Features
Politics and Administrators in the 20th Century

The Kandy Man – An Autobiography, Volume one (1939-1977),
By Sarath Amunugam. Vijitha Yapa Publications (2020).548 pages
Reviewed by Leelananda De Silva
Introduction
In two years, Sri Lanka should celebrate 75 years since independence. During this period, there have been dramatic social, cultural and economic changes. The British inheritance is fading fast, whether it be in Government and administration, politics and constitution making, in education and in foreign relations. It is time for the university academics or some others to consider writing the history of Sri Lanka these last 75 years and capture the momentous changes that have occurred. Whether that history will be written in Sinhalese, Tamil or English is yet to be seen. Sarath Amunugama’s volume is an important building block in constructing that history.
Amunugama is one of the outstanding personalities of Sri Lanka in our generation. An academic, top administrator and leading politician, he has played an important role in Sri Lankan public life. He has lived in and served the country in an era of rapid change. Amunugama is one of the very few members of the Ceylon Civil Service to have moved into high level politics after 1948. The others were C. Suntheralingam, C. Sittampalam, Walwin. A. de Silva, Ronnie de Mel and Nissanka Wijeyaratne. The volume under review is only the first part of a three-volume autobiography. Broadly, the current volume addresses three broad areas – his education at Trinity College, Kandy in the 1940s and at the University of Ceylon at Peradeniya in the 1950s; as a high level district administrator in the 1960s; and at the centre of Government as Director of Information in the 1970s. He has straddled the demarcations between administration and politics with ease and he has worked with politicians of all hues comfortably.
Trinity College, Kandy
The first chapter of this volume deals with his school days at Trinity College, Kandy. He offers us a wide ranging picture of Trinity and also of Kandy of that time. He describes College academic life, sports and cadeting and student debates with other schools, especially the girls’ schools in Kandy. Regrettably, there is no reference to the subjects they debated about. Amunugama has great admiration for some of his teachers. Hillary Abeyaratne was one of his heroes, and others were R.R. Breckenridge, Willy Hensman and Gordon Burrows. He greatly admired his Principal, Norman Walter, probably one of the last school principals of British origin in Sri Lanka. Walter wrote to the Vice Chancellor of the University requesting that Amunugama be admitted to the University although he was underage, a request that could not be granted.
Our generation, whether it be from schools in Colombo or Galle, knew of Trinity largely because of a famous Principal, A.G. Fraser and a British teacher and preacher, Rev. W.S. Senior, who wrote some delightful, haunting poetry about Kandy. Amunugama’s story of Trinity could have been better if he dealt with the history of Trinity and the influence the College had on the Kandyan middle and upper classes. Trinity was a great inheritance from British days.
The University at Peradeniya
 In the 1950s, the University at Peradeniya (part of the University of Ceylon) was unique in the history of universities in Sri Lanka. It had only about a thousand students, and the faculties were almost entirely of the Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences. There was no Physical Science, Engineering or Medicine. This lasted for only a decade. The undergraduates lived in halls of residence not far from each other. All this tended to make the university a friendly and even homely place, with friendships across disciplines and residencies.
In the 1950s, the University at Peradeniya (part of the University of Ceylon) was unique in the history of universities in Sri Lanka. It had only about a thousand students, and the faculties were almost entirely of the Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences. There was no Physical Science, Engineering or Medicine. This lasted for only a decade. The undergraduates lived in halls of residence not far from each other. All this tended to make the university a friendly and even homely place, with friendships across disciplines and residencies.
Amunugama seems to have enjoyed the university in his four years there and was fully engaged in its academic, political and cultural life. He was active in various groups, especially with E.R. Sarachchandra and Siri Gunasinghe. This was the time of Maname, a Sarachchandra play which revolutionized Sri Lankan drama and with which Amunugama was closely associated. He offers us an excellent picture of the cultural activities of the university at that time. This was also a time when undergraduates studied in the English medium and yet Sinhala culture was flourishing.
He offers us a fascinating picture of the Sociology department at the university in its early days. S.J. Thambiah and Gananath Obeysekara were students and lecturers. Later on, they were to become world class academics, teaching at Princeton and Harvard in the U.S.A. Laksiri Jayasuriya and Ralph Pieris were other leading academics. There are engaging pen portraits of these academics. Amunugama appears to be an admirer of Ralph Pieris, who was his teacher. He tells us the story of Jennings’s hesitation in setting up departments of Sinhala culture and sociology as these subjects were strange to the Oxbridge traditions from which Jennings had emerged. He also tells us of the differences that Martin Wickramasinghe had with Jennings’ approach to Sinhala cultural studies and also of the pioneering role played by Professor Ratnasuriya who died young. The volume also offers us some insight into university politics but there is no space to get into detail here. However it must be noted that Amunugama was President of the Union Society at Peradeniya during his time there. Overall, the volume offers an engaging picture of the University at Peradeniya of the 1950s.
District Administration
Since Amunugama entered the Ceylon Civil Service in 1963 (the CCS was abolished soon after), the next seven years of his career was in district administration. He served as AGA and Additional GA in Galle, Ratnapura and Kandy districts. Amunugama’s academic background was ideal to deal with the range of issues that he had to face in the districts. His 200-page story of his engagement in district administration reminds me of Leonard Woolf’s volume “Growing 1904 – 1911” (the second volume of his five volume autobiography, published in the 1960s), which is about his seven years in Ceylon and when he was engaged in district administration. Unlike in imperial days, the district administrator in the 1960s had to deal with politicians and a democratic government. They were no longer the rulers like Leonard Woolf.
The young Civil Servant’s interests were so expansive that he was in a position to fruitfully interact in the area of agriculture and lands and irrigation, culture, the arts and the temples and with the politics of these districts. In the Galle district, where he served for nearly three years, he established a good relationship with the legendary W. Dahanayake, MP for Galle and his Minister of Home Affairs in later years. Amunugama was immersed in the cultural life of the Galle district and he had a friendly relationship with the DROs of the area. When in Galle, he became very familiar with the backgrounds of two of the great cultural figures of our time – Martin Wickramasinghe and Gunadasa Amarasekara, visiting many of the villages and the scenes depicted in their novels.
In the Kandy district, Amunugama was again very involved in the political and cultural life of the district. He initiated the concept of mobile kacheries which enabled the villagers, instead of coming to Kandy, to have their problems addressed near their own villages. He also initiated a more effective approach to increase the productive capacity of farmers. Local village level officials who should assist the farmers were not living in the villages they were officially attached to, but were commuting to their own homes. Amunugama started the practice of giving these field officers lands of their own, so that they will live with the farmers and work with them. He has many stories to relate about his relationships with the politicians of the day like Anuruddha Ratwatte in Kandy. In the Ratnapura district, he was deeply engaged in land development in the Udawalawe and Chandrika weva colonization schemes.
Overall, the chapters entitled “The Ceylon Civil Service” and “Government Agent”, are in effect addressing issues in district administration. It’s a matter of some curiosity why he titled these two chapters in this way instead of making them chapters on district administration. By the time he was AGA and Additional GA and serving in the districts, the CCS had been abolished. The CCS lasted only the first year of his public service career. Since that time, he and other ex-CCS officers were members of the Ceylon Administrative Service (CAS).
I understand the hesitations of some of the ex-CCS personnel to use the new CAS nomenclature. However, difficult it is for them, to call themselves CCS after its abolition in 1963, is like Grama Sevakas calling themselves village headmen and DROs calling themselves Mudliyars. These were denominations of an imperial era. Amunugama tells us that when their batch joined the CCS, on their first day, the then Secretary to the Treasury and Head of the CCS, Shirley Amarasinghe addressed them on how to behave. Interestingly, within one year of that day, Shirley Amarasinghe (who was only 50 years old at the time) himself left the CCS and joined the Ceylon Overseas Service to go as High Commissioner to India.
Director of Information
Amunugama moved into the centre of Government when he was appointed Director of Information in 1968 when Dudley Senanayake was Prime Minister. He continued his tenure under Mrs. Sirima Bandaranaike when she became Prime Minister in 1970. This is an assignment which suited Amunugama’s academic, administrative and political skills. His story of these years is compulsive reading and there are entertaining stories of politics at the highest level. At a young age, he was able to interact with the top politicians of his day. During this period, he also engaged in what looks to be his pastime – international travel – which he has done extensively over the years. In fact, the volume has many paragraphs and stories of his foreign travels including a long spell in Canada reading for a postgraduate degree.
As Director of Information, he was privy to much of the politics of his time. There are fascinating stories of the tensions between the LSSP and the SLFP when they were in coalition in the 1970s. There are engaging portraits of R. Premadasa when he was Minister of Local Government. Who could have known that Premadasa, when he was Deputy Minister of Local Government, had a very high regard for his Minister M. Tiruchelvam at the time when the UNP had formed a coalition with the Federal Party.
The writer relates the story of how the State Film Corporation was shifted from his ministry to the Ministry of Planning and Economic Affairs, where I had to handle its affairs. There are many other vignettes of his time as Director of Information of top politicians like Dudley Senanayake, Mrs. Bandaranaike, N.M. Perera and many others.
Conclusion
To conclude my review, let me refer to the long Preface of this book which addresses questions of writing biographies and autobiographies. Many biographies in Sri Lanka of leading politicians are largely hagiographies, praising them no end. This was the pattern of autobiographical writing too. In the early 1920s, there was a dramatic change in the art of biographical writing. Lytton Strachey, a member of the Bloomsbury group (a close friend of Leonard and Virginia Woolf) wrote his “Eminent Victorians” which changed the art of biography. Of his chosen few biographical topics, which included Queen Victoria and Florence Nightingale, he wrote about these leading icons of that generation, warts and all, bringing them down a peg or two.
This introduced a new form of biography, which was more investigative, critical and more true to the lives of their subjects. Autobiographies can never be swallowed whole. To paraphrase Robert Burns, the great Scottish poet, no power has given us the gift “to see ourselves as others see us.” That is the inherent weakness of autobiography. Amunugama’s first volume of a three volume autobiography is an outstanding work in its field, and is a great addition to our knowledge of our contemporary times. It was a pleasure to read.
Features
Following the Money: Tourism’s revenue crisis behind the arrival numbers – PART II

(Article 2 of the 4-part series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation)
 If Sri Lanka’s tourism story were a corporate income statement, the top line would satisfy any minister. Arrivals went up 15.1%, targets met, records broke. But walk down the statement and the story darkens. Revenue barely budges. Per-visitor yield collapses. The money that should accompany all those arrivals has quietly vanished, or, more accurately, never materialised.
If Sri Lanka’s tourism story were a corporate income statement, the top line would satisfy any minister. Arrivals went up 15.1%, targets met, records broke. But walk down the statement and the story darkens. Revenue barely budges. Per-visitor yield collapses. The money that should accompany all those arrivals has quietly vanished, or, more accurately, never materialised.
This is not a recovery. It is a volume trap, more tourists generating less wealth, with policymakers either oblivious to the math or unwilling to confront it.
Problem Diagnosis: The Paradox of Plenty:
The numbers tell a brutal story.
Read that again: arrivals grew 15.1% year-on-year, but revenue grew only 1.6%. The average tourist in 2025 left behind $181 less than in 2024, an 11.7% decline. Compared to 2018, the drop is even sharper. In real terms, adjusting for inflation and currency depreciation, each visitor in 2025 generates approximately 27-30% less revenue than in 2018, despite Sri Lanka being “cheaper” due to the rupee’s collapse. This is not marginal variance. This is structural value destruction. (See Table 1)
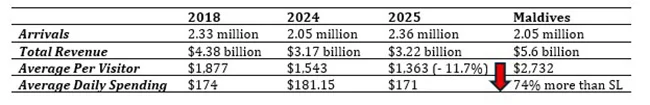
The math is simple and damning: Sri Lanka is working harder for less. More tourists, lower yield, thinner margins. Why? Because we have confused accessibility with competitiveness. We have made ourselves “affordable” through currency collapse and discounting, not through value creation.
Root Causes: The Five Mechanisms of Value Destruction
The yield collapse is not random. It is the predictable outcome of specific policy failures and market dynamics.
1. Currency Depreciation as False Competitiveness
The rupee’s collapse post-2022 has made Sri Lanka appear “cheap” to foreigners. A hotel room priced at $100 in 2018 might cost $70-80 in effective purchasing power today due to depreciation. Tour operators have aggressively discounted to fill capacity during the crisis recovery.
This creates the illusion of competitiveness. Arrivals rise because we are a “bargain.” But the bargain is paid for by domestic suppliers, hotels, transport providers, restaurants, staff, whose input costs (energy, food, imported goods) have skyrocketed in rupee terms while room rates lag in dollar terms.
The transfer is explicit: value flows from Sri Lankan workers and businesses to foreign tourists. The tourism “recovery” extracts wealth from the domestic economy rather than injecting it.
2. Market Composition Shift: Trading European Yields for Asian Volumes
SLTDA data shows a deliberate (or accidental—the policy opacity makes it unclear) shift in source markets. (See Table 2)
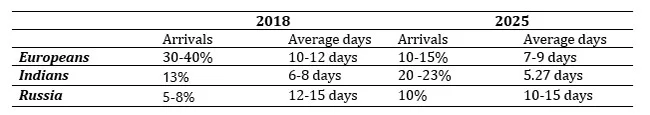
The problem is not that we attract Indians or Russians, it is that we attract them without strategies to optimise their yield. As the next article in this series will detail, Indian tourists average approximately 5.27 nights compared to the 8-9 night overall average, with lower per-day spending. We have built recovery on volume from price-sensitive segments rather than value from high-yield segments.
This is a choice, though it appears no one consciously made it. Visa-free entry, aggressive India-focused marketing, and price positioning have tilted the market mix without any apparent analysis of revenue implications.
3. Length of Stay Decline and Activity Compression
Average length of stay has compressed. While overall averages hover around 8-9 nights in recent years, the composition matters. High-yield European and North American tourists who historically spent 10-12 nights are now spending 7-9. Indian tourists spend 5-6 nights.
Shorter stays mean less cumulative spending, fewer experiences consumed, less distribution of value across the tourism chain. A 10-night tourist patronises multiple regions, hotels, guides, restaurants. A 5-night tourist concentrates spending in 2-3 locations, typically Colombo, one beach, one cultural site.
The compression is driven partly by global travel trends (shorter, more frequent trips) but also by Sri Lanka’s failure to develop compelling multi-day itineraries, adequate inter-regional connectivity, and differentiated regional experiences. We have not given tourists reasons to stay longer.
4. Infrastructure Decay and Experience Degradation
Tourists pay for experiences, not arrivals. When experiences degrade, airport congestion, poor road conditions, inadequate facilities at cultural sites, safety concerns, spending falls even if arrivals hold.
The 2024-2025 congestion at Bandaranaike International Airport, with reports of tourists nearly missing flights due to bottlenecks, is the visible tip. Beneath are systemic deficits: poor last-mile connectivity to tourism sites, deteriorating heritage assets, unregistered businesses providing sub-standard services, outbound migration of trained staff.
An ADB report notes that tourism authorities face resource shortages and capital expenditure embargoes, preventing even basic facility improvements at major revenue generators like Sigiriya (which charges $36 per visitor and attracts 25% of all tourists). When a site generates substantial revenue but lacks adequate lighting, safety measures, and visitor facilities, the experience suffers, and so does yield.
5. Leakage: The Silent Revenue Drain
Tourism revenue figures are gross. Net foreign exchange contributions after leakages, is rarely calculated or published.
Leakages include:
· Imported food, beverages, amenities in hotels (often 30-40% of operating costs)
· Foreign ownership and profit repatriation
· International tour operators taking commissions upstream (tourists book through foreign platforms that retain substantial margins)
· Unlicensed operators and unregulated businesses evading taxes and formal banking channels
Industry sources estimate leakages can consume 40-60% of gross tourism revenue in developing economies with weak regulatory enforcement. Sri Lanka has not published comprehensive leakage studies, but all indicators, weak licensing enforcement, widespread informal sector activity, foreign ownership concentration in resorts, suggest leakages are substantial and growing.
The result: even the $3.22 billion headline figure overstates actual net contribution to the economy.
The Way Forward: From Volume to Value
Reversing the yield collapse requires
systematic policy reorientation, from arrivals-chasing to value-building.
First
, publish and track yield metrics as primary KPIs. SLTDA should report:
· Revenue per visitor (by source market, by season, by purpose)
· Average daily expenditure (disaggregated by accommodation, activities, food, retail)
· Net foreign exchange contribution after documented leakages
· Revenue per room night (adjusted for real exchange rates)
Make these as visible as arrival numbers. Hold policy-makers accountable for yield, not just volume.
Second
, segment markets explicitly by yield potential. Stop treating all arrivals as equivalent. Conduct market-specific yield analyses:
· Which markets spend most per day?
· Which stays longest?
· Which distributes spending across regions vs. concentrating in Colombo/beach corridors?
· Which book is through formal channels vs. informal operators?
Target marketing and visa policies accordingly. If Western European tourists spend $250/day for 10 nights while another segment spends $120/day for 5 nights, the revenue difference ($2,500 vs. $600) dictates where promotional resources should flow.
Third
, develop multi-day, multi-region itineraries with compelling value propositions. Tourists extend stays when there are reasons to stay. Create integrated experiences:
· Cultural triangle + beach + hill country circuits with seamless connectivity
· Themed tours (wildlife, wellness, culinary, adventure) requiring 10+ days
· Regional spread of accommodation and experiences to distribute economic benefits
This requires infrastructure investment, precisely what has been neglected.
Fourth
, regulations to minimise leakages. Enforce licensing for tourism businesses. Channel bookings through formal operators registered with commercial banks. Tax holiday schemes should prioritise investments that maximise local value retention, staff training, local sourcing, domestic ownership.
Fifth
, stop using currency depreciation as a competitive strategy. A weak rupee makes Sri Lanka “affordable” but destroys margins and transfers wealth outward. Real competitiveness comes from differentiated experiences, quality standards, and strategic positioning, not from being the “cheapest” option.
The Hard Math: What We’re Losing
Let’s make the cost explicit. If Sri Lanka maintained 2018 per-visitor spending levels ($1,877) on 2025 arrivals (2.36 million), revenue would be approximately $4.43 billion, not $3.22 billion. The difference: $1.21 billion in lost revenue, value that should have been generated but wasn’t.
That $1.21 billion is not a theoretical gap. It represents:
· Wages not paid
· Businesses not sustained
· Taxes not collected
· Infrastructure not funded
· Development not achieved
This is the cost of volume-chasing without yield discipline. Every year we continue this model; we lock in value destruction.
The Policy Failure: Why Arrivals Theater Persists
Why do policymakers fixate on arrivals when revenue tells the real story?
Because arrivals are politically legible. A minister can tout “record tourist numbers” in a press conference. Revenue per visitor requires explanation, context, and uncomfortable questions about policy choices.
Arrivals are easy to manipulate upward, visa-free entry, aggressive discounting, currency depreciation. Yield is hard, it requires product development, market curation, infrastructure investment, regulatory enforcement.
Arrivals theater is cheaper and quicker than strategic transformation. But this is governance failure at its most fundamental. Tourism’s contribution to economic recovery is not determined by how many planes land but by how much wealth each visitor creates and retains domestically. Every dollar spent celebrating arrival records while ignoring yield collapse is a waste of dollars.
The Uncomfortable Truth
Sri Lanka’s tourism “boom” is real in volume, but it is a value bust. We are attracting more tourists and generating less wealth. The industry is working harder for lower returns. Margins are compressed, staff are paid less in real terms, infrastructure decays, and the net contribution to national recovery underperforms potential.
This is not sustainable. Eventually, operators will exit. Quality will degrade further. The “affordable” positioning will shift to “cheap and deteriorating.” The volume will follow yield down.
We have two choices: acknowledge the yield crisis and reorient policy toward value creation or continue arrivals theater until the hollowness becomes undeniable.
The money has spoken. The question is whether anyone in power is listening.
Features
Misinterpreting President Dissanayake on National Reconciliation

President Anura Kumara Dissanayake has been investing his political capital in going to the public to explain some of the most politically sensitive and controversial issues. At a time when easier political choices are available, the president is choosing the harder path of confronting ethnic suspicion and communal fears. There are three issues in particular on which the president’s words have generated strong reactions. These are first with regard to Buddhist pilgrims going to the north of the country with nationalist motivations. Second is the controversy relating to the expansion of the Tissa Raja Maha Viharaya, a recently constructed Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai which has become a flashpoint between local Tamil residents and Sinhala nationalist groups. Third is the decision not to give the war victory a central place in the Independence Day celebrations.
Even in the opposition, when his party held only three seats in parliament, Anura Kumara Dissanayake took his role as a public educator seriously. He used to deliver lengthy, well researched and easily digestible speeches in parliament. He continues this practice as president. It can be seen that his statements are primarily meant to elevate the thinking of the people and not to win votes the easy way. The easy way to win votes whether in Sri Lanka or elsewhere in the world is to rouse nationalist and racist sentiments and ride that wave. Sri Lanka’s post independence political history shows that narrow ethnic mobilisation has often produced short term electoral gains but long term national damage.
Sections of the opposition and segments of the general public have been critical of the president for taking these positions. They have claimed that the president is taking these positions in order to obtain more Tamil votes or to appease minority communities. The same may be said in reverse of those others who take contrary positions that they seek the Sinhala votes. These political actors who thrive on nationalist mobilisation have attempted to portray the president’s statements as an abandonment of the majority community. The president’s actions need to be understood within the larger framework of national reconciliation and long term national stability.
Reconciler’s Duty
When the president referred to Buddhist pilgrims from the south going to the north, he was not speaking about pilgrims visiting long established Buddhist heritage sites such as Nagadeepa or Kandarodai. His remarks were directed at a specific and highly contentious development, the recently built Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai and those built elsewhere in the recent past in the north and east. The temple in Kankesanturai did not emerge from the religious needs of a local Buddhist community as there is none in that area. It has been constructed on land that was formerly owned and used by Tamil civilians and which came under military occupation as a high security zone. What has made the issue of the temple particularly controversial is that it was established with the support of the security forces.
The controversy has deepened because the temple authorities have sought to expand the site from approximately one acre to nearly fourteen acres on the basis that there was a historic Buddhist temple in that area up to the colonial period. However, the Tamil residents of the area fear that expansion would further displace surrounding residents and consolidate a permanent Buddhist religious presence in the present period in an area where the local population is overwhelmingly Hindu. For many Tamils in Kankesanturai, the issue is not Buddhism as a religion but the use of religion as a vehicle for territorial assertion and demographic changes in a region that bore the brunt of the war. Likewise, there are other parts of the north and east where other temples or places of worship have been established by the military personnel in their camps during their war-time occupation and questions arise regarding the future when these camps are finally closed.
There are those who have actively organised large scale pilgrimages from the south to make the Tissa temple another important religious site. These pilgrimages are framed publicly as acts of devotion but are widely perceived locally as demonstrations of dominance. Each such visit heightens tension, provokes protest by Tamil residents, and risks confrontation. For communities that experienced mass displacement, military occupation and land loss, the symbolism of a state backed religious structure on contested land with the backing of the security forces is impossible to separate from memories of war and destruction. A president committed to reconciliation cannot remain silent in the face of such provocations, however uncomfortable it may be to challenge sections of the majority community.
High-minded leadership
The controversy regarding the president’s Independence Day speech has also generated strong debate. In that speech the president did not refer to the military victory over the LTTE and also did not use the term “war heroes” to describe soldiers. For many Sinhala nationalist groups, the absence of these references was seen as an attempt to diminish the sacrifices of the armed forces. The reality is that Independence Day means very different things to different communities. In the north and east the same day is marked by protest events and mourning and as a “Black Day”, symbolising the consolidation of a state they continue to experience as excluding them and not empathizing with the full extent of their losses.
By way of contrast, the president’s objective was to ensure that Independence Day could be observed as a day that belonged to all communities in the country. It is not correct to assume that the president takes these positions in order to appease minorities or secure electoral advantage. The president is only one year into his term and does not need to take politically risky positions for short term electoral gains. Indeed, the positions he has taken involve confronting powerful nationalist political forces that can mobilise significant opposition. He risks losing majority support for his statements. This itself indicates that the motivation is not electoral calculation.
President Dissanayake has recognized that Sri Lanka’s long term political stability and economic recovery depend on building trust among communities that once peacefully coexisted and then lived through decades of war. Political leadership is ultimately tested by the willingness to say what is necessary rather than what is politically expedient. The president’s recent interventions demonstrate rare national leadership and constitute an attempt to shift public discourse away from ethnic triumphalism and toward a more inclusive conception of nationhood. Reconciliation cannot take root if national ceremonies reinforce the perception of victory for one community and defeat for another especially in an internal conflict.
BY Jehan Perera
Features
Recovery of LTTE weapons

I have read a newspaper report that the Special Task Force of Sri Lanka Police, with help of Military Intelligence, recovered three buried yet well-preserved 84mm Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers used by the LTTE, in the Kudumbimalai area, Batticaloa.
These deadly weapons were used by the LTTE SEA TIGER WING to attack the Sri Lanka Navy ships and craft in 1990s. The first incident was in February 1997, off Iranativu island, in the Gulf of Mannar.
Admiral Cecil Tissera took over as Commander of the Navy on 27 January, 1997, from Admiral Mohan Samarasekara.
The fight against the LTTE was intensified from 1996 and the SLN was using her Vanguard of the Navy, Fast Attack Craft Squadron, to destroy the LTTE’s littoral fighting capabilities. Frequent confrontations against the LTTE Sea Tiger boats were reported off Mullaitivu, Point Pedro and Velvetiturai areas, where SLN units became victorious in most of these sea battles, except in a few incidents where the SLN lost Fast Attack Craft.

Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers
The intelligence reports confirmed that the LTTE Sea Tigers was using new recoilless rocket launchers against aluminium-hull FACs, and they were deadly at close quarter sea battles, but the exact type of this weapon was not disclosed.
The following incident, which occurred in February 1997, helped confirm the weapon was Carl Gustaf 84 mm Recoilless gun!
DATE: 09TH FEBRUARY, 1997, morning 0600 hrs.
LOCATION: OFF IRANATHIVE.
FACs: P 460 ISRAEL BUILT, COMMANDED BY CDR MANOJ JAYESOORIYA
P 452 CDL BUILT, COMMANDED BY LCDR PM WICKRAMASINGHE (ON TEMPORARY COMMAND. PROPER OIC LCDR N HEENATIGALA)
OPERATED FROM KKS.
CONFRONTED WITH LTTE ATTACK CRAFT POWERED WITH FOUR 250 HP OUT BOARD MOTORS.
TARGET WAS DESTROYED AND ONE LTTE MEMBER WAS CAPTURED.
LEADING MARINE ENGINEERING MECHANIC OF THE FAC CAME UP TO THE BRIDGE CARRYING A PROJECTILE WHICH WAS FIRED BY THE LTTE BOAT, DURING CONFRONTATION, WHICH PENETRATED THROUGH THE FAC’s HULL, AND ENTERED THE OICs CABIN (BETWEEN THE TWO BUNKS) AND HIT THE AUXILIARY ENGINE ROOM DOOR AND HAD FALLEN DOWN WITHOUT EXPLODING. THE ENGINE ROOM DOOR WAS HEAVILY DAMAGED LOOSING THE WATER TIGHT INTEGRITY OF THE FAC.
THE PROJECTILE WAS LATER HANDED OVER TO THE NAVAL WEAPONS EXPERTS WHEN THE FACs RETURNED TO KKS. INVESTIGATIONS REVEALED THE WEAPON USED BY THE ENEMY WAS 84 mm CARL GUSTAF SHOULDER-FIRED RECOILLESS GUN AND THIS PROJECTILE WAS AN ILLUMINATER BOMB OF ONE MILLION CANDLE POWER. BUT THE ATTACKERS HAS FAILED TO REMOVE THE SAFETY PIN, THEREFORE THE BOMB WAS NOT ACTIVATED.

Sea Tigers
Carl Gustaf 84 mm recoilless gun was named after Carl Gustaf Stads Gevärsfaktori, which, initially, produced it. Sweden later developed the 84mm shoulder-fired recoilless gun by the Royal Swedish Army Materiel Administration during the second half of 1940s as a crew served man- portable infantry support gun for close range multi-role anti-armour, anti-personnel, battle field illumination, smoke screening and marking fire.
It is confirmed in Wikipedia that Carl Gustaf Recoilless shoulder-fired guns were used by the only non-state actor in the world – the LTTE – during the final Eelam War.
It is extremely important to check the batch numbers of the recently recovered three launchers to find out where they were produced and other details like how they ended up in Batticaloa, Sri Lanka?
 By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
WV, RWP and Bar, RSP, VSV, USP, NI (M) (Pakistan), ndc, psn, Bsc (Hons) (War Studies) (Karachi) MPhil (Madras)
Former Navy Commander and Former Chief of Defence Staff
Former Chairman, Trincomalee Petroleum Terminals Ltd
Former Managing Director Ceylon Petroleum Corporation
Former High Commissioner to Pakistan
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Editorial7 days ago
Editorial7 days agoAll’s not well that ends well?
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check












