Opinion
The PTA and defending the human rights of a sovereign people

By Harim Peiris
The onset of the bi-annual sessions of the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), in which Sri Lanka features prominently on the agenda through UNHRC Resolution 46/1, contributes to several local activities. It results in an increased public debate about the state of our nation’s human rights situation, witnesses a hand-picked team from the Attorney General’s department enplaning for Geneva as essentially the Government’s defence attorneys and a flurry of activities, currently completely inconsequential, coordinated by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs, to assure the world that the state of human rights in Sri Lanka, is not really as bad as it is made out to be.
This brief commentary seeks to contribute to the public debate about human rights, in the context of one of the entrenched, inalienable features of our republican constitution. Namely that sovereignty lies with and is riposte with the people of Sri Lanka. Article 3 of the 1978 Constitution states “In the Republic of Sri Lanka sovereignty is in the People and is inalienable. Sovereignty includes the powers of government, fundamental rights and the franchise”. We will look at the arguments about the inalienable fundamental rights of the people and in practice of persons, in the context where the state and / or elements of the state, rouge or otherwise are alleged to be complicit or instrumental in violating the same.
Firstly, the state faced a protracted decades long civil war, preceded and interspersed with two armed insurrections which led to our nation’s governance for long, being under emergency rule, regulations under which, essentially superseded the constitution. During the conflict period, there was a tacit social compact, understandably so, that the state, facing an armed rebellion required to curtail the personal liberty of citizens. This social compact was aided by the absolute brutality of the armed opponents of the state, even against the very constituency it claimed to represent. The LTTE was most brutal on the Tamil people, their kids conscripted and their old traditional political leaders assassinated, while the JVP in the South, was murderous in their rebellion, their nadir being assaults on the families of military personnel. The real issue then is that post war since 2009, there has been no significant improvement in Sri Lanka’s human rights situation or indeed any meaningful post war reconciliation, say for instance as recommended by the Government’s own Lessons Learnt and Reconciliation Commission (LLRC). Sri Lankans have not really received a post war peace dividend, either economic, social or political.
Ten years after the war, when the expectations of a peace dividend were increasing, come April 2019 and the devastating Easter Sunday bombings, the answer by the entrenched establishment if not the deep state (Sonic/Sonic), was that we are again under threat, this time from yet another internal enemy, with external connections. How much credibility that claim holds, just two years after it was made, is perhaps best denoted by the fact that His Eminence Malcom Cardinal Ranjith is this week at meetings with His Holiness Pope Francis, enroute to Geneva, where in both the Vatican and in Geneva, as a high level representative of the victims of the Easter Sunday attacks, Cardinal Ranjith will, internationally articulate what he and Catholic Church spokesmen have decried locally, the absolute lack of progress by the Sri Lankan State authorities in identifying and holding to account the master mind(s) or conspirators of the devastating attacks, given the increasing consensus that the trigger pullers pulverized in their own blasts were clearly not the mastermind(s). On the contrary the State, armed with the PTA, for public safety and security has arrested Attorney Hejaz Hizbulla, Poet Anaf Jazeem, Government medical officer Dr. Shafi Shabdeen, activist Shehan Malaka and attempted the arrest of Harin Fernando and Rev.Fr. Cyril Gamini, in the latter two cases, stopped from doing so, by Sri Lanka’s apex Court. In all honesty, the public security, threat perception from the Harin Fernando and the Rev. Cyril Gamini is rather low and if the argument is that their actions are a violation of the law and the law in question is the PTA, therein lies a serious problem.
The PTA is bad in law and worse in practice. Current Court of Appeal Justice Meneka Wijesundara in a recent judgement noted “…. four decades have past and the PTA has strayed from its historical context. The PTA, if in its application and implementation, creates a vicious cycle of abuse, the very purpose of the statute will be defeated”. The PTA, as it now stands, originally a temporary provision brought in by an arrogant presidency does not conform with Sri Lanka’s international human rights obligations. There is no argument about that. Its most problematic features being the admissibility as evidence of “confessions” made to a police officer and a completely vague definition of terrorism which makes all political dissenters of the government, terrorists. A strange construct in a democratic republic of a sovereign people.
The safety, security and well-being of all Sri Lankans is better served, when the state is required and the judiciary enforces the protection and promotion of our people’s inalienable fundamental rights and freedoms. Indeed, Sri Lanka’s first decade after the end of the war and two years after the deadly Easter Sunday bomb attacks, emerging issues, not just in Geneva but also in Sri Lanka, are, besides the repeal or reform of the PTA, the independence of the Attorney General’s Department, parliamentary oversight of the State’s intelligence services and de-politicization of the nation’s police force.
(The writer served as Advisor, Ministry of Foreign Affairs from 2016-17)
Opinion
U.S. foreign policy double standards and Iran’s Iron theocracy

The world’s most theatrical stage
Welcome to the Grand Circus
 If global geopolitics were a TV show, it would be cancelled after the first season for being too unbelievable. Consider the plot: the world’s largest arms exporter lectures others about peace; a government that executed over 500 people in a single year tells its citizens it governs by divine law; and international bodies created to enforce rules seem to apply those rules with remarkable … flexibility. Welcome to the real world of international relations, where the rules are made up and the principles don’t matter.
If global geopolitics were a TV show, it would be cancelled after the first season for being too unbelievable. Consider the plot: the world’s largest arms exporter lectures others about peace; a government that executed over 500 people in a single year tells its citizens it governs by divine law; and international bodies created to enforce rules seem to apply those rules with remarkable … flexibility. Welcome to the real world of international relations, where the rules are made up and the principles don’t matter.
This analysis examines two of the most consequential actors shaping global instability today: the United States of America, a democracy that can’t quite decide whether it believes in democracy, and the Islamic Republic of Iran, a theocracy that has perfected the art of punishing its own people for simply existing.
Episode I: The United States, ‘Do as I Say, Not as I Do’
The Democracy Export Business
The United States has, for decades, positioned itself as the global guardian of democracy, freedom, and human rights. It is a noble brand. The marketing budget alone, in the form of military expenditure at $886 billion in 2023, is staggering. And yet, the product being sold and the product being delivered have often been … different things.
The CIA-backed coup of 1953, codenamed Operation Ajax, removed Iran’s democratically elected Prime Minister Mohammad Mosaddegh and reinstated the autocratic Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, primarily to protect Anglo-American oil interests.
Nuclear Exceptionalism: The World’s Worst-Kept Secret
The United States currently holds approximately 5,044–5,177 nuclear warheads (depending on the source and year), while Russia being the largest with a stockpile estimated at approximately 5,580 warheads. yet it leads international campaigns demanding that other nations not develop nuclear weapons. This is a bit like the world’s most heavily armed person standing at the door of a gun shop, telling customers they cannot purchase firearms.
Furthermore, Israel is widely believed to possess 80–90 nuclear warheads. The United States has never imposed sanctions on Israel for this. India and Pakistan, both outside the NPT, were rewarded with nuclear cooperation deals after the tested nuclear weapons.
The Saudi Arabia Paradox
Perhaps, no relationship illustrates U.S. foreign policy hypocrisy more vividly than Washington’s alliance with Saudi Arabia. The Kingdom is an absolute monarchy with no elections, no free press, where women were legally barred from driving until 2018, and where the murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi, carried out, according to U.S. intelligence, on orders from Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman, resulted in … arms sales continuing and diplomatic ties intact.
The United States sold Saudi Arabia over $37 billion in arms between 2015 and 2020, weapons used in a Yemen war that the United Nations described as one of the world’s worst humanitarian catastrophes. Yet the U.S. simultaneously held press conferences about human rights. The cognitive dissonance is not a bug. It is the feature.
Iraq: The Weapons of Mass Distraction
In 2003, the United States invaded Iraq on the basis of alleged weapons of mass destruction (WMD) that did not exist. The invasion resulted in an estimated 150,000–1,000,000 Iraqi civilian deaths depending on methodology, the displacement of millions, the destabilization of an entire region, and the rise of the Islamic State, none of which appeared in the original brochure. The officials responsible for this foreign policy catastrophe faced no international tribunal. No sanctions were imposed on the United States. Several architects of the war are today respected media commentators.
Meanwhile, the International Criminal Court (ICC), an institution the United States has never ratified, is expected to hold others to account for far lesser offenses. As of 2024, the U.S. has actively sanctioned ICC officials who attempted to investigate American personnel for potential war crimes in Afghanistan.
Episode II: Iran, The People’s Nightmare
Iran’s political system is built on the concept of Velayat-e Faqih, the Guardianship of the Islamic Jurist, a political-theological doctrine holding that a senior Islamic cleric should govern society. In practice, this means that Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei, unelected by the general public, holds veto power over all branches of government, controls the military, the judiciary, state media, and the powerful Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
The elected president, whether ‘moderate’ or ‘hardliner’, operates within a system where real power resides with the Supreme Leader and an unelected Guardian Council that vets all candidates and can disqualify anyone it deems insufficiently Islamic. In the 2021 presidential election, the Guardian Council disqualified over 590 candidates out of 592 who applied. The word ‘election’ is being used loosely here.
Women’s Rights: A Systematic Dismantling
Since the 1979 Islamic Revolution, Iranian women have endured one of the most comprehensive rollbacks of rights in modern history. Within weeks of the revolution, mandatory hijab laws were imposed, women were barred from serving as judges, and the minimum marriage age for girls was reduced to 9 years (later revised to 13 in 1982). This was not incidental policy; it was ideological architecture.
Today, Iranian women face legal discrimination across virtually every domain. Under the Iranian Civil Code, a woman’s testimony in court counts as half that of a man’s. Women cannot travel abroad without the written permission of their husband or male guardian. Married women cannot work without spousal consent in many circumstances. The diyeh (blood money) for a woman’s life is legally valued at half that of a man.
In September 2022, 22-year-old Mahsa (Zhina) Amini died in the custody of Iran’s Morality Police, after being arrested for allegedly wearing her hijab improperly. Her death triggered the Woman, Life, Freedom uprising, one of the largest protest movements in Iranian history. The government’s response was to kill over 500 protesters, arrest more than 19,000, and execute at least four people in connection with the protests by early 2023.
The IRGC and State-Sponsored Repression
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps is a military-economic-political entity unlike any other in the region. It controls an estimated 20–40% of Iran’s economy through businesses, construction contracts, and import monopolies. It commands proxy militias across Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Yemen. And it suppresses domestic dissent with a ruthlessness that has drawn consistent condemnation from United Nations human rights bodies.
Amnesty International’s 2022-2023 annual report documented the IRGC and security forces using live ammunition, birdshot, and metal pellets against protesters, deliberately targeting eyes, resulting in hundreds being blinded. The UN Special Rapporteur on Iran documented ‘serious, widespread and systematic human rights violations’ constituting potential crimes against humanity.
Episode III: Where the Two Hypocrisies Meet
The relationship between the United States and Iran is, in many ways, a story of two entities who deserve each other in the sense that the behavUior of each government has fed the domestic narrative of the other for decades.
Washington uses Iran as justification for its military presence in the Gulf, its arms sales to autocratic Gulf states, and its general posture as indispensable regional hegemon. Tehran uses American hostility and sanctions as justification for economic failure, political repression, and nuclear advancement. Both governments’ hard-liners need each other to remain in power.
The Iranian people, 85 million of them, majority under 35, highly educated, and overwhelmingly wanting engagement with the world, are trapped between a government that treats them as subjects and an international sanctions regime that punishes them for their government’s choices. The American people, meanwhile, continue paying for a foreign policy architecture that serves arms manufacturers, defense contractors, and geopolitical abstractions more than it serves democratic values or human security.
Some Uncomfortable Truths
The United States is not the villain of every story, nor is Iran irredeemably authoritarian in the hearts of its people. What is consistent, and what this analysis has documented, is that both governments operate by standards they refuse to apply to themselves.
Tehran’s theocratic governance has failed its population economically, politically, and most visibly in its treatment of women and dissidents. The Woman, Life, Freedom movement showed the world what Iranian society wants. The government’s violent response showed the world what the Islamic Republic fears.
The lesson, uncomfortable as it is, is that powerful states, whether wielding aircraft carriers or theology, tend to exempt themselves from the rules they want others to follow. The only antidote is an informed public that refuses to accept these double standards as the natural order of things. Read critically. Follow the money. And remember: when a government tells you it acts in the name of God or democracy.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT, Malabe. The views and opinions expressed in this article are personal.)
Opinion
SLC Grants to clubs and associations under scrutiny

The scale and manner of grant distributions underscore the urgent need to rectify the weaknesses identified by the Auditor General. Remarkably, the accounts for the years 2024 and 2025 are still not published and only the 2023 accounts are available for public scrutiny.
Grants to clubs and associations increased from LKR 1.30 billion in the prior year to LKR 2.46 billion in 2023, representing an escalation of over LKR 1.15 billion year-on-year. These grants were distributed among 36 recipient clubs and associations, with individual allocations ranging from approximately LKR 1.5 million to almost LKR 300 million. Such wide variation and substantial growth warrant clear public disclosure of the allocation framework, the approval processes, and the beneficiary criteria.
While it is understandable that higher profitability enables greater financial support to clubs, the absence of a transparent, rule-based grant policy gives rise to governance concerns, and unless properly explained, leaves room for malicious or unfounded allegations that grant allocations may be used to influence voting behaviour or entrench existing officials. Robust disclosure and effective oversight are therefore essential to safeguard institutional credibility. The precise immediate need for high funding and their monitoring processes need to be divulged.
A case in point is Colombo Cricket Club (CCC), which received LKR 279,531,827 in 2023, making it the highest individual club recipient. As disclosed under the related-party notes to the financial statements, the President of Sri Lanka Cricket is also the President of Colombo Cricket Club, resulting in this transaction being classified as a related-party transaction.
In contrast to several grant recipient entities reporting profits, Sri Lanka Cricket recorded a deficit of approximately Rs. 2 billion in its Statement of Financial Performance for 2023.
It is also noteworthy from the cash flow statement that cash and fund balances declined sharply, from approximately LKR 10.8 billion in the previous year to around LKR 5.6 billion in 2023, representing a significant depletion of liquid resources within a single financial year.
A more meaningful and complete evaluation of these developments—particularly the position of funds available as at 31 December 2024 and 31 December 2025—will only be possible once the financial statements for 2024 and 2025 are released and subjected to public scrutiny.
A cricket enthusiast – Moratuwa
Opinion
Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Act 2026 fails all affacted communities
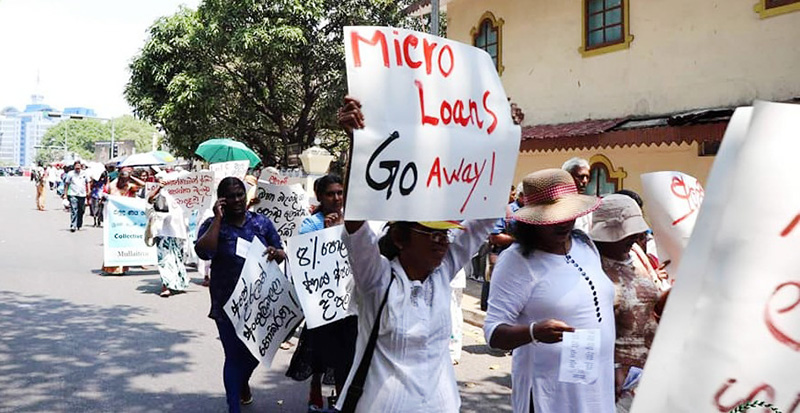
The Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill was passed into law by the Parliament of Sri Lanka on 4 March. According to Deputy Minister of Finance and Planning Dr. Anil Jayantha, the main object of the Act is to establish an Authority to “license and supervise the under-regulated microfinance and moneylending sector, aiming to protect borrowers from exploitation and ensure financial stability”.
However, the Yukthi Collective is saddened and disappointed that a government which pledged to take “measures to alleviate the burden of predatory microfinance loans with high interest rates on women” (NPP Manifesto, 2024: Page no. 44), will now add to their unbearable weight.
The new Act, as virtually all legislation enacted by Anura Kumara Dissanayake’s government, is a legacy of the anti-working class Ranil Wickremesinghe regime. It evades the root causes of the microfinance trap, and ignores debt justice for women borrowers.
It fails in understanding the connections between household debt and public debt. The vicious cycle of national debt is sustained by lack of growth in economic activity because of poor access to affordable credit.
It fails to make equal representation of women mandatory in the new Authority. If representatives of women borrowers and their self-run organisations are not present in the regulatory body, how will its members know of their lived experiences and make decisions that value women’s unpaid and paid contributions to sustaining life?
System Change
Millions of indebted households voted for the NPP with hope and expectation of ‘system change’. But instead of honouring its manifesto promise to them, the government has let them down in the law-making process; as well as the focus and substance of the new Act.
It is appalling that NPP parliamentarians, including some of its women members, appear not to have read and understood the bill they enacted into law, nor spoke to the rural credit community providers in their electorates for their views.
Predatory lending exists in the formal and informal sectors. Within this ecosystem, the Act fails to understand, identify, and prohibit predatory lending and recovery practices. It is a cover for the Central Bank’s failure to properly regulate ‘Licensed Finance Companies’ in the interests of citizens.
The biggest offenders are the big finance companies, in which some parliamentarians are deposit-holders. Therefore, some lawmakers benefit from excess profitmaking through exploitative practices, at the expense of poor mostly rural women.
Where law reform should discipline the bullies and thugs in credit delivery, it will instead wipe out, through over-regulation, community-based and managed lenders such as death donation societies, farmer associations, and urban and rural women’s collectives, which have been a lifeline for vulnerable working-class women and a defence from harmful recovery practices.
Structural Adjustment Programmes
The motivation for this new law are the market- and capital- friendly structural reforms insisted by International Financial Institutions; not the concerns and needs of those at the mercy of predatory lenders.
From the Microfinance Act 2016, to the 2023 version of the Ranil Wickremesinghe regime, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) through its loans has been a promoter of these regressive reforms.
The 2026 Act, with some changes suggested by the Supreme Court in 2024 and hardly any of the changes demanded by affected communities, has been moved forward by the NPP government in line with ADB loan conditionalities.
The path of de-regulation for banking, finance, trade, and investment; and over-regulation of poor people’s savings and credit institutions, smacks of the bias to big capital, which the NPP in opposition once criticised.
Reforms needed
The financial and banking reforms we want to see are to make credit from state banks and public funds accessible and affordable to women producers in agriculture and micro and small business operators; with decent wages and social protection for workers; that improve household opportunity for a dignified livelihood and decent lives.
Yukthi is a forum supporting working people’s movements and people’s struggles for democracy and justice in Sri Lanka.
by Yukthi Collective
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoUniversity of Wolverhampton confirms Ranil was officially invited
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoLegal experts decry move to demolish STC dining hall
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoFemale lawyer given 12 years RI for preparing forged deeds for Borella land
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoLibrary crisis hits Pera university
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days ago‘IRIS Dena was Indian Navy guest, hit without warning’, Iran warns US of bitter regret













