Features
RESEARCH AT 16 FIVE-STAR HOTELS – PART ‘A’

CONFESSIONS OF A GLOBAL GYPSY
By Dr. Chandana (Chandi) Jayawardena DPhil
President – Chandi J. Associates Inc. Consulting, Canada
Founder & Administrator – Global Hospitality Forum
chandij@sympatico.ca

I was very pleased when in 1984 the University of Surrey (UoS) in the UK approved ‘Food and Beverage operations in the context of five-star London hotels’ as my M.Sc. dissertation topic. As directed by my supervisor, Professor Richard Kotas, I read all of the books – cover to cover and journal articles ever written in English about Food and Beverage management and operations. That took over two months. I was also directed by him to answer three questions, to provide context in my research undertaking:
-
= What are luxury hotels?
-
=What is the history of British luxury hotels?
-
=How does Food and Beverage management play a vital role in London five-star hotels?
What are Luxury Hotels?
Many have attempted to define a luxury hotel. The word ‘luxury’ has different meanings to different people depending on their experiences and expectations. In many classification guides in 1984, words such as ‘de-luxe’, five-star’, ‘first-class’ or ‘exclusive’ were used by hoteliers and writers.
Some felt that the large size of a hotel was a disadvantage for the hoteliers to maintain true ‘five-star’ standards. In 1984, none of the largest 18 hotels (with between 1,029 and 530 rooms) in UK, were five-star ranked. The average size of the 21 five-star hotels in UK, was 261 rooms (ranging from 509 to 86 rooms). In 1984, the average age of these 21 hotels was 55 years. A majority (16) of them were in London.
The 16 five-star London hotels had a total of 48 food and beverage outlets (an average of three per hotel). Average banqueting capacity for sit-down meals was 406. Grosvenor House had the largest banqueting operation able to accommodate 1,500 guests for a sit-down meal.
Most countries in the world use some form of hotel classification system, out of which 65 systems in 1984 were enforced by the public sector. In UK, in 1984, the key hotel grading schemes were carried out by private organizations. The most famous and respected hotel grading scheme was done by the Automobile Association (AA). In my research, I found that up to 1984, nothing academically significant had been written about the British hotel classification schemes or the five-star hotel grading. That gap provided me an opportunity.
What is the History of British Luxury Hotels?
During the eleventh century, a few monastic institutions as well as private homes in Britain were used to provide accommodation to travellers. The English inn had probably originated from the practice of receiving travellers by private householders. Religion played a vital part determining people’s habits in consumption of food and beverages. Towards the late fourteenth century, solid-stone built structures replaced the sheds operated as ale-houses and taverns in the provinces and inns in London.
With the popularity of wagons and other wheeled transport towards the end of the 16th century, a larger scale Tudor Inn operation replaced the Medieval Inn. The eighteenth century was the turning point for gastronomy in Britain. Influenced by major cities in continental Europe, such as Paris, Vienna, as well as the main cities of Switzerland, the word ‘Hotel’ became common in Britain after 1760.
Proper hotels, with managers, receptionists, porters and page-boys, gradually became common in Britain only at the beginning of the nineteenth century. Large British hotels such as The Grand, The Great Eastern, The Euston, The Charing Cross, The Great Western Royal, and The Grosvenor were developed in that era. One common feature of these hotels was that all of them were located near major railway terminals in London.
The opening of The Langham on Regent Street, London in 1865, is generally considered the origin of true luxury hotels in UK. Bailey’s Hotel was opened eleven years after that in 1876, and the world-famous London hotel, The Savoy, opened in 1889. Around the same time, a few luxury hotels were opened in well-known resort cities and towns. In 1984, the oldest British hotel with a five-star rating was The Imperial in Torquay, which was opened in 1866.

Using all British Connections for M.Sc. Research
The British hotel industry looked to London for the latest trends and London emerged easily as the trend setter of the industry. Within the five-star London hotels, the food and beverage departments appeared to be the most complex and versatile. In answering my third and most important research question – ‘How does food and beverage management play a vital role in London five-star hotels?’ I decided to work or observe in all 16 five-star hotels in London, and interview dozens of relevant managers.
During the first half of the twentieth century, most five-star hotels around the world did not make much profits from their food and beverage operations. From an economic stand point it was important to attempt to break even. More emphasis was given to rooms, because this was where the money was made. The concept of food and beverage manager or director was relatively new in the world. This concept was developed only in the 1960s by major hotel chains in USA, combining the technical know-how with the business administration skills, aiming to optimize profits.
The food and beverage manager/director of a five-star hotel usually was responsible for nearly half the hotel’s employees (in 1984, in London it was 48%) and administered a range of complex departments such as kitchens, restaurants, bars, banqueting, events, room service, stewarding, and at times, mini bars, as well as, food and beverage controls. Having gained experience as an executive chef and food and beverage manager of two small resort hotels in Sri Lanka in mid-1970s, I focused on securing the position of the food and beverage manager/director of a large five-star international hotel, by mid-1980s.
I developed a one-page research questionnaire which was mailed to all 16 five-star hotels in London. I used my previously established contacts in UK to ensure that I received prompt and positive responses from each hotel. For my research interviews, I used 14 open ended questions. I loved this research undertaking, and was passionate about it. I knew that it would help me to reach my next career goal. I wanted to do much more than what was required of me by the university. I was hungry for useful knowledge.

I commenced my research interviews with people I knew well. I travelled to Cosham and Portsmouth to interview a couple of hospitality experts who supported me during my ILO/UNDP fellowship in 1982. I also contacted two Senior Lecturers of the South Devon Technical College, who had presented a two-week Hotel Management seminar in Sri Lanka in 1982. Having attended this seminar, I became friends with them.
“Chandi, why don’t you take a break from your hectic schedule in London and visit Dr. David Dann and I in Torquay? You both spend a weekend at my home and try my wife, Clair’s British cooking skills”, Tim Hornsey invited us over the telephone. Torquay is a beautiful seaside town in Devon, with numerous archaeological remains dating back to pre-historic times. In addition to hosting us, Tim and David and their wives took us to see The Imperial. They also arranged for me to interview the renowned hotelier who managed it, Harry Murray.
Using Part-time Work for Research
My readings, research interviews and informal discussions provided an enormous amount of data pertaining to my research topic. In addition, I collected many brochures, menus, wine cards, promotional material, control documents etc. from most of the London five-star hotels. These were carefully analysed prior to writing the dissertation. However, mid-way during the research activity, I felt strongly that in order to obtain insight into the actual hotel operations, it would be ideal to work in different capacities in various hotels.
I continued to work at The Dorchester as a part-time banquet waiter. Due to that valuable experience in the best hotel in UK, I was able to find part-time work in two other five-star hotels on Park Lane – London Hilton and InterContinental London. I also began working as a part-time banquet waiter at Claridge’s, which had opened in the nineteenth century. Doing similar work in four five-star hotels concurrently, provided me an excellent opportunity to compare and contrast their standards in food and beverage operations and banqueting.
Although I liked the old-world charm of Claridge’s and The Dorchester, I found that the food and beverage operations of the newer (originally) American chain hotels, InterContinental and Hilton, were far more efficient. Having previously worked at two InterContinental hotels in two other countries (Sri Lanka in 1973 and Hong Kong in 1981), I was familiar with their standards of operation in banquets. I was most impressed with the London Hilton, which had the most efficiently managed banquet operation in London.
As the demand on me to work as a banquet waiter in London increased, I became very busy. Often, I did three-hour shifts for meal services only. For such a short shift, I was paid only £8.40. On some days, I did three shifts in three hotels for breakfast, lunch and dinner. In between, I did research interviews. I became keen in gaining different types of five-star hotel experiences in London at a higher level.

Using Management Trainee Positions for Research
I spoke with my friend, Mr. Wilfred Weragoda, the Food & Beverage Controller of The Dorchester. Based on my new request, he arranged for me to spend two weeks in his department as a Food & Beverage Controls Trainee. In addition to learning different aspects of Food and Beverage operations, that brief exposure opened new doors for me.
One day, I interviewed W. A. Lipscombe, Managing Director of Hallway Hotels in his office in London. He was a friend of Mark Bostock, then Chairman of John Keells Group, who arranged my first Management Trainee assignment in UK with Trust House Forte in 1979. Due to their friendship, I was able to secure with good pay an excellent management trainee position in a 500-room five-star hotel in London. Lipscombe told me, “Chandi, hotels in my company are not five-star. Therefore, I will use a good contact of mine – The Managing Director of The Churchill, to arrange six weeks exposure in six departments for you. I will tell Mark that I did you a favour.”
The Churchill experience was excellent. I spent a week each in six departments – purchasing, receiving bay and stores, food and beverage controls and accounts department, reservations, banquets, restaurants and room service, and finally, kitchen. I also did a few research interviews, there. The most useful interview was given to me on my last day at The Churchill, by the company’s Managing Director, G. Webb. I was also exposed to The Churchill’s four-star sister hotel in London, The Montcalm.
I was encouraged with the success of my Management Trainee assignments at The Dorchester and The Churchill, in the context of enhancing my graduate research and acquiring experience and knowledge. These exposures also improved my résumé. With that enthusiasm, I approached my contacts at Trust House Forte, who arranged a short Management Trainee assignment for me at the 85-year-old five-star, The Hyde Park Hotel. There, I worked directly under its veteran General Manager, A. Grosso, who also gave me an opportunity to conduct one of my longest and useful research interviews.
Soon after that I was sent to the Trust House Forte Group’s flagship hotel, Grosvenor House, for a couple of weeks. I was pleased with this opportunity as Grosvenor House had the largest five-star Food and Beverage operations in UK. I did a few more research interviews there. One of those I interviewed was Ben Davis, the Food & Beverage Manager. In 1990’s both Ben and I held the same position in the Caribbean, as the General Manager of Trust House Forte’s 360-room five-star hotel – Jamaica Pegasus/Forte Grand.

I enjoyed full-day orientations at four five-star hotels in London at the commencement of each of my Management Trainee assignments. The most memorable orientation was at The Dorchester, due to one gentleman who made a big, positive impact. It was Udo Schlentrich, General Manager of The Dorchester. He was the only General Manager who met each group of new employees during their orientation. This Austrian-born hotelier trained in the best two hotel schools in the world (Lausanne in Switzerland and Cornell in USA), said something during the orientation, which remained permanently in my mind.
Udo Schlentrich said, “Thank you for joining the best British hotel – The Dorchester. Ladies and gentleman, as the General Manager I am just the conductor of the orchestra, but it is all of you who provide the music. Please do your best, to make our customer happy.” After that he had his lunch at the staff cafeteria with the new employees in the orientation. He sat next to me and had a friendly chat over lunch. He also gave me a research interview. Udo was a big inspiration to me. In later years, like me, at the hight of his hotel career he did a doctorate and became a professor.
The rest of my career, whenever there was an orientation in a hotel which I managed, I thought of what Udo Schlentrich did at the Dorchester in 1984, and I did something similar. The best practices one learns in the real-world trumps academic learning in universities.
Will continue in next week’s column: ‘Research at 16 Five-star Hotels – Part ‘B”.
Features
Crucial test for religious and ethnic harmony in Bangladesh
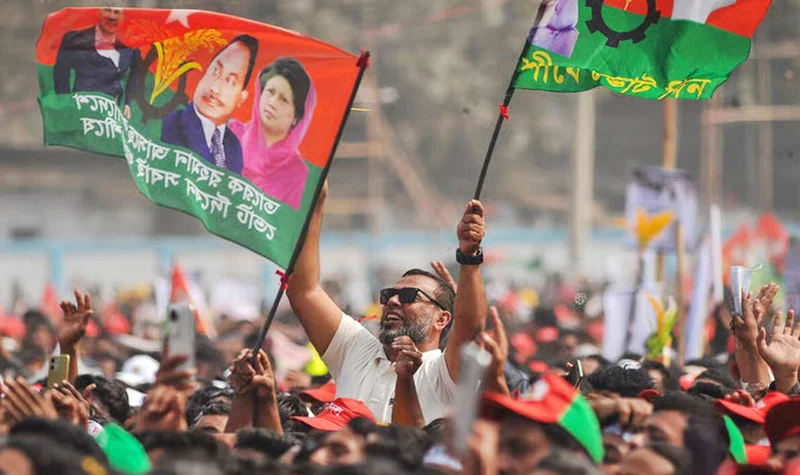

 Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
The apprehensions are mainly on the part of religious and ethnic minorities. The parliamentary poll of February 12th is expected to bring into existence a government headed by the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) and the Islamist oriented Jamaat-e-Islami party and this is where the rub is. If these parties win, will it be a case of Bangladesh sliding in the direction of a theocracy or a state where majoritarian chauvinism thrives?
Chief of the Jamaat, Shafiqur Rahman, who was interviewed by sections of the international media recently said that there is no need for minority groups in Bangladesh to have the above fears. He assured, essentially, that the state that will come into being will be equable and inclusive. May it be so, is likely to be the wish of those who cherish a tension-free Bangladesh.
The party that could have posed a challenge to the above parties, the Awami League Party of former Prime Minister Hasina Wased, is out of the running on account of a suspension that was imposed on it by the authorities and the mentioned majoritarian-oriented parties are expected to have it easy at the polls.
A positive that has emerged against the backdrop of the poll is that most ordinary people in Bangladesh, be they Muslim or Hindu, are for communal and religious harmony and it is hoped that this sentiment will strongly prevail, going ahead. Interestingly, most of them were of the view, when interviewed, that it was the politicians who sowed the seeds of discord in the country and this viewpoint is widely shared by publics all over the region in respect of the politicians of their countries.
Some sections of the Jamaat party were of the view that matters with regard to the orientation of governance are best left to the incoming parliament to decide on but such opinions will be cold comfort for minority groups. If the parliamentary majority comes to consist of hard line Islamists, for instance, there is nothing to prevent the country from going in for theocratic governance. Consequently, minority group fears over their safety and protection cannot be prevented from spreading.
Therefore, we come back to the question of just and fair governance and whether Bangladesh’s future rulers could ensure these essential conditions of democratic rule. The latter, it is hoped, will be sufficiently perceptive to ascertain that a Bangladesh rife with religious and ethnic tensions, and therefore unstable, would not be in the interests of Bangladesh and those of the region’s countries.
Unfortunately, politicians region-wide fall for the lure of ethnic, religious and linguistic chauvinism. This happens even in the case of politicians who claim to be democratic in orientation. This fate even befell Bangladesh’s Awami League Party, which claims to be democratic and socialist in general outlook.
We have it on the authority of Taslima Nasrin in her ground-breaking novel, ‘Lajja’, that the Awami Party was not of any substantial help to Bangladesh’s Hindus, for example, when violence was unleashed on them by sections of the majority community. In fact some elements in the Awami Party were found to be siding with the Hindus’ murderous persecutors. Such are the temptations of hard line majoritarianism.
In Sri Lanka’s past numerous have been the occasions when even self-professed Leftists and their parties have conveniently fallen in line with Southern nationalist groups with self-interest in mind. The present NPP government in Sri Lanka has been waxing lyrical about fostering national reconciliation and harmony but it is yet to prove its worthiness on this score in practice. The NPP government remains untested material.
As a first step towards national reconciliation it is hoped that Sri Lanka’s present rulers would learn the Tamil language and address the people of the North and East of the country in Tamil and not Sinhala, which most Tamil-speaking people do not understand. We earnestly await official language reforms which afford to Tamil the dignity it deserves.
An acid test awaits Bangladesh as well on the nation-building front. Not only must all forms of chauvinism be shunned by the incoming rulers but a secular, truly democratic Bangladesh awaits being licked into shape. All identity barriers among people need to be abolished and it is this process that is referred to as nation-building.
On the foreign policy frontier, a task of foremost importance for Bangladesh is the need to build bridges of amity with India. If pragmatism is to rule the roost in foreign policy formulation, Bangladesh would place priority to the overcoming of this challenge. The repatriation to Bangladesh of ex-Prime Minister Hasina could emerge as a steep hurdle to bilateral accord but sagacious diplomacy must be used by Bangladesh to get over the problem.
A reply to N.A. de S. Amaratunga
A response has been penned by N.A. de S. Amaratunga (please see p5 of ‘The Island’ of February 6th) to a previous column by me on ‘ India shaping-up as a Swing State’, published in this newspaper on January 29th , but I remain firmly convinced that India remains a foremost democracy and a Swing State in the making.
If the countries of South Asia are to effectively manage ‘murderous terrorism’, particularly of the separatist kind, then they would do well to adopt to the best of their ability a system of government that provides for power decentralization from the centre to the provinces or periphery, as the case may be. This system has stood India in good stead and ought to prove effective in all other states that have fears of disintegration.
Moreover, power decentralization ensures that all communities within a country enjoy some self-governing rights within an overall unitary governance framework. Such power-sharing is a hallmark of democratic governance.
Features
Celebrating Valentine’s Day …
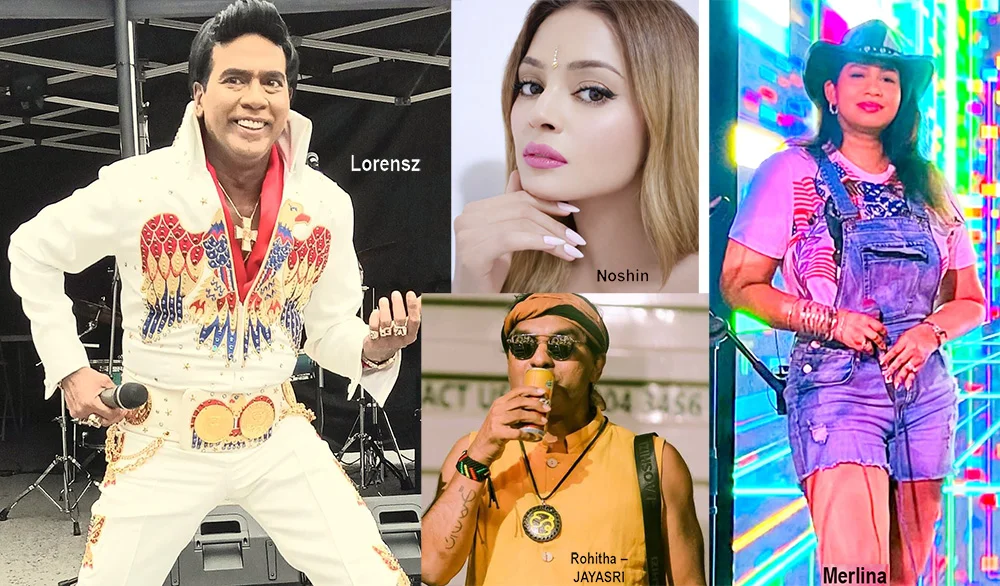

 Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
Merlina Fernando (Singer)
Yes, it’s a special day for lovers all over the world and it’s even more special to me because 14th February is the birthday of my husband Suresh, who’s the lead guitarist of my band Mission.
We have planned to celebrate Valentine’s Day and his Birthday together and it will be a wonderful night as always.
We will be having our fans and close friends, on that night, with their loved ones at Highso – City Max hotel Dubai, from 9.00 pm onwards.
Lorensz Francke (Elvis Tribute Artiste)
On Valentine’s Day I will be performing a live concert at a Wealthy Senior Home for Men and Women, and their families will be attending, as well.
I will be performing live with romantic, iconic love songs and my song list would include ‘Can’t Help falling in Love’, ‘Love Me Tender’, ‘Burning Love’, ‘Are You Lonesome Tonight’, ‘The Wonder of You’ and ‘’It’s Now or Never’ to name a few.
To make Valentine’s Day extra special I will give the Home folks red satin scarfs.
Emma Shanaya (Singer)
I plan on spending the day of love with my girls, especially my best friend. I don’t have a romantic Valentine this year but I am thrilled to spend it with the girl that loves me through and through. I’ll be in Colombo and look forward to go to a cute cafe and spend some quality time with my childhood best friend Zulha.
JAYASRI
Emma-and-Maneeka
This Valentine’s Day the band JAYASRI we will be really busy; in the morning we will be landing in Sri Lanka, after our Oman Tour; then in the afternoon we are invited as Chief Guests at our Maris Stella College Sports Meet, Negombo, and late night we will be with LineOne band live in Karandeniya Open Air Down South. Everywhere we will be sharing LOVE with the mass crowds.
Kay Jay (Singer)
I will stay at home and cook a lovely meal for lunch, watch some movies, together with Sanjaya, and, maybe we go out for dinner and have a lovely time. Come to think of it, every day is Valentine’s Day for me with Sanjaya Alles.
Maneka Liyanage (Beauty Tips)
On this special day, I celebrate love by spending meaningful time with the people I cherish. I prepare food with love and share meals together, because food made with love brings hearts closer. I enjoy my leisure time with them — talking, laughing, sharing stories, understanding each other, and creating beautiful memories. My wish for this Valentine’s Day is a world without fighting — a world where we love one another like our own beloved, where we do not hurt others, even through a single word or action. Let us choose kindness, patience, and understanding in everything we do.
Janaka Palapathwala (Singer)

Janaka
Valentine’s Day should not be the only day we speak about love.
From the moment we are born into this world, we seek love, first through the very drop of our mother’s milk, then through the boundless care of our Mother and Father, and the embrace of family.
Love is everywhere. All living beings, even plants, respond in affection when they are loved.
As we grow, we learn to love, and to be loved. One day, that love inspires us to build a new family of our own.
Love has no beginning and no end. It flows through every stage of life, timeless, endless, and eternal.
Natasha Rathnayake (Singer)
We don’t have any special plans for Valentine’s Day. When you’ve been in love with the same person for over 25 years, you realise that love isn’t a performance reserved for one calendar date. My husband and I have never been big on public displays, or grand gestures, on 14th February. Our love is expressed quietly and consistently, in ordinary, uncelebrated moments.
With time, you learn that love isn’t about proving anything to the world or buying into a commercialised idea of romance—flowers that wilt, sweets that spike blood sugar, and gifts that impress briefly but add little real value. In today’s society, marketing often pushes the idea that love is proven by how much money you spend, and that buying things is treated as a sign of commitment.
Real love doesn’t need reminders or price tags. It lives in showing up every day, choosing each other on unromantic days, and nurturing the relationship intentionally and without an audience.
This isn’t a judgment on those who enjoy celebrating Valentine’s Day. It’s simply a personal choice.
Melloney Dassanayake (Miss Universe Sri Lanka 2024)
 I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I’m incredibly blessed because, for me, every day feels like Valentine’s Day. My special person makes sure of that through the smallest gestures, the quiet moments, and the simple reminders that love lives in the details. He shows me that it’s the little things that count, and that love doesn’t need grand stages to feel extraordinary. This Valentine’s Day, perfection would be something intimate and meaningful: a cozy picnic in our home garden, surrounded by nature, laughter, and warmth, followed by an abstract drawing session where we let our creativity flow freely. To me, that’s what love is – simple, soulful, expressive, and deeply personal. When love is real, every ordinary moment becomes magical.
Noshin De Silva (Actress)
Valentine’s Day is one of my favourite holidays! I love the décor, the hearts everywhere, the pinks and reds, heart-shaped chocolates, and roses all around. But honestly, I believe every day can be Valentine’s Day.
It doesn’t have to be just about romantic love. It’s a chance to celebrate love in all its forms with friends, family, or even by taking a little time for yourself.
Whether you’re spending the day with someone special or enjoying your own company, it’s a reminder to appreciate meaningful connections, show kindness, and lead with love every day.
And yes, I’m fully on theme this year with heart nail art and heart mehendi design!
Wishing everyone a very happy Valentine’s Day, but, remember, love yourself first, and don’t forget to treat yourself.
Sending my love to all of you.
Features
Banana and Aloe Vera
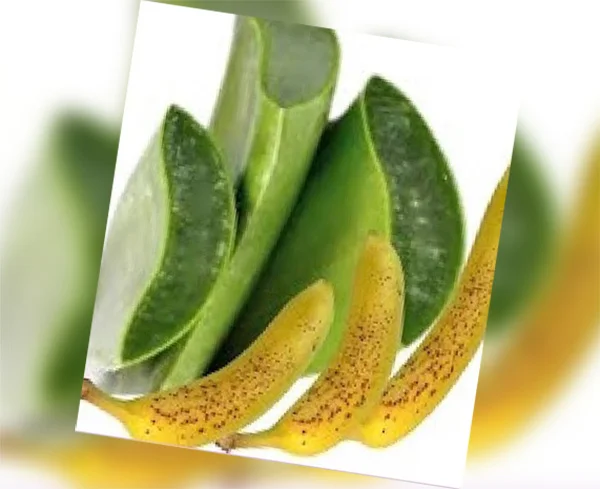

 To create a powerful, natural, and hydrating beauty mask that soothes inflammation, fights acne, and boosts skin radiance, mix a mashed banana with fresh aloe vera gel.
To create a powerful, natural, and hydrating beauty mask that soothes inflammation, fights acne, and boosts skin radiance, mix a mashed banana with fresh aloe vera gel.
This nutrient-rich blend acts as an antioxidant-packed anti-ageing treatment that also doubles as a nourishing, shiny hair mask.
* Face Masks for Glowing Skin:
Mix 01 ripe banana with 01 tablespoon of fresh aloe vera gel and apply this mixture to the face. Massage for a few minutes, leave for 15-20 minutes, and then rinse off for a glowing complexion.
* Acne and Soothing Mask:
Mix 01 tablespoon of fresh aloe vera gel with 1/2 a mashed banana and 01 teaspoon of honey. Apply this mixture to clean skin to calm inflammation, reduce redness, and hydrate dry, sensitive skin. Leave for 15-20 minutes, and rinse with warm water.
* Hair Treatment for Shine:
Mix 01 fresh ripe banana with 03 tablespoons of fresh aloe vera gel and 01 teaspoon of honey. Apply from scalp to ends, massage for 10-15 minutes and then let it dry for maximum absorption. Rinse thoroughly with cool water for soft, shiny, and frizz-free hair.
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Midweek Review2 days ago
Midweek Review2 days agoA question of national pride













