Features
Shared Sanctities

Book Review
A few weeks ago, I embarked on a long journey from Colombo to Toronto, with a short transit in Doha. It was a long 16-hour journey by air. Though one may say that was “long”, in the good (or bad) old days, such a trip, including crossing the Atlantic would take weeks if not months. However, I carried one book with me, a tradition I keep even when I go on a 10-minute drive. The book that I carried this time was Hasini Haputhanthri’s and Sujeewa de Silva’s Shared Sancties, the revised and enlarged second edition.
With the very many books I have read over the years, especially on this genre of conserving and sharing a common ground for heritage, I found this work a moving and creative masterpiece that needs a closer attention. Hence, this comment or “review,” that would possibly draw upon my understanding of this work and my perspectives of how I see the writer build this much appreciative narrative.
Geopolitically and by history, Sri Lanka, is an island nation that has given abode to people of very many nations of both the Western and Eastern hemisphere. Irrespective of how much the most arduous extremist may want to claim about racial purity, it is beyond any doubt that we are a perfectly mixed set of people that have a shared and common heritage.
For centuries, this land absorbed ideas, faiths, and artistic forms with a confidence modern Sri Lanka struggles to reclaim. What makes this book compelling is not simply its content, but the way Hasini reanimates that forgotten spirit of confluence.
From the very beginning, she anchors her narrative in the history of movement—oceans, islands, and trade routes. Her encounter with the Nestorian Cross at a Buddhist pilgrimage site sets the tone: Sri Lanka’s past is rarely tidy, never strictly defined, and far more entangled than our schoolbooks suggest. In chapters like Greater World: Islands, Oceans and Beyond, she places the island firmly on the maritime highways of the ancient world, illustrating how ships, ideas, and communities shaped our art, architecture, and ritual practices long before the arrival of the Portuguese or the shadow of the British Empire.
One of my favourite extracts from the book is the following: “We never quite realize that the history we learn in school is ‘land-locked’. No one thinks that history ever happened out there at sea. This is possibly because history was held hostage by post-colonial nationalisms, where their scopes was defined by newly drawn ‘national borders’. Oceans were nationalized too, but to a lesser extent than the land. After all, there are no ‘sons of the sea’; only ‘sons of the soil’!”
This is where the book excels: Hasini does not merely describe syncretism; she allows the reader to stand inside it. Nalanda Gedige, that enigmatic fusion of Hindu and Buddhist symbolism, becomes not only a monument but a question—one that challenges our obsessive need to categorize heritage into neat ethnic boxes. Throughout, she nudges us to accept that ambiguity itself is part of our inheritance.
Her exploration of Polonnaruwa in Temple as Museum; Religion as Art is one of the book’s finest sections. The Tivanka Image House, with its Hindu architectural frame sheltering a towering Buddha and 11th-century murals, becomes a living example of artistic and spiritual dialogue. Hasini’s prose here is sharp and almost lyrical, reminding us that the ancient capital was not merely a seat of kings, but a sanctuary shaped by multiple hands and imaginations. This chapter lifts Polonnaruwa out of its familiar postcard frame and restores its true complexity.
While the world knows the calm grandeur of Gal Vihara, Hasini turns our gaze to the island’s deeper layers of confluence—Hindu shrines, South Indian–inspired bronzes, and the evocative Tivanka Image House with its medieval murals. Her storytelling blends archaeology, art history, and memory, reminding us that Polonnaruwa was never a singular Buddhist space, but a sanctuary shaped by movement, borrowing, and imagination. Through her eyes, the city becomes a living museum, where faith, artistry, and cultural inheritance coexist in quiet, powerful harmony.
The chapters set in Kandy extend this idea into the colonial and modern eras. The architectural blend in the Trinity College Chapel, enhanced by David Paynter’s iconic murals, stands beside the Embekke Devale’s mythical carvings—each revealing the layered identities of a kingdom negotiating faith, power, and art. Hasini’s ability to weave these strands across centuries without losing focus is one of her strongest gifts.
A Tale of Two Masjids
is equally evocative. The contrast between Galle’s coastal Jumma Meeran Mosque and the flamboyant Red Masjid in Pettah becomes a meditation on how Islam, too, adapted, absorbed, and reshaped itself within the island’s cosmopolitan spaces. Hasini reminds us that these structures are more than architecture; they are arguments in brick and mortar for coexistence.
The Blonde Behind the Buddha
is a richly textured meditation on Karagampitiya’s layered spiritual world, where colonial memory, Buddhist devotion, and artistic hybridity collide. Moving from art historian Maria Graham’s gaze to the quiet enigmas of the temple’s murals, the chapter beautifully captures how European motifs seeped into a deeply Sinhala-Buddhist universe. The mysterious blonde figure becomes a metaphor for cultural intrusion and adaptation, revealing a faith that survives not by purity, but by transformation.
“City of Gods” is one of the most evocative chapters in Shared Sanctities, stitching together maritime history, sacred geography, and memory with impressive ease. Tenavaram emerges not merely as a ruined shrine on the southern tip of the island, but as a cosmopolitan temple-city where peacocks from Sandesha poetry, merchants from Sumatra, Tamil Brahmins, Sinhala kings and Ming admirals all intersect. Hasini handles maps, Tevaram, chronicles and colonial violence without losing the lyrical, almost cinematic quality of her prose. Especially powerful is the tracing of Tenavaram’s afterlives – from Pancha Ishvaram lore to the blue god Upulvan and the half-forgotten lingam and Nandi that still haunts the site.
The later chapters—the shifting representation of women in temple art—push the narrative into cultural politics. Here, Hasini confronts how colonial morality attempted to tame the female body and how nationalist revivalism reshaped identity, dress, and artistic convention. Her reflections on the transformation from sensuous murals to demure, Victorianised figures are particularly striking and reveal how power quietly negotiates aesthetics.
Ultimately, Shared Sanctities is not just a catalogue of syncretic sites. It is a gentle but firm challenge to monolithic histories. The book urges us to discard the rigid frameworks that have dominated Sri Lankan historical discourse and to embrace a narrative that is layered, porous, and proudly plural. Supported by Sujeewa de Silva’s superb photography and the accompanying documentaries, this volume becomes both an academic resource and a heartfelt tribute to an island that once thrived on openness.
Hasini’s account is both compelling and wonderfully lucid; anyone with even a half-curious mind will find it hard to put this book down once they begin. She writes with a distinctly romantic overtone, yet never loses control of a tightly argued, historically grounded narrative—a balance many would struggle to maintain when dealing with such a wide and complex constellation of syncretic shrines in Sri Lanka. Her prose at times recalls the best of H. W. Cave and William Skeen, those early chroniclers of Ceylon’s landscapes and sanctities, whose work quietly shaped our understanding of the island’s cultural memory.
Her careful use of both well-known and lesser-known sources gives the book real scholarly weight, without ever becoming dry. The visual layer provided by Sujeewa de Silva’s photographs—the murals, façades, statues, and architectural details—is not ornamental but essential. His images do not merely illustrate; they converse with the text, and for a reader less inclined to long passages of prose, they offer an inviting, almost meditative way into the material. His craft deserves very warm praise.
If a third edition is ever contemplated, a closer engagement with Donald Stadtner’s Sacred Sites of Sri Lanka would be valuable, as it offers complementary readings of some of these spaces. But that is a suggestion at the margins. For me, reading Shared Sanctities on an otherwise monotonous, long-haul flight was an unexpected delight. It is a book that should be read by anyone who wishes to grasp the essence of the Sri Lankan story—a story still very much being written.
‘Shared Sanctities’ by Hasini Haputhanthri and Sujeewa de Silva
Second edition, 2025,
Published by the International Centre for Ethnic StudiesSecond
Review by Avishka Mario Senewiratne
Features
Wishes, Resolutions and Climate Change

Exchanging greetings and resolving to do something positive in the coming year certainly create an uplifting atmosphere. Unfortunately, their effects wear off within the first couple of weeks, and most of the resolutions are forgotten for good. However, this time around, we must be different, because the nation is coming out of the most devastating natural disaster ever faced, the results of which will impact everyone for many years to come. Let us wish that we as a nation will have the courage and wisdom to resolve to do the right things that will make a difference in our lives now and prepare for the future. The truth is that future is going to be challenging for tropical islands like ours.
We must not have any doubts about global warming phenomenon and its impact on local weather patterns. Over its 4.5-billion-year history, the earth has experienced drastic climate changes, but it has settled into a somewhat moderate condition characterised by periods of glaciation and retreat over the last million years. Note that anatomically modern Homo sapiens have been around only for two to three hundred thousand years, and it is reasoned that this stable climate may have helped their civilisation. There have been five glaciation periods over the last five hundred thousand years, and these roughly hundred-thousand-year cycles are explained by the astronomical phenomenon known as the Milankovitch Cycle (the lows marked with stars in Figure 1). At present, the earth is in an inter glacial period and the next glaciation period will be in about eighty thousand years.
 (See Figure 1. Glaciation Cycles)
(See Figure 1. Glaciation Cycles)
During these cycles, the global mean temperature has changed by about 7-8 degrees Centigrade. In contrast to this natural variation, earth has been experiencing a rapid temperature increase over the past hundred years. There is ample scientific evidence from multiple sources that this is caused by the increase in carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere, which has seen a 50% increase over the historical levels in just hundred years (Figure 2). Carbon dioxide is one of the greenhouse gases which traps heat from the sun and slows the natural cooling process of the earth. This increase of carbon dioxide is due to human activities: fossil fuel burning, industrial processes, deforestation, and agricultural practices. Ironically, those who suffer from the consequences did not contribute to these changes; those who did contribute are trying their best to convince the world that the temperature changes we see are natural, and nothing should be done. We must have no illusions that global warming is a human-caused phenomenon, and it has serious repercussions.
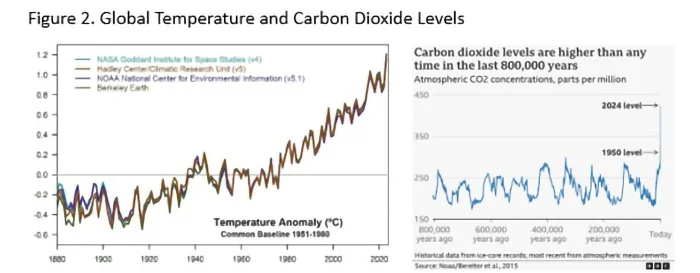
(See Figure 2. Global Temperature and Carbon Dioxide Levels)
Why should we care about global warming? Well, there are many reasons, but let us focus on earth’s water cycle. Middle schoolers know that water evaporates from the oceans, rises into the atmosphere where it cools, condenses, and falls back onto earth as rain or snow. When the oceans warm, the evaporation increases, and the warmer atmosphere can hold more water vapour. Water laden atmosphere results in severe and erratic weather. Ironically, water vapour is also a greenhouse gas, and this has a snowballing effect. The increased ocean temperature also disrupts ocean currents that influence the weather on land. The combined result is extreme and severe weather: violent storms and droughts depending on the geographic location. What is happening on the West coast of the USA is an example. The net result will be major departures from what is considered normal weather over millennia.
International organisations have been talking for 30 years about limiting global temperature increase to 1.5oC above pre-industrial levels by curtailing greenhouse gas emissions. But not much has been done and the temperature has risen by 1.2oC already. The challenge is that even if we can stop greenhouse gas emissions completely, right now, we have the problem of removing already existing 2,500 billion tons of carbon from the atmosphere, for which there are no practical solutions yet. Scientists worry about the consequences of runaway temperature increase and its effect on human life, which are many. It is not a doomsday prediction of life disappearing from earth, but a warning that life will be quite different from what humans are used to. All small tropical nations like ours are burdened with mitigating the consequences; in other words, get ready for more Ditwahs, do not wait for the twelve-day forecast.
Some opined that not enough warning was given regarding Ditwah; the truth is that the tools available for long-term prediction of the path or severity of a weather event (cyclone, typhoon, hurricane, tornado) are not perfect. There are multitude of rapidly changing factors contributing to the behavior of weather events. Meteorologists feed most up to date data to different computer models and try to identify the prediction with the highest probability. The multiple predictions for the same weather event are represented by what is known as spaghetti plots. Figure 3 shows the forecasted paths of a 2019 Atlantic hurricane five days ahead on the right and the actual path it followed on the left. While the long-term prediction of the path of a cyclone remains less accurate, its strength can vary within hours. There are several Indian ocean cyclones tracking sites online accessible to the public.

Figure 3. Forecasting vs Reality
There is no argument that short-term forecasts of this nature are valuable in saving lives and movable assets, but having long term plans in place to mitigate the effects of natural disasters is much more important than that. If a sizable section of the population must start over their lives from ground zero after every storm, how can a country economically develop?
The degree of our unpreparedness came to light during Ditwah disaster. It is not for lack of awareness; judging by the deluge of newspaper articles, blogs, vlogs, and speeches made, there is no shortage of knowledge and technical expertise to meet the challenge. The government has assured the necessary resources, and there is good reason to trust that the funds will be spent properly and not to line the pockets as happened during previous disasters. However, history tells us that despite the right conditions and good intentions, we could miss the opportunity again. Reasons for such skepticisms emerged during the few meetings the President held with the bureaucrats while visiting effected areas. Also, the COPE committee meetings plainly display the inherent inefficiencies and irregularities of our system and the absence of work ethics among all levels of the bureaucracy.
What it tells us is that we as a nation have an attitude problem. There are ample scholarly analyses by local as well as international researchers on this aspect of Sri Lankan psyche, and they label it as either island or colonial mentality. The first refers to the notion of isolated communities perceiving themselves as exceptional or superior to the rest of the world, and that the world is hell-bent on destroying or acquiring what they have. This attitude is exacerbated by the colonial mentality that promoted the divide and conquer rules and applied it to every societal characteristic imaginable; and plundered natural resources. As a result, now we are divided along ethnic, linguistic, religious, political, class, caste, geography, wealth, and many more real and imagined lines. Sadly, politicians, some religious leaders, and other opportunists keep inflaming these sentiments for their benefit when most of the population is willing to move on.
The first wish, therefore, is to get the strength, courage, and wisdom to think rationally, and discard outdated and outmoded belief systems that hinder our progress as a nation. May we get the courage to stop venerating elite who got there by exploiting the masses and the country’s wealth. More importantly, may we get the wisdom to educate the next generation to be free thinkers, give them the power and freedom to reject fabrications, myths, and beliefs that are not based on objective facts.
This necessitates altering our attitude towards many aspects of life. There is no doubt that free thinking does not come easily, it involves the proverbial ‘exterminating the consecrated bull.’ We are rightfully proud about our resplendent past. It is true that hydraulic engineering, art, and architecture flourished during the Anuradhapura period.
However, for one reason or another, we have lost those skills. Nowadays, all irrigation projects are done with foreign aid and assistance. The numerous replicas of the Avukana statue made with the help of modern technology, for example, cannot hold a candle to the real one. The fabled flying machine of Ravana is a figment of marvelous imagination of a skilled poet. Reality is that today we are a nation struggling with both natural and human-caused disasters, and dependent on the generosity of other nations, especially our gracious neighbor. Past glory is of little help in solving today’s problems.
Next comes national unity. Our society is so fragmented that no matter how beneficial a policy or an idea for the nation could be, some factions will oppose it, not based on facts, but by giving into propaganda created for selfish purposes. The island mentality is so pervasive, we fail to trust and respect fellow citizens, not to mention the government. The result is absence of long-term planning and stability. May we get the insight to separate policy from politics; to put nation first instead of our own little clan, or personal gains.
With increasing population and decreasing livable and arable land area, a national land management system becomes crucial. We must have an intelligent zoning system to prevent uncontrolled development. Should we allow building along waterways, on wetlands, and road easements? Should we not put the burden of risk on the risk takers using an insurance system instead of perpetual public aid programs? We have lost over 95% of the forest cover we had before European occupation. Forests function as water reservoirs that release rainwater gradually while reducing soil erosion and stabilizing land, unlike monocultures covering the hill country, the catchments of many rivers. Should we continue to allow uncontrolled encroachment of forests for tourism, religious, or industrial purposes, not to mention personal enjoyment of the elite? Is our use of land for agricultural purposes in keeping with changing global markets and local labor demands? Is haphazard subsistence farming viable? What would be the impact of sea level rising on waterways in low lying areas?
These are only a few aspects that future generations will have to grapple with in mitigating the consequences of worsening climate conditions. We cannot ignore the fact that weather patterns will be erratic and severe, and that will be the new normal. Survival under such conditions involves rational thinking, objective fact based planning, and systematic execution with long term nation interests in mind. That cannot be achieved with hanging onto outdated and outmoded beliefs, rituals, and traditions. Weather changes are not caused by divine interventions or planetary alignments as claimed by astrologers. Let us resolve to lay the foundation for bringing up the next generation that is capable of rational thinking and be different from their predecessors, in a better way.
by Geewananda Gunawardana
Features
From Diyabariya to Duberria: Lanka’s Forgotten Footprint in Global Science

For centuries, Sri Lanka’s biological knowledge travelled the world — anonymously. Embedded deep within the pages of European natural history books, Sinhala words were copied, distorted and repurposed, eventually fossilising into Latinised scientific names of snakes, bats and crops found thousands of kilometres away.
Africa’s reptiles, Europe’s taxonomic catalogues and global field guides still carry those echoes, largely unnoticed and uncredited.
Now, a Sri Lankan herpetologist is tracing those forgotten linguistic footprints back to their source.
Through painstaking archival research into 17th- and 18th-century zoological texts, herpetologist and taxonomic researcher Sanjaya Bandara has uncovered compelling evidence that several globally recognised scientific names — long assumed to be derived from Greek or Latin — are in fact rooted in Sinhala vernacular terms used by villagers, farmers and hunters in pre-colonial Sri Lanka.
“Scientific names are not just labels. They are stories,” Bandara told The Island. “And in many cases, those stories begin right here in Sri Lanka.”

Sanjaya Bandara
At the heart of Bandara’s work is etymology — the study of word origins — a field that plays a crucial role in zoology and taxonomy.
While classical languages dominate scientific nomenclature, his findings reveal that Sinhala words were quietly embedded in the foundations of modern biological classification as early as the 1700s.
One of the most striking examples is Ahaetulla, the genus name for Asian vine snakes. “The word Ahaetulla is not Greek or Latin at all,” Bandara explained. “It comes directly from the Sinhala vernacular used by locals for the Green Vine Snake.” Remarkably, the term was adopted by Carl Linnaeus himself, the father of modern taxonomy.
Another example lies in the vespertilionid bat genus Kerivoula, described by British zoologist John Edward Gray. Bandara notes that the name is a combination of the Sinhala words kiri (milky) and voula (bat). Even the scientific name of finger millet, Eleusine coracana, carries linguistic traces of the Sinhala word kurakkan, a cereal cultivated in Sri Lanka for centuries.
Yet Bandara’s most intriguing discoveries extend far beyond the island — all the way to Africa and the Mediterranean.
In a research paper recently published in the journal Bionomina, Bandara presented evidence that two well-known snake genera, Duberria and Malpolon, both described in 1826 by Austrian zoologist Leopold Fitzinger, likely originated from Sinhala words.
The name Duberria first appeared in Robert Knox’s 1681 account of Ceylon, where Knox refers to harmless water snakes called “Duberria” by locals. According to Bandara, this was a mispronunciation of Diyabariya, the Sinhala term for water snakes.
“Mispronunciations are common in Knox’s writings,” Bandara said. “English authors of the time struggled with Sinhala phonetics, and distorted versions of local names entered European literature.”
Over time, these distortions became formalised. Today, Duberria refers to African slug-eating snakes — a genus geographically distant, yet linguistically tethered to Sri Lanka.
Bandara’s study also proposes the long-overdue designation of a type species for the genus, reviving a 222-year-old scientific name in the process.
Equally compelling is the case of Malpolon, the genus of Montpellier snakes found across North Africa, the Middle East and southern Europe. Bandara traced the word back to a 1693 work by English zoologist John Ray, which catalogued snakes from Dutch India — including Sri Lanka.
“The term Malpolon appears alongside Sinhala vernacular names,” Bandara noted. “It is highly likely derived from Mal Polonga, meaning ‘flowery viper’.” Even today, some Sri Lankan communities use Mal Polonga to describe patterned snakes such as the Russell’s Wolf Snake.
Bandara’s research further reveals Sinhala roots in the African Red-lipped Herald Snake (Crotaphopeltis hotamboeia), whose species name likely stems from Hothambaya, a regional Sinhala term for mongooses and palm civets.
“These findings collectively show that Sri Lanka was not just a source of specimens, but a source of knowledge,” Bandara said. “Early European naturalists relied heavily on local names, local guides and local ecological understanding.”
 Perhaps the most frequently asked question Bandara encounters concerns the mighty Anaconda. While not a scientific name, the word itself is widely believed to be a corruption of the Sinhala Henakandaya, another snake name recorded in Ray’s listings of Sri Lankan reptiles.
Perhaps the most frequently asked question Bandara encounters concerns the mighty Anaconda. While not a scientific name, the word itself is widely believed to be a corruption of the Sinhala Henakandaya, another snake name recorded in Ray’s listings of Sri Lankan reptiles.
“What is remarkable,” Bandara reflected, “is that these words travelled across continents, entered global usage, and remained there — often stripped of their original meanings.”
For Bandara, restoring those meanings is about more than taxonomy. It is about reclaiming Sri Lanka’s rightful place in the history of science.
“With this study, three more Sinhala words formally join scientific nomenclature,” he said.
“Who would have imagined that a Sinhala word would be used to name a snake in Africa?”
Long before biodiversity hotspots became buzzwords and conservation turned global, Sri Lanka’s language was already speaking through science — quietly, persistently, and across continents.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
Children first – even after a disaster

However, the children and their needs may be forgotten after a disaster.
Do not forget that children will also experience fear and distress although they may not have the capacity to express their emotions verbally. It is essential to create child-friendly spaces that allow them to cope through play, draw, and engage in supportive activities that help them process their experiences in a healthy manner.
The Institute for Research & Development in Health & Social Care (IRD), Sri Lanka launched the campaign, titled “Children first,” after the 2004 Tsunami, based on the fundamental principle of not to medicalise the distress but help to normalise it.

The Island picture page
The IRD distributed drawing material and play material to children in makeshift shelters. Some children grabbed drawing material, but some took away play material. Those who choose drawing material, drew in different camps, remarkably similar pictures; “how the tidal wave came”.
“The Island” supported the campaign generously, realising the potential impact of it.
The campaign became a popular and effective public health intervention.
“A public health intervention (PHI) is any action, policy, or programme designed to improve health outcomes at the population level. These interventions focus on preventing disease, promoting health, and protecting communities from health threats. Unlike individual healthcare interventions (treating individuals), which target personal health issues, public health interventions address collective health challenges and aim to create healthier environments for all.”
The campaign attracted highest attention of state and politicians.
The IRD continued this intervention throughout the protracted war, and during COVID-19.
The IRD quick to relaunch the “children first” campaign which once again have received proper attention by the public.
While promoting a public health approach to handling the situation, we would also like to note that there will be a significant smaller percentage of children and adolescents will develop mental health disorders or a psychiatric diagnosis.
We would like to share the scientific evidence for that, revealed through; the islandwide school survey carried out by the IRD in 2007.
 During the survey, it was found that the prevalence of emotional disorder was 2.7%, conduct disorder 5.8%, hyperactivity disorder was 0.6%, and 8.5% were identified as having other psychiatric disorders. Absenteeism was present in 26.8%. Overall, previous exposure to was significantly associated with absenteeism whereas exposure to conflict was not, although some specific conflict-related exposures were significant risk factors. Mental disorder was strongly associated with absenteeism but did not account for its association with tsunami or conflict exposure.
During the survey, it was found that the prevalence of emotional disorder was 2.7%, conduct disorder 5.8%, hyperactivity disorder was 0.6%, and 8.5% were identified as having other psychiatric disorders. Absenteeism was present in 26.8%. Overall, previous exposure to was significantly associated with absenteeism whereas exposure to conflict was not, although some specific conflict-related exposures were significant risk factors. Mental disorder was strongly associated with absenteeism but did not account for its association with tsunami or conflict exposure.
The authors concluded that exposure to traumatic events may have a detrimental effect on subsequent school attendance. This may give rise to perpetuating socioeconomic inequality and needs further research to inform policy and intervention.
Even though, this small but significant percentage of children with psychiatric disorders will need specialist interventions, psychological treatment more than medication. Some of these children may complain of abdominal pain and headaches or other physical symptoms for which doctors will not be able to find a diagnosable medical cause. They are called “medically unexplained symptoms” or “somatization” or “bodily distress disorder”.
Sri Lanka has only a handful of specialists in child and adolescent psychiatric disorders but have adult psychiatrists who have enough experience in supervising care for such needy children. Compared to tsunami, the numbers have gone higher from around 20 to over 100 psychiatrists.
Most importantly, children absent from schools will need more close attention by the education authorities.
In conclusion, going by the principles of research dissemination sciences, it is extremely important that the public, including teachers and others providing social care, should be aware that the impact of Cyclone Ditwah, which was followed by major floods and landslides, which is a complex emergency impact, will range from normal human emotional behavioural responses to psychiatric illnesses. We should be careful not to medicalise this normal distress.
It’s crucial to recall an important statement made by the World Health Organisation following the Tsunam
Prof. Sumapthipala MBBS, DFM, MD Family Medicine, FSLCFP (SL), FRCPsych, CCST (UK), PhD (Lon)]
Director, Institute for Research and Development in Health and Social Care, Sri Lanka
Emeritus Professor of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences, Keele University, UK
Emeritus Professor of Global Mental Health, Kings College London
Secretary General, International society for Twin Studies
Visiting Professor in Psychiatry and Biomedical Research at the Faculty of Medicine, Kotelawala Defence University, Sri Lanka
Associate Editor, British Journal Psychiatry
Co-editor Ceylon Medical Journal.
Prof. Athula Sumathipala
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoMembers of Lankan Community in Washington D.C. donates to ‘Rebuilding Sri Lanka’ Flood Relief Fund
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoBritish MP calls on Foreign Secretary to expand sanction package against ‘Sri Lankan war criminals’
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoGeneral education reforms: What about language and ethnicity?
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoSuspension of Indian drug part of cover-up by NMRA: Academy of Health Professionals
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoChief selector’s remarks disappointing says Mickey Arthur
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoStreet vendors banned from Kandy City
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoA very sad day for the rule of law
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoUS Ambassador to Sri Lanka among 29 career diplomats recalled













