few institutions engaging in frontier areas of fundamental science. Unfortunately, these intuition grab technological themes in disguise of relevance, avoiding curiosity driven original investigation. Universities have academic freedom to choose their research themes but duty bound to absorb themselves in highest level intellectual pursuits for the shake of knowledge. Those few institutions should necessarily follow the mandated theme with gross deviations.
One of the most effective ways of introducing scientific attitude to a society would be to arouse curiosity. Developing countries need to strengthen research and education in fundamental science and highlight world’s achievements to motivate general public – particularly the younger who are more curious.
The benefit of science is not only finding ways to provide material needs to improve the quality of living but also the enrichment of the way of our thinking. The latter facilitates building the capacity to solve problems. Questions also arise as result of imagination and curiosity. Puzzles of this natures have paved the way towards ground breaking discoveries.
The most effective way to inculcate science into the society would be to highlight and popularize the intrinsic value of science as a thought process so powerful enough to resolve many issues, confronting the society. Such an approach will naturally drive the minds towards technological innovations.
The inculcation of scientific attitude into a society does not mean converting every citizen to a scientist. A society needs persons dedicated to their profession and varying individual interests, whether it farming, carpentry or stamp collecting. Yet exposing all of them to scientific method and motivation of its usage in appropriate occasions will pay the dividend.
Features
Trump’s Delinquent War Game: No Early End in Sight

It is fruitless analyzing US President Trump’s reasons for going to war with Iran or the conflicting outcomes he says he is looking to have in the end. It is quite possible that he may have made the decision to attack Iran after being cajoled by Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. It is a good time to attack because Iran is at its weakest moment yet posing an imminent threat warranting a pre-emptive attack. Strange and circular reasoning is needed to justify unnecessary wars.
True to form, Trump did not consult any of his western allies the way his predecessors did in similar situations. He ignored NATO as much as he ignored the UN. Nor did Trump go through the internally established broad consultation and focused decision making processes that US presidents usually undertake before committing American forces abroad. The Congress, the institution under Article I of the American Constitution, was also habitually ignored .
It is likely that Trump secured tacit support from other Middle East governments, especially the Gulf states of Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, UAE and Oman that are Iran’s neighbours. The latter may seem to have been hoping to have it both ways – letting US and Israel take out Iran’s reprehensible regime while appearing to stay neutral in the fight. That calculation or miscalculation explosively backfired when Iran started firing drones and missiles not only into Israel but practically into every Arabian (Persian) Gulf country, hitting not only American bases but also civilian centres. The welcoming reputation of the Gulf countries as secure oases for foreign investment, tourism, sports and entertainment has been seriously shattered.
Escalating War
In addition to the six Gulf states, Iranian missiles have reached Iraq, Jordan and far away Cyprus. Even Turkey and Azerbaijan have been targeted. Israel has been hit and has suffered casualties far more in the few days of fighting than it has in all the past aerial skirmishes. The US outposts are under attack as well. The Embassy in Kuwait was hit on Monday. The next day two drones fell on the US Embassy in Riyad, Saudi Arbia, apparently the most fortified American outpost abroad. This was followed by drone attacks on the US Consulate in Dubai and on the American military base in Qatar, the largest in the region. Six American servicemen have been killed and 18 injured in the first four days of the war.
The Trump Administration that has been notorious for picking countries to deny US visas, is now asking Americans to return home from 14 Middle East countries for the sake of their own safety. Washington has closed its embassies in Riyadh and in Kuwait and has ordered non-emergency staff and families to depart from its other embassies in the region. But leaving the embattled region is not easy with flights cancelled and air space closed. Belatedly, the State Department is scrambling to make arrangements to help stranded Americans find their way out by air or by land to neighbouring countries. It is the same story with governments of other countries whose citizens are living and working in large numbers in the Middle East. The monarchs of Middle East depend on migrants of many hues to do their blue collar and white collar labour while keeping their citizens in cocoons of comfort. That equilibrium is now under threat.
Iran’s losses are of course significantly higher, already hit by over 2,000 Israeli and US missiles reaching multiple targets in 26 of Iran’s 31 provinces. Over a thousand people have been killed including 180 students in a girls’ school in the south. Buildings and infrastructure and installations are being devastated. Israel has opened a full second front in Lebanon using the thoughtless Hezbollah’s aerial provocation as excuse for once again badgering Beirut and its suburbs. A week into the war there is no early end in sight. Only escalation.
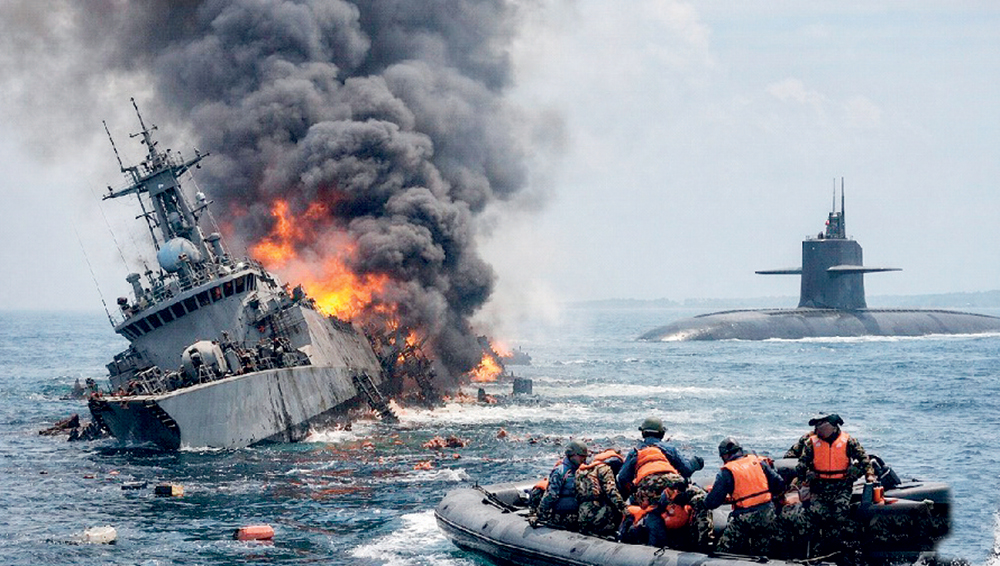
Not only Iran but even the US is extending the waves of war. A US submarine torpedoed without warning and sank the IRIS Dena, a Moudge-class Iranian frigate, in the Indian Ocean not far from Galle. The frigate had about 130 sailors on board and was sailing home after participating in the International Fleet Review (IFR) and multilateral exercise, MILAN-2026, organized by the Indian Navy at Visakhapatnam. The frigate was reportedly not carrying weapons in keeping with the protocol for international naval exercises. Also, according to reports, Americans were in the know of the Fleet Review in India and its participants. Yet the US Secretary of War, Pete Hegseth, went on public television to say: “An American submarine sunk an Iranian warship that thought it was safe in international waters,. Instead, it was sunk by a torpedo. Quiet death.” How tragically surreal!
It fell to little Sri Lanka to respond to the distress call of the sinking sailors. Sri Lanka’s navy and emergency services have done an admirable job in fulfilling their humanitarian responsibilities. The Sri Lankan government has also handled a difficult situation, complicated by a second Iranian ship, with poise and purpose. On the other hand, unless I missed it, I have not seen any official reaction by the Indian government to the reckless sinking of one of its guest ships. An opposition parliamentarian of the Congress Party, Pawan Khera, has been cited as asking on X, “Does India have no influence left in its own neighbourhood? Or has that space also been quietly ceded to Washington and Tel Aviv?”
India is not the only one that has ceded space and time to the bullying whims of Donald Trump. With the exception of Spain, the entire West is literally genuflecting for fear of getting hit by tariffs. Notwithstanding the US Supreme Court ruling much of Trump’s tariffs to be illegal, and a Federal Court now ordering that the collected monies should be paid back to those who had paid them. The situation is a far cry from the European reaction and the public lampooning of Bush and Blair when they went to war in Iraq two decades ago.
The Missile Math
Two factors may objectively determine the course and the duration of Trump’s war: weapons stockpiles and the oil and natural gas markets. Higher prices of oil and natural gas will increase domestic pressure on Washington to find an offramp to the war sooner than later. Other countries may have to suffer not only higher prices but also shortages of fuel. The weapons are a different matter.
The ongoing aerial warfare involves the use of drones and missiles to attack as well using defensive missiles to detect and destroy incoming projectiles before they hit their targets. After the beating it took last year and this week, Iran has no missile defense system to speak of, but it has both a stockpile of drones and missiles and capacity for rapidly producing them. The military question is whether Iran’s stockpile of offensive drones and missiles can outlast the combined defensive missile stockpile of the US, Israel and the Middle Eastern countries. There is no clear answer, only speculations about Iran and US concerns over its own stockpile.
The “troubling missile math,” as it has been called is underscored by the concern expressed by US Secretary of State Marco Rubio, that Iran has the capacity for “producing, by some estimates, over 100 of these missiles a month. Compare that to the six or seven interceptors that can be built a month.” The worry is also about the depleting impact that the extended use of interceptors against Iran will have on American stockpiles elsewhere in the world, especially in areas involving China. That is part of the standard military calculation. What is bizarre now is that after starting the war on a whim last Saturday, Trump is convening a meeting within a week on Friday with weapon manufacturers to urge them to produce more.
Secretary Rubio also added that destroying Iran’s missile capacity is the goal of the US campaign. Iran’s missile capacity involves different missiles with different flight ranges. The shorter the range the larger the stock. Iran does not have the standard two-way intercontinental ballistic missile, and it is nowhere near developing them. The current Administration has recklessly claimed that Iran is capable of launching missiles to hit America and has unfairly named and blamed all previous presidents for not doing anything about it.
Trump’s predecessors were fully aware of America’s unmatched military superiority and Iran’s utter limitations. They were also aware that going to war with Iran to destroy its drones and limited range missiles will create more problems without solving any. The Obama Administration in consort with China, UK, France, Germany and Russia produced the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) committing Iran to have nuclear programs for peaceful uses only. Trump tore up the Obama plan and instead of using the opportunity this year to create a new and stronger program, chose to start a war instead.
As things are, unless the US-Israel axis succeeds in literally obliterating all drones and missile production resources in Iran, Iran will retain the capacity to produce drones and short-range missiles with which it could torment its neighbours for long after Trump and Netanyahu declare the war to be over. It may never be a long-range menace – in fact, it never was – but it could become an even greater short-range nuisance.
The US is no longer indicating a time limit for the war to end. For Netanyahu, it is not going to be an endless war. Of the two, Israel might be having some clear objectives to be achieved before ending the war. For Trump and his Administration, on the other hand, the objectives of the war are chaotically evolving on a daily basis, and the world will have to wait till the man of the deal finds some outcome or outcomes that can be shown as success and call it quits.
Regime Change: Insult after Injury
Iran’s Supreme Leader and forty or so other top Iranian leaders were taken out in the first minute of the fight by “pinpoint bombing”, as Trump boasted in his auto-poetic truth social post. But the Iranian regime has not collapsed. It has shown remarkable structure and durability despite the death of its Supreme Leader. It is America that is showing its inability to contain its Supreme Leader from going berserk on the world through tariff and bombing terror – in spite of all the checks and balances that Americans thought they have constitutionally practised and honed over 250 years. It is also poetic comeuppance for the Iranian regime that, after 47 years, it should now face its undoing by an unhinged American hegemon for theocratically subverting the 1979 revolution from realizing any of its secular possibilities.
Trump now wants to add insult to injury by forcing himself into the succession process for selecting a successor to Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. Iran has a well-established succession process, almost akin to the conclave in the Vatican, in which a body of 88 elder clerics, the Assembly of Experts, are convened to elect through a secret vote the new Supreme Leader. Over the last few days, it has been widely reported that the late Khamenei’s 56 year old son Mojtaba Khamenei has emerged as the leading candidate to succeed his father as the next Supreme Leader. His political strength and leadership claim are reportedly based on his close connections to the powerful Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
Mojtaba is said to have been the shadow Supreme Leader in recent years making decisions in place of his ageing father. For that reason, he is reviled by Iranians who are opposed to the regime and who have been oppressed by the regime. There are also allegations and rumours about his amassing wealth and investing in properties and opening bank accounts in London and Geneva. At the same time, there could also be sympathy for him in the ruling circles because it was not only his father and his mother who were killed in the first minute bombing but also his wife and his son. While ideologically he has been a hawk, Mojtaba is also described as a “pragmatist.” Being pragmatic in the current context, according an unnamed Tehran academic, would imply that Mojtaba Khamenei will be seeking revenge for the US-Israeli attacks on his family and his country – not through victory in war but by ensuring “the survival of the Islamic Republic.”
President Trump is not bothered about the dynamics and nuances of Iranian leadership politics and has no hesitation in inserting himself into the succession process. In an interview with the American news website Axios, Trump has declared that he wants to be personally involved in the Iranian succession process, and that the selection of the younger Khamenei would be “unacceptable” to him, because “Khamenei’s son is a lightweight.” “I have to be involved in the appointment, like with Delcy [Rodríguez] in Venezuela,” Trump went on, because “we want someone that will bring harmony and peace to Iran.”
Comparing Venezuela and Iran is no less preposterous than the Bush Administration’s decision to invade Iraq in addition to Afghanistan in order to punish Al Quaeda for 9/11. Trump now appears to be seeking not a wholesale regime change but a retail leadership change in the old regime. This is only the latest addition to his lengthening wish list for the war with no method or plan to achieve any of them. Add to the growing list the news that the CIA is putting together a Kurdish insurgent force to foment “a popular uprising” within Iran.
That would be back to the future and the return of the CIA, but in a totally different situation from what it was 73 years ago when the CIA, in partnership with Britain’s MI6, staged the 1953 coup that ousted the government of then Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh and reinforced the monarchical rule of Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, the Shah of Iran. The purported plan now is to arm and organize Kurdish forces in Iran and Iraq to engage the Iranian security forces and thereby to create internal spaces for Iranian civilians to come out to the streets and take over their country. Those who are entertaining this plan are also aware of its inherent dangers and cross-border and pan-ethnic implications for Iraq and even Turkey and Syria. Trump is reportedly aware of the plan but may not be bothered about its unintended consequences.
by Rajan Philips
Features
How Helmut Kohl braved the tsunami, P-TOMs and Kadirgamar assassination

This is the place to introduce the episode of ex-Chancellor Helmut Kohl of Germany. “This legendary unifier of post war Germany was at a small hotel in Hikkaduwa undergoing Ayurveda treatment when the Tsunami struck. A German Minister who owned a house in Hikkaduwa and visited Lanka regularly had recommended Ayurveda treatment to The Chancellor and head of her party- the Christian Democrats.
The German Embassy was at its wits end because Kohl had disappeared without a trace. They contacted us and we activated our Grama Sevaka network to find that Kohl had been taken to the safety of his home by a hotel employee. When we offered to send a helicopter to bring him to Colombo the Chancellor had replied that it was not necessary as he was well looked after by his host. He came by car the following day in order to thank CBK for her help.
I went to President’s House with Kohl who seemed quite relaxed in his coloured shirt, crumpled pants, a grey seersucker coat and rough boots. He was full of praise for the Sri Lankan people who had helped him and all the tourists in distress due to the Tsunami. Kohl said that he wanted to help in the rehabilitation of the south in his personal capacity. When he got back to Germany he set up a group of rich friends called “Friends of Helmut Kohl” who sent money to build a hospital in Mahamodera, Galle.
The money was lodged in the German Embassy. But the usually lethargic Health department dragged its feet on the construction work on the guise that the money was not sufficient for their grandiose hospital plans ignoring the value of the superb gesture by Kohl. Unfortunately he died before the completion of the project and therefore could not keep his pledge to come to Galle for its opening.
Later in time I was a member of a Parliamentary delegation led by Speaker Karu Jayasuriya which included Sampanthan, Rauf Hakeem, Anura Dissanayake and several others. I suggested to our group that we pay a belated tribute to Helmut Kohl who had died a few months previously. This was immediately welcomed by the parliamentarians and the organizers of the tour and we jointly paid our heartfelt tribute to a great friend of Sri Lanka who was an eye witness to the success of our rehabilitation effort.
Post Tsunami Operational Management Structure (P-TOMS)
The Tsunami was particularly harsh on the eastern and northern coastline because it was directly in the way of the giant waves created in Indonesia and deflected to our shores. It also created a transformation of the political scene and the nature of the war. The LTTE had invested considerable resources in building up its “Sea Tigers”. They wanted control of the northern seas in order to increase their supply of weapons and ammunition. The Sea Tigers established a presence in east Thailand so that arms could be purchased from Cambodia, Vietnam and Thailand. The fighting in the Indo-China theatre was over and the cut rate weapons market was flourishing.
Our embassy in Bangkok had an army officer who was monitoring terrorist activities but he was helpless because Thai officials in the lower echelons were in the pay of the LTTE. In addition to that problem, the mediocre officials of our Foreign Ministry were no match for the determined LTTEers one of whom had married an influential Thai lady. With money coming in from expatriates they had even set up a shipping line which was so well run that they could finance weapons buying for the LTTE with its profits.
We had received intelligence that the LTTE was preparing for a major “Sea Tiger” operation from their base in Mullaitivu. This base area concept shows the advanced thinking of the LTTE which was attempting – then unsuccessfully – to even manufacture a low cost submarine. Fortunately for us the Tsunami wiped out the base of the “Sea Tigers” together with many of their assets such as boats, proto-type submarines and diving gear.
True to form they sent signals for talks which they had earlier broken. Their diaspora had mounted a campaign to collect funds for rehabilitation. At this stage the UN got into the act and with the World Bank and IMF persuaded the CBK government to consider a power sharing arrangement principally for the rehabilitation of the North and East. It was to be called P-TOMS. CBK appointed Jayantha Dhanapala as the head of SCOPP – a secretariat to coordinate the relief effort in the North and East. The World Bank appointed Peter Harrold, its representative in Colombo, to coordinate the P-TOMS effort with SCOPP.
Estimates were made by SCOPP regarding the amount necessary for the rehabilitation of the North and East. This budget became the talking point of several successive regimes who promised to allocate such funds in exchange for Tamil votes in the North. Mahinda Rajapaksa’s agents held this figure as a bait to promote a boycott of the Presidential poll in 2005 which threw the election which was in Ranil’s pocket to MR thereby changing the destiny of the LTTE as well of the country. [MR cleared the 50 percent hurdle by only 25,000 votes].
Perhaps to strengthen the push for P-TOMS, Kofi Annan the Secretary General of the UN arrived with a large contingent of staffers and I was asked to meet and greet him in Katunayake. We gave Annan a grand welcome but he seemed distracted and was only interested in getting his Swedish wife who was hanging back, into the spotlight. CBK had several discussions with him but we ran into a snag in that he wanted to visit the North and meet Prabhakaran.
Perhaps some of the big powers had got to him as he was in the midst of a scandal about his son from his first marriage who was facing charges of corruption. The scandal was rocking UN headquarters. Annan who was elevated from his earlier status as a UN functionary to satisfy African members, was according to several biographers, indebted to the west and could not end his tenure to the satisfaction of the majority of the UN membership.
CBK, already under pressure for mishandling the P-TOMS campaign, was adamant that Annan should not meet the LTTE which would have given the terrorists parity of status with the SL state. Since such an interpretation was circulated by virtually all political parties in the South she was pushed to a very difficult position. After much discussion Annan settled for a helicopter tour of the North. I found that he was a weak leader who was led by his nose by Mark Mallock Brown – his chief of staff, who had been in charge of UN operations even during its disastrous forays in the Congo.
Mallock Brown was later identified as a camp follower of the West who compromised the credibility of the UN. I have memories of Mallock Brown holding forth on their next step here while Annan and Dhanapala were mere passive listeners. This Western initiative of P-TOMS did not finally see the light of day. But it split the ruling coalition of the PA and JVP irrevocably and Mahinda Rajapaksa burnished his credentials as an opponent of the project. He became popular with the PA and its allied parties over and above CBK.
When the P-TOMS project was to be placed before Parliament Mahinda as Prime Minister refused to present it on the floor of the House. CBK was too weak to dismiss him partly because Lakshman Kadirgamar also was a strong opponent of P-TOMS. Instead she got Maithripala Sirisena to present the proposal. But the Opposition which was joined by the JVP including its functioning Ministers, took to the streets. The JVP members demonstrated and disturbed the proceedings from the well of the House and then resigned “en masse” from the government putting its majority in jeopardy. Mahinda’s anti-P-TOMS stand endeared him to the JVP, which had earlier preferred Kadirgamar to him, and helped him to garner votes which went a long way in ensuring his ultimate victory. He had become so powerful that CBK had no option but to accommodate him.
Assassination of Lakshman Kadirgamar
Another blow was struck at CBK and the government by the I TTE when they assassinated Lakshman Kadirgamar near the swimming pool of his house. He had a successful kidney transplant in India – with a Buddhist monk from Balangoda donating a kidney – and was asked to swim regularly as exercise by his doctors. I knew of this arrangement because when we travelled together he always asked the Foreign Office to put him tip in a hotel with a heated swimming pool.
He was about to enter the water in the swimming pool when a LTTE sniper shot him through a window in a neighbourhood flat. This dastardly crime wits condemned unanimously by the international community. India sent her Foreign Minister to attend the funeral. Ksdirgamar’s death brought CBK’s Government to the brink of collapse. The JVP though leaving the Government respected LK and paid a tribute to him by arranging for their leaders to follow his hearse on foot to Kanatte.
It must be mentioned here that LK nearly pipped Mahinda for the post of PM in 2004. He had the backing of the JVP who wanted CBK to appoint LK and in the alternative appoint Maithripala Sirisena as PM. He was also supported by India but CBK was afraid that Mahinda will break up the party if he was deprived of the Premiership. After LK’s demise she undertook a mini reshuffle and Anura Bandaranaike had his ambition of being Foreign Minister realized.
To succeed him as Minister of Industries and Foreign Investment she appointed me in addition to my portfolio of Minister of Finance. Arjuna Ranatunga was the Deputy Minister of Industries and I left most of the administrative work to him. When we had an investment promotion meeting in Delhi I invited Arjuna and Aravinda de Silva to be our delegates and they stole the show among the cricket mad Indian investors. All the tables at dinners hosted by us were taken and we had many friends appealing to us to get them reservations even at the last minute.
We had such good relations that I was invited to take part in popular TV talk shows. I remember that Shekhar Gupta invited me for a discussion on our health services with Kajol – the top Hindi film actress who was brand ambassador for Narendra Modis “clean Bharat” campaign. She was a charming young lady who recounted her enjoyable stay in Sri Lanka when she accompanied her mother Tanuja who was shooting a film in Colombo with Vijaya Kumaratunga as her co-star.
After LKs murder the fear of the LTTE was so strong that CBK could not even attend the funeral ceremony. PM Mahinda Rajapaksa represented her. This death was a bitter blow to me because as an old Trinitian friend he would always consult me on party matters. I still have a letter he wrote to me about a coffee t able book on the art of Stanley Kirinde which he sponsored in honour of our mutual college friend.
(This book is available at the Vijitha Yapa bookshops)
(Excerpted from vol. 3 of the Sarath Amunugama autobiography)
Features
The amazing biodiversity of Sri Lanka:

Nations Trust WNPS Monthly Lecture
An overview of the plants & animals on this magical island
Thursday 19 March 2026, 6.00 pm, Jasmine Hall, BMICH
In the first part of this talk, Author-Photographer Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne points out that Sri Lanka is disproportionately rich in species. He presents possible reasons for this and then makes the case that Sri Lanka is one of the best all-round wildlife destinations in the world. In the second part of the talk, he takes a whirlwind tour of several branches of the tree of life from bacteria to elephants. He uses this tour of life forms as a framework to showcase the richness of biodiversity in Sri Lanka.
He points out that very little has been done on the study of groups such as fungi and mosses and remarks how his proposal for a special visa for exchange programs, internships and volunteering could enable local academics to gain access to expertise and experienced volunteer hours from people overseas who have a passion for these areas of natural history.
With plants, he outlines the major groups of plants which are the bryophytes, lycopods, ferns and spermatophytes. The latter also knows as seed plants include the conifers (gymnosperms) and flowering plants (angiosperms). He makes reference to what is found in Sri Lanka to illustrate the importance of certain groups, such as the dipterocarp trees which are the giants of the rainforest. His photographs will illustrate examples such as carnivory, because plants employ a wide range of life strategies.
The talk will provide a very brief outline of the animal kingdom with its vast and sprawling evolutionary tree. Starting with animals that evolved early such as the sponges, he will draw attention to a few of the phyla which holds larger animals. Not surprisingly, more attention will be given to the vertebrates which command most of the popular attention. However, he will also reference invertebrate groups such as the butterflies and dragonflies, the two most popular groups of insects. Although Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne was the first to brand Sri Lanka for big game safaris, in this talk, he will bring in many of the other plant and animal groups which although lacking ‘safari appeal’ are nevertheless important in terms of biodiversity and being the subjects of research.
As Sri Lanka positions itself as a destination for high-value, experience-driven tourism, the conservation of its natural heritage becomes not just an environmental priority but an economic imperative. This lecture will be especially valuable for tourism professionals, hospitality leaders, policymakers, conservationists, students, photographers, and nature enthusiasts seeking to understand the true asset underpinning Sri Lanka’s future.
According to Rohan Pethiyagoda, ‘Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne is without question the most celebrated field naturalist the country has produced’. Bill Oddie (British TV Naturalist) has said no single individual has done so much to publicise a country for its wildlife. The speaker has authored and photographed more than 25 books and 400 articles and has played a pivotal role in branding Sri Lanka as a wildlife destination.
The WNPS Monthly Lecture Series, established in 2000, is one of Sri Lanka’s longest-running and most respected conservation knowledge platforms. Featuring leading local and international experts, the series addresses critical environmental issues through science-based insights and open public dialogue. Beyond the lecture hall, these sessions foster collaboration, inspire research, and often seed conservation projects and advocacy initiatives. The series remains a cornerstone of Sri Lanka’s conservation community—connecting knowledge with action
The Lecture is supported by Nations Trust Bank and is open all, entrance free
- Sloth Bear – Yala (pix by Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne)
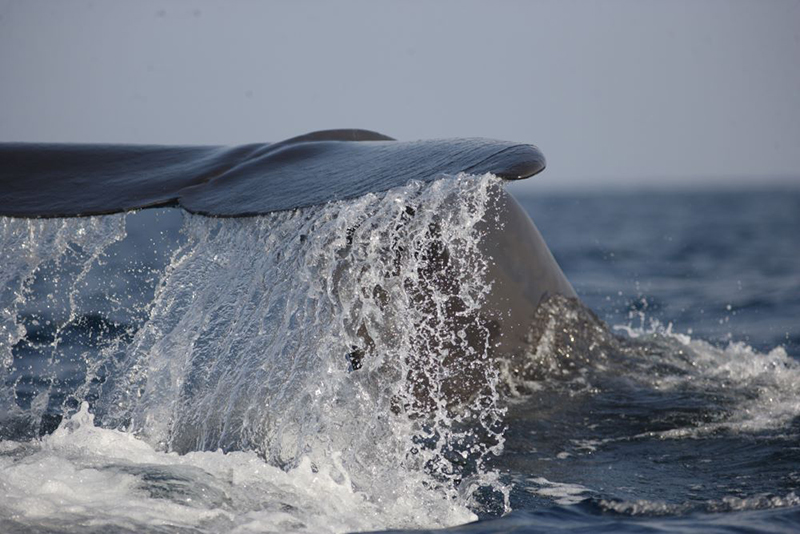
- Sperm Whale – Kalpitiya
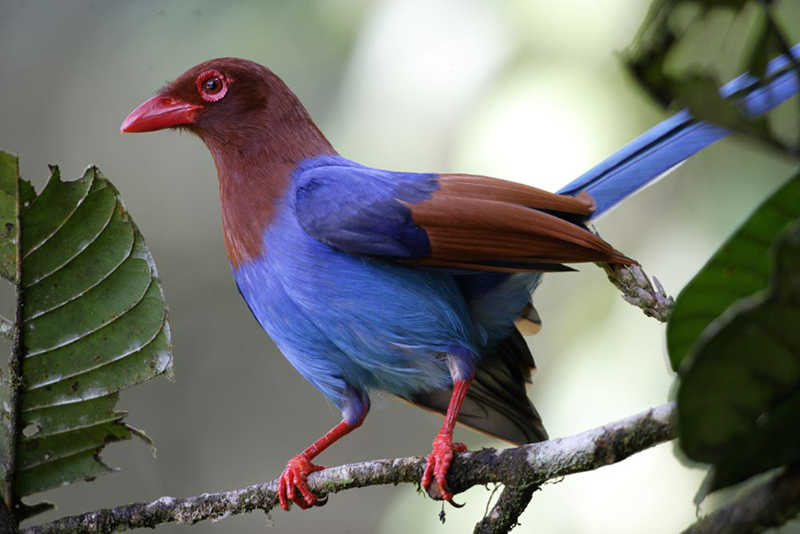
- Sri Lanka Blue Magpie – Sinharaja
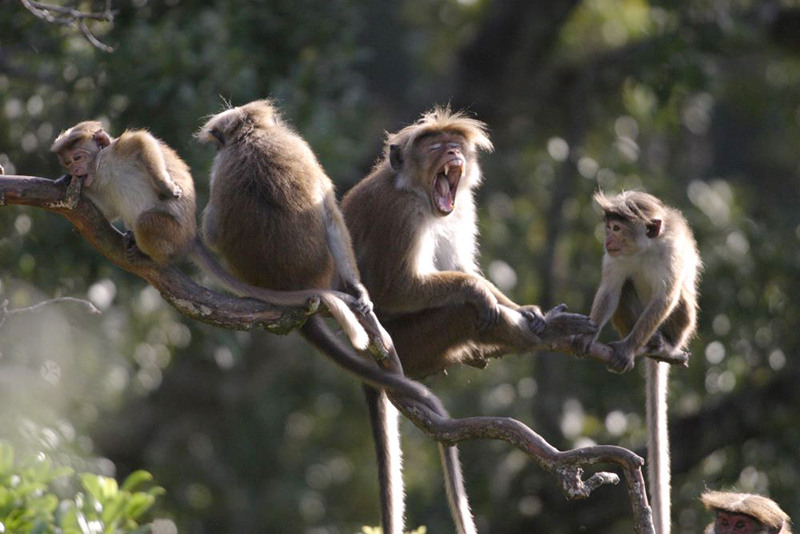
- Toque Monkey – Hakgala
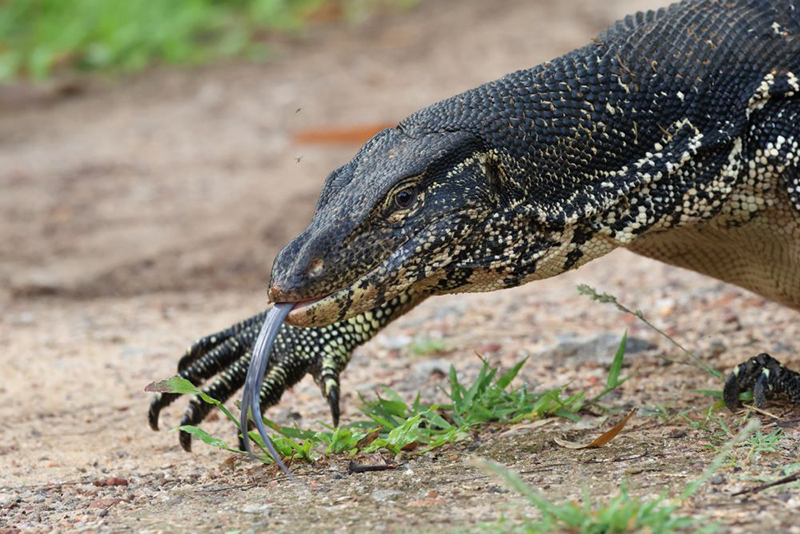
- Water Monitor – Diyasaru
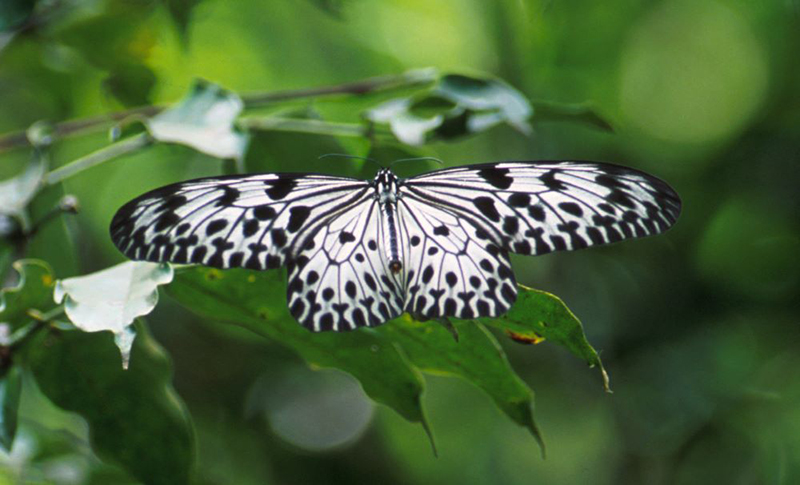
- Ceylon Tree Nymph
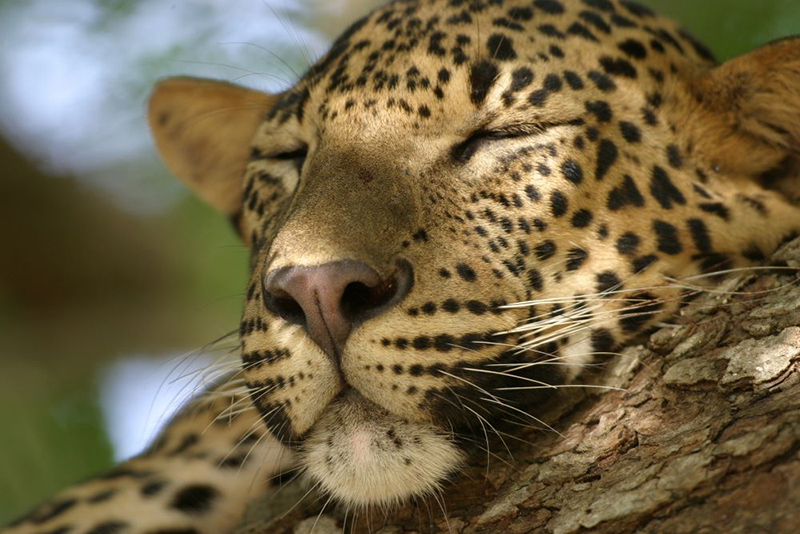
- Leopard
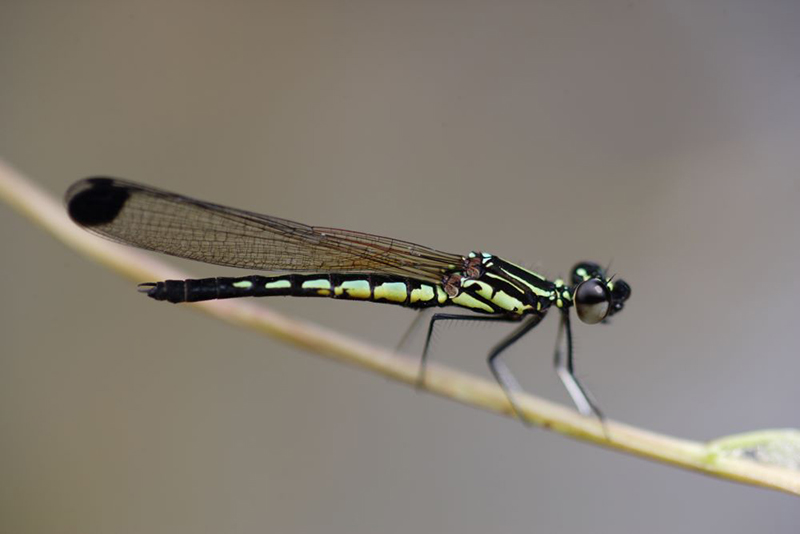
- Adam’s Gem (Libellago greeni) male – Talangama
- Indian Sunbeam – Beddegana
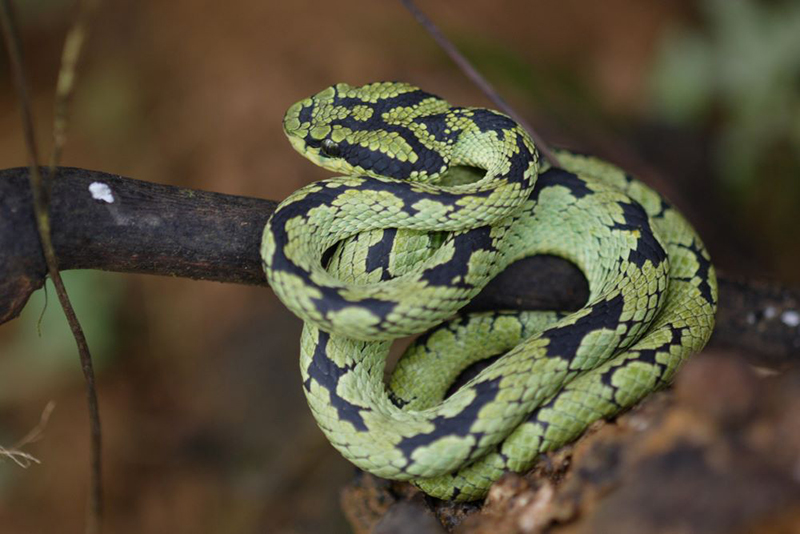
- Green Pit Viper – Sinharaja
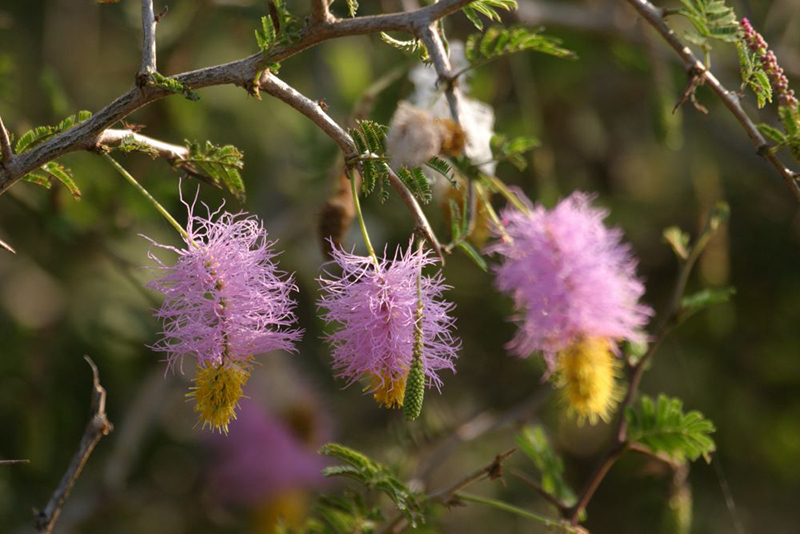
- Dichrostachys cinera – (Andara) Yala
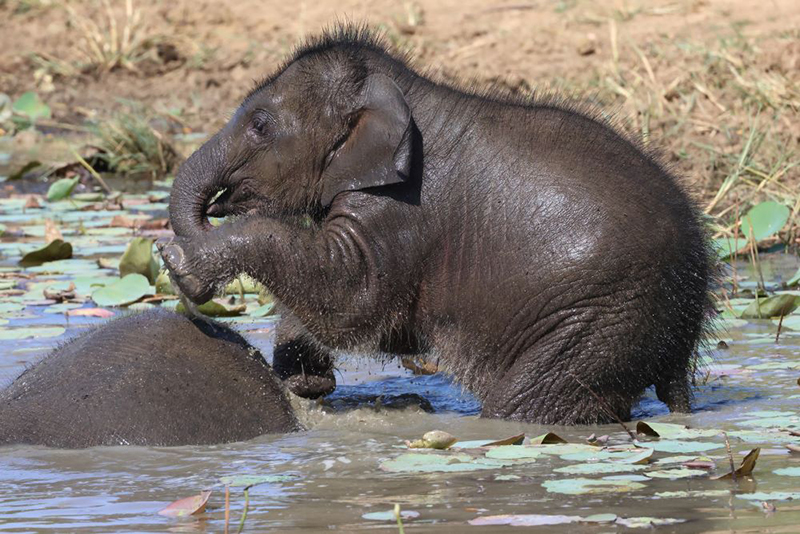
- Asian Elephant – Yala
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLegal experts decry move to demolish STC dining hall
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoA life in colour and song: Rajika Gamage’s new bird guide captures Sri Lanka’s avian soul
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCabinet nod for the removal of Cess tax imposed on imported good
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoWar in Middle East sends shockwaves through Sri Lanka’s export sector