Features
That Midnight Knock on the Door:Sundarampuram: Janel Piyanpath

English name: ‘Jaffna Doors and Windows’
Concept, Design, Editing: Sarath Chandrajeeva
Layout: Kanishka Vijayapura
Printed and bound by Neo Graphics Pvt (Ltd)
Sales points: Barefoot Book shop Galle road Colombo 03, Sarasavi Book shops, Sakura agencies Colombo 04, Plate Pvt. (Ltd) Colombo 03.
Selling price: Rs.10,000.00 (below cost)
by Laleen Jayamanne
Jaffna Doors and Windows is the blunt English title of a large book of multilingual poems, each written in relation to a specific photograph of bomb-blasted buildings of Jaffna during the civil war. Each poem is printed on the partnered photographic image which covers an entire page or two. At a glance the Jaffna ruins feel like a vast overgrown archaeological site, intertwined with wild creepers, tangled roots, green foliage, trees, teeming with vitality.
The project was born on the 31st January 2021 when the Sinhala poet Lal Hegoda sent his friend Hiniduma Sunil Senevi a poem and the latter responded with one himself, within 45 minutes! (I love this innate skill and impulse, which I have observed on FaceBook as well, among Sinhala poets). Then, Lal sent both poems to several friends, including Sarath Chandrajeewa.
Sarath, in turn, then decided to send a photograph from his collection of destroyed buildings of Jaffna and asked each recipient to write a poem (in any of our three languages), in relation to the image. While there are wonderful Muslim, Tamil and Sinhala poets among them, many are not poets but have felt impelled to write a poem when the request came with an image that moved them, spoke to them, perhaps even with a ‘foreign’ script like Brahmi. As the project expanded, many other photographers contributed their own images of destroyed buildings, houses, kovils, mosques, churches, etc. Fourteen photographers and 86 writers participated in the project creating 108 poems.
Thus was born, not quite a Kavi Maduwa (poetry-shed), nor exactly a Raga Mala (garland of melody), but what I like to imagine as an electronic, wild Mycelial Network (a fungal web), growing under the rubble, entwined with human bones in that blood-soaked earth of Jaffna, emerging into the sunlight like fungi (mushrooms, hathu), in all their colourful variety of shapes and sizes. Such was the chance beginnings of this interethnic, networked collective project of friendship and solidarity, expressed in this singular book, coordinated and edited by Sarath and published by The Contemporary Art & Crafts Association of Sri Lanka in October 2022.
It’s been launched in Jaffna but not in Colombo, nor even reviewed as yet. The Jaffna Doors and Windows have stories to tell, stories of fear, terror, death and destruction and systematic, well-planned theft, during the civil war years, of these valued, detachable artefacts from Tamil and Muslim homes. The Tamil title, ‘Displaced Doors and Windows’, captures this history precisely. It is this aspect of war profiteering that has galvanised many to reflect and write a poem, even though some have never done that before.
This carefully crafted ‘Artists’ Book’, must surely be of interest to institutions such as the International Centre for Ethnic Studies, Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art and the Geoffrey Bawa Foundation, in particular. A book launch and a moderated discussion at any of these institutions (at the forefront of work on the cultural intersection of ethnicity with photography, poetry, art & crafts, art history and architecture), could provide a hospitable forum for ‘Truth-Telling’, enhancing the ongoing processes of ‘Reconciliation,’ after the long civil war (1983-2009).
These Doors and Windows are booty, and might well haunt the conscience of the good folk sleeping in houses well secured with them, if they did know the full story. A Southern book launch would be something of an exorcism I imagine, leading to reparation through a return of the looted precious objects, laden with generational family memories and scarred with historical trauma, varnished and polished over no doubt.
The looted Jaffna Doors and Windows are made of hardwood and crafted with traditional decorative patterns such as I have not seen in the South. Some are painted. They are palpable evidence of traditions of craft practices of Jaffna. Who were these craftsmen? Are they still alive? Are they both Muslim and Tamil? I imagine Geoffrey Bawa would have been interested in answers to these questions. I heard a formal discussion at an exhibition of Bawa’s architectural drawings once (accessed on YouTube), where Channa Daswatte mentioned pointedly that Bawa hired Muslim builders for his projects.
Clearly, these doors and windows were made to last generations, like Kandalama. And no doubt, these sturdy antique artefacts must now grace architect-designed houses in the South, especially in Colombo. These items, along with the sturdy cross beams (uluwahu), were wrenched out and transported to Colombo during the war, openly sold at a brisk pace and bought by eager architects and other middle-class folk with antiquarian interest in craft, for their cool new houses. There is a recorded instance where shop owners prevented Hegoda from photographing a stack of these doors on display at a store front, on the outskirts of Colombo with the signage, ‘Jaffna Doors and Windoors’. This was to be the impetus for Hegoda’s inaugural poem sent to Sunil, which then led to the long process of creating this collaborative and moving book.
Sundarampuram Janel Piyanpath
, the poetic title in Sinhala, is taken from Hegoda’s own poem called Hogana Pokuna (a beautiful vernacular phrase for the ocean, to those from inland who have never heard the ‘roaring’ ocean and imagine it to be a ‘pond’!). The poet muses, where the doors and windows of Jaffna might have gone to, and responds, perchance to see the Hogana Pokuna in Colombo!
Restitution of Stolen Artefacts
It would be an interesting art-historical based activist project of reclamation of a lost tradition, to try to find these doors and windows and photograph them if visible from outside. The photographs can then be components of an installation and/or the matrix for another book of trilingual poetry. Such a project would excite poets and others keen to work across the three languages and cultures and media, to create robust networks of exchange across wounding divides. Perhaps, even, the owners can be persuaded to return the stolen artefacts, which is now global best practice in art institutions and among respectable ethical collectors.
This issue reminds me of the paintings stolen by the Nazis from wealthy Jewish homes and the struggles to reclaim them by the descendants. There was a film recently about one of Klimt’s most famous paintings which, after a legal drama, was finally given to its rightful inheritor. Of course, these beautifully crafted or even purely functional solid doors don’t share the aesthetic and monetary values of high modernist European art, but given the revival of Lankan arts & crafts in the wake of Bawa’s visionary, celebrated project, those astute architects who formulated and activated the idea of ‘Tropical Modernism’ might take up this activist project as a challenge in Lanka now. It could take the once radical idea out of its comfort zone of South Asian cool and give it a further ethical resonance for the region too.
When flicking through the book full of colour, with the profuse green foliage, the splashes of abstract colours on the pages, the intensity of sun- light, the blue sky and randomly reading a stanza or two that caught my eye, one sees the empty holes on walls, a recurring visual motif. Then, the memory of reading accounts of how Richard de Zoysa, the Lankan journalist, was taken away by government law enforcement officials, from his home one night, never to return, came to mind. Was there a knock on his door late that night? I wondered. Richard’s abduction, torture and murder brought home to the Sinhala middle classes in Colombo and those of us living outside the country, what had in fact been happening to countless unknown young persons, right across the country. Many knew Richard as a charismatic actor and fearless journalist.
I remember hearing Richard’s mother, Dr Manorani Saravanamuttu, talk about the state of terror in Sri Lanka (that of the state, the LTTE and JVP), and also about Richard’s death, at an Amnesty International meeting in Sydney in 1991 perhaps. I still remember Richard and his mother playing as mother and son in Aeschylus’s Agamemnon in Colombo, in the late 70s, in the open, perhaps at the British Council. Manorani was Clytemnestra and Richard Orestes, duty bound to kill his mother, because she killed his father, because he killed their daughter, so as to placate the wind god to set sail to sack Troy. This cycle of relentless mythic violence the mother and son enacted in the Greek tragedy, appeared to have gripped Lanka too. But the play is a part of a trilogy, which concludes with the establishment of trial by jury where the principle of Justice, rather than vengeance, is established in Athens, through argument and a spirit of reconciliation led by Athena, governed by reason. This too appears relevant to Lanka now where the state enacts vengeful violence on peaceful protestors and journalists and the independence of the judiciary is eroded.
Sundarampuram
is dedicated to Dr Rajani Thiranagama, Professor of Anatomy at the University of Jaffna, also a well-known human rights activist, who was gunned down by a member of the LTTE. There is an image in the book of her smiling at us and her long poem ‘Letter from Jaffna’, printed beside it in the three languages. Her poem describes the quotidian, ceaseless mass violence and sense of terror they all experienced caught between the IPKF, LTTE and the Lankan Army. She speaks on behalf of the nameless victims. Her sister Sumathy writes of the mass eviction of Muslims from Jaffna by the LTTE, and of their abandoned homes then subject to acts of vandalism.
Hiniduma Sunil’s poem describes the interior of a posh Colombo home where a Tamil servant-girl finds herself alone in the living room where one of those Jaffna windows and doors have landed. Her silent thoughts are given poetic expression. Priyantha Fonseka apostrophises a Jaffna window in happier times, when it opened on its intact hinges, to let in a gentle breeze in a moonlit night and the beloved. Readers will no doubt pick up poems that appeal to them from its large selection and the images themselves will lure us despite all, because they have become allegorical, like all ruins, and as such, have the power to address us with the injunction, ‘Read Me!’ ‘Say something,’ they whisper to our ears. (To be continued)
Features
Misinterpreting President Dissanayake on National Reconciliation

President Anura Kumara Dissanayake has been investing his political capital in going to the public to explain some of the most politically sensitive and controversial issues. At a time when easier political choices are available, the president is choosing the harder path of confronting ethnic suspicion and communal fears. There are three issues in particular on which the president’s words have generated strong reactions. These are first with regard to Buddhist pilgrims going to the north of the country with nationalist motivations. Second is the controversy relating to the expansion of the Tissa Raja Maha Viharaya, a recently constructed Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai which has become a flashpoint between local Tamil residents and Sinhala nationalist groups. Third is the decision not to give the war victory a central place in the Independence Day celebrations.
Even in the opposition, when his party held only three seats in parliament, Anura Kumara Dissanayake took his role as a public educator seriously. He used to deliver lengthy, well researched and easily digestible speeches in parliament. He continues this practice as president. It can be seen that his statements are primarily meant to elevate the thinking of the people and not to win votes the easy way. The easy way to win votes whether in Sri Lanka or elsewhere in the world is to rouse nationalist and racist sentiments and ride that wave. Sri Lanka’s post independence political history shows that narrow ethnic mobilisation has often produced short term electoral gains but long term national damage.
Sections of the opposition and segments of the general public have been critical of the president for taking these positions. They have claimed that the president is taking these positions in order to obtain more Tamil votes or to appease minority communities. The same may be said in reverse of those others who take contrary positions that they seek the Sinhala votes. These political actors who thrive on nationalist mobilisation have attempted to portray the president’s statements as an abandonment of the majority community. The president’s actions need to be understood within the larger framework of national reconciliation and long term national stability.
Reconciler’s Duty
When the president referred to Buddhist pilgrims from the south going to the north, he was not speaking about pilgrims visiting long established Buddhist heritage sites such as Nagadeepa or Kandarodai. His remarks were directed at a specific and highly contentious development, the recently built Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai and those built elsewhere in the recent past in the north and east. The temple in Kankesanturai did not emerge from the religious needs of a local Buddhist community as there is none in that area. It has been constructed on land that was formerly owned and used by Tamil civilians and which came under military occupation as a high security zone. What has made the issue of the temple particularly controversial is that it was established with the support of the security forces.
The controversy has deepened because the temple authorities have sought to expand the site from approximately one acre to nearly fourteen acres on the basis that there was a historic Buddhist temple in that area up to the colonial period. However, the Tamil residents of the area fear that expansion would further displace surrounding residents and consolidate a permanent Buddhist religious presence in the present period in an area where the local population is overwhelmingly Hindu. For many Tamils in Kankesanturai, the issue is not Buddhism as a religion but the use of religion as a vehicle for territorial assertion and demographic changes in a region that bore the brunt of the war. Likewise, there are other parts of the north and east where other temples or places of worship have been established by the military personnel in their camps during their war-time occupation and questions arise regarding the future when these camps are finally closed.
There are those who have actively organised large scale pilgrimages from the south to make the Tissa temple another important religious site. These pilgrimages are framed publicly as acts of devotion but are widely perceived locally as demonstrations of dominance. Each such visit heightens tension, provokes protest by Tamil residents, and risks confrontation. For communities that experienced mass displacement, military occupation and land loss, the symbolism of a state backed religious structure on contested land with the backing of the security forces is impossible to separate from memories of war and destruction. A president committed to reconciliation cannot remain silent in the face of such provocations, however uncomfortable it may be to challenge sections of the majority community.
High-minded leadership
The controversy regarding the president’s Independence Day speech has also generated strong debate. In that speech the president did not refer to the military victory over the LTTE and also did not use the term “war heroes” to describe soldiers. For many Sinhala nationalist groups, the absence of these references was seen as an attempt to diminish the sacrifices of the armed forces. The reality is that Independence Day means very different things to different communities. In the north and east the same day is marked by protest events and mourning and as a “Black Day”, symbolising the consolidation of a state they continue to experience as excluding them and not empathizing with the full extent of their losses.
By way of contrast, the president’s objective was to ensure that Independence Day could be observed as a day that belonged to all communities in the country. It is not correct to assume that the president takes these positions in order to appease minorities or secure electoral advantage. The president is only one year into his term and does not need to take politically risky positions for short term electoral gains. Indeed, the positions he has taken involve confronting powerful nationalist political forces that can mobilise significant opposition. He risks losing majority support for his statements. This itself indicates that the motivation is not electoral calculation.
President Dissanayake has recognized that Sri Lanka’s long term political stability and economic recovery depend on building trust among communities that once peacefully coexisted and then lived through decades of war. Political leadership is ultimately tested by the willingness to say what is necessary rather than what is politically expedient. The president’s recent interventions demonstrate rare national leadership and constitute an attempt to shift public discourse away from ethnic triumphalism and toward a more inclusive conception of nationhood. Reconciliation cannot take root if national ceremonies reinforce the perception of victory for one community and defeat for another especially in an internal conflict.
BY Jehan Perera
Features
Recovery of LTTE weapons
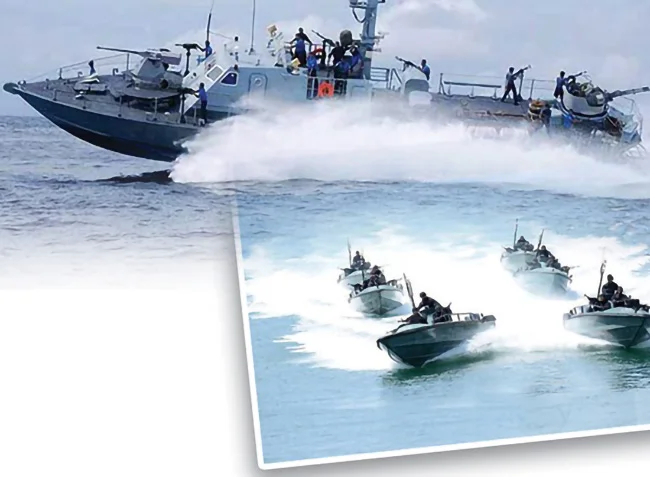

I have read a newspaper report that the Special Task Force of Sri Lanka Police, with help of Military Intelligence, recovered three buried yet well-preserved 84mm Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers used by the LTTE, in the Kudumbimalai area, Batticaloa.
These deadly weapons were used by the LTTE SEA TIGER WING to attack the Sri Lanka Navy ships and craft in 1990s. The first incident was in February 1997, off Iranativu island, in the Gulf of Mannar.
Admiral Cecil Tissera took over as Commander of the Navy on 27 January, 1997, from Admiral Mohan Samarasekara.
The fight against the LTTE was intensified from 1996 and the SLN was using her Vanguard of the Navy, Fast Attack Craft Squadron, to destroy the LTTE’s littoral fighting capabilities. Frequent confrontations against the LTTE Sea Tiger boats were reported off Mullaitivu, Point Pedro and Velvetiturai areas, where SLN units became victorious in most of these sea battles, except in a few incidents where the SLN lost Fast Attack Craft.

Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers
The intelligence reports confirmed that the LTTE Sea Tigers was using new recoilless rocket launchers against aluminium-hull FACs, and they were deadly at close quarter sea battles, but the exact type of this weapon was not disclosed.
The following incident, which occurred in February 1997, helped confirm the weapon was Carl Gustaf 84 mm Recoilless gun!
DATE: 09TH FEBRUARY, 1997, morning 0600 hrs.
LOCATION: OFF IRANATHIVE.
FACs: P 460 ISRAEL BUILT, COMMANDED BY CDR MANOJ JAYESOORIYA
P 452 CDL BUILT, COMMANDED BY LCDR PM WICKRAMASINGHE (ON TEMPORARY COMMAND. PROPER OIC LCDR N HEENATIGALA)
OPERATED FROM KKS.
CONFRONTED WITH LTTE ATTACK CRAFT POWERED WITH FOUR 250 HP OUT BOARD MOTORS.
TARGET WAS DESTROYED AND ONE LTTE MEMBER WAS CAPTURED.
LEADING MARINE ENGINEERING MECHANIC OF THE FAC CAME UP TO THE BRIDGE CARRYING A PROJECTILE WHICH WAS FIRED BY THE LTTE BOAT, DURING CONFRONTATION, WHICH PENETRATED THROUGH THE FAC’s HULL, AND ENTERED THE OICs CABIN (BETWEEN THE TWO BUNKS) AND HIT THE AUXILIARY ENGINE ROOM DOOR AND HAD FALLEN DOWN WITHOUT EXPLODING. THE ENGINE ROOM DOOR WAS HEAVILY DAMAGED LOOSING THE WATER TIGHT INTEGRITY OF THE FAC.
THE PROJECTILE WAS LATER HANDED OVER TO THE NAVAL WEAPONS EXPERTS WHEN THE FACs RETURNED TO KKS. INVESTIGATIONS REVEALED THE WEAPON USED BY THE ENEMY WAS 84 mm CARL GUSTAF SHOULDER-FIRED RECOILLESS GUN AND THIS PROJECTILE WAS AN ILLUMINATER BOMB OF ONE MILLION CANDLE POWER. BUT THE ATTACKERS HAS FAILED TO REMOVE THE SAFETY PIN, THEREFORE THE BOMB WAS NOT ACTIVATED.
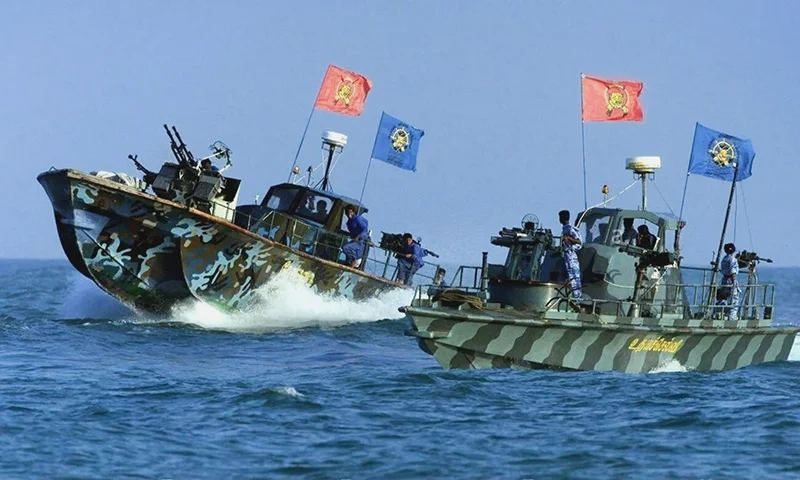

Sea Tigers
Carl Gustaf 84 mm recoilless gun was named after Carl Gustaf Stads Gevärsfaktori, which, initially, produced it. Sweden later developed the 84mm shoulder-fired recoilless gun by the Royal Swedish Army Materiel Administration during the second half of 1940s as a crew served man- portable infantry support gun for close range multi-role anti-armour, anti-personnel, battle field illumination, smoke screening and marking fire.
It is confirmed in Wikipedia that Carl Gustaf Recoilless shoulder-fired guns were used by the only non-state actor in the world – the LTTE – during the final Eelam War.
It is extremely important to check the batch numbers of the recently recovered three launchers to find out where they were produced and other details like how they ended up in Batticaloa, Sri Lanka?
 By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
WV, RWP and Bar, RSP, VSV, USP, NI (M) (Pakistan), ndc, psn, Bsc (Hons) (War Studies) (Karachi) MPhil (Madras)
Former Navy Commander and Former Chief of Defence Staff
Former Chairman, Trincomalee Petroleum Terminals Ltd
Former Managing Director Ceylon Petroleum Corporation
Former High Commissioner to Pakistan
Features
Yellow Beatz … a style similar to K-pop!
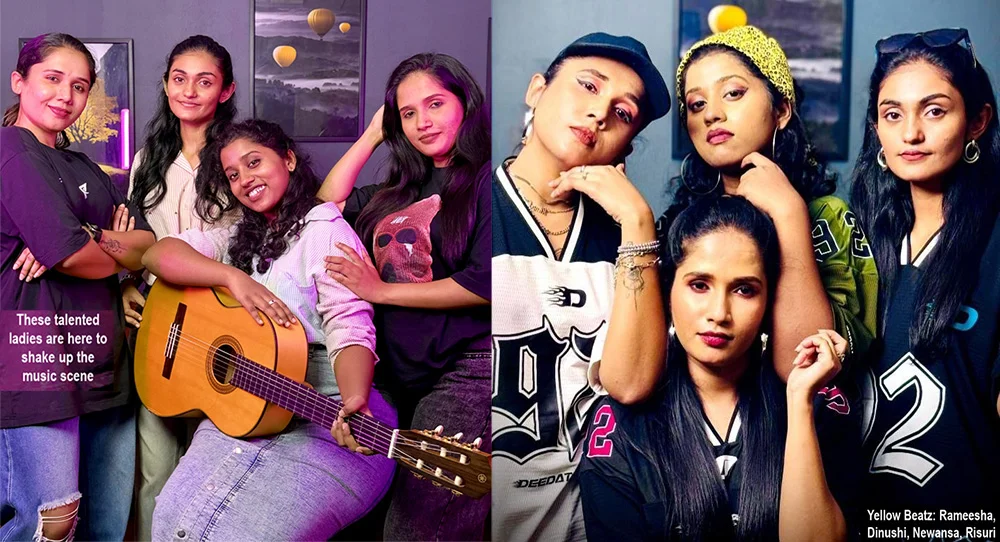
 Yes, get ready to vibe with Yellow Beatz, Sri Lanka’s awesome girl group, keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-pop!
Yes, get ready to vibe with Yellow Beatz, Sri Lanka’s awesome girl group, keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-pop!
With high-energy beats and infectious hooks, these talented ladies are here to shake up the music scene.
Think bold moves, catchy hooks, and, of course, spicy versions of old Sinhala hits, and Yellow Beatz is the package you won’t want to miss!
According to a spokesman for the group, Yellow Beatz became a reality during the Covid period … when everyone was stuck at home, in lockdown.
“First we interviewed girls, online, and selected a team that blended well, as four voices, and then started rehearsals. One of the cover songs we recorded, during those early rehearsals, unexpectedly went viral on Facebook. From that moment onward, we continued doing cover songs, and we received a huge response. Through that, we were able to bring back some beautiful Sri Lankan musical creations that were being forgotten, and introduce them to the new generation.”
The team members, I am told, have strong musical skills and with proper training their goal is to become a vocal group recognised around the world.
Believe me, their goal, they say, is not only to take Sri Lanka’s name forward, in the music scene, but to bring home a Grammy Award, as well.
“We truly believe we can achieve this with the love and support of everyone in Sri Lanka.”
The year 2026 is very special for Yellow Beatz as they have received an exceptional opportunity to represent Sri Lanka at the World Championships of Performing Arts in the USA.
Under the guidance of Chris Raththara, the Director for Sri Lanka, and with the blessings of all Sri Lankans, the girls have a great hope that they can win this milestone.
“We believe this will be a moment of great value for us as Yellow Beatz, and also for all Sri Lankans, and it will be an important inspiration for the future of our country.”
Along with all the preparation for the event in the USA, they went on to say they also need to manage their performances, original song recordings, and everything related.

The year 2026 is very special for Yellow Beatz
“We have strong confidence in ourselves and in our sincere intentions, because we are a team that studies music deeply, researches within the field, and works to take the uniqueness of Sri Lankan identity to the world.”
At present, they gather at the Voices Lab Academy, twice a week, for new creations and concert rehearsals.
This project was created by Buddhika Dayarathne who is currently working as a Pop Vocal lecturer at SLTC Campus. Voice Lab Academy is also his own private music academy and Yellow Beatz was formed through that platform.
Buddhika is keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-Pop and Yellow Beatz began as a result of that vision. With that same aim, we all work together as one team.
“Although it was a little challenging for the four of us girls to work together at first, we have united for our goal and continue to work very flexibly and with dedication. Our parents and families also give their continuous blessings and support for this project,” Rameesha, Dinushi, Newansa and Risuri said.
Last year, Yellow Beatz released their first original song, ‘Ihirila’ , and with everything happening this year, they are also preparing for their first album.
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoAll’s not well that ends well?
















