Features
Myth of unemployable arts graduates

(This is a response by a group of Sri Lankan university teachers to the audit report Propensity to tend education under the Arts stream and the unemployment of Arts Graduates.
Recently, the Committee on Public Accounts discussed a report prepared by the audit office, entitled “Propensity to tend education under the Arts stream and the unemployment of Arts Graduates.” The somewhat awkwardly titled report attempts to connect graduate unemployment to Arts Education at secondary and tertiary levels. The report is useful in that it locates some of the problems of tertiary education in a failing secondary educational system. The recommendations made in the report are also, for the most part, salutary. However, the assumptions that inform the body of the report, the material that it uses to come to conclusion regarding arts education, and the manner in which it is committed to undervaluing Arts Education, merits comment, especially in a policy environment where Arts Education is under attack. Arguably the manner in which it conceptualizes the role of education in society is limited and reflects all current policy making on the subject. We provide this analysis, therefore, to broaden the conversation driving the policy discourse regarding higher education in the country and to move it away from its current unhelpful preoccupation with employability. We argue in this response that to formulate policy on a narrowly defined understanding of “employability” is insufficient and does not adequately encompass areas in Humanities and Social Science higher education that require strengthening through reform and support. Currently, policies driven by “employability” are, in fact, negatively impacting Humanities and Social Science programmes within the university system.
The report usefully highlights a fundamental problem in our education system – the failing secondary schools – as impacting Arts Education in general. Using a range of data, the report is able to demonstrate how the system is fundamentally unequal and makes clear that the policy of free education is failing the most marginalized members and communities in our society. The report highlights the fact that many schools do not have resources to provide Advanced Level science education. And states also that many parents are not able to support Advanced Level science education due to their inability to provide funds for extra classes. Therefore, many who are economically marginalized are unable to pursue education in STEM subjects. The report also demonstrates that the provinces, where poverty is greatest, have the largest percentages of Arts students entering university.
In terms of the numbers taking up subjects for the Advanced Level examination, the largest percentage opt for the Arts stream. The report claims that students choose Arts subjects because they are “easy” and students can enter university quickly (through their first shy). The numbers of students that choose the Arts stream for the A-Levels have ranged between 40-50 percent in 2017/2018. Other than in the Western Province, where the numbers are slightly lower, (20-35%), all other provinces had close to 50% of all A-Level students follow Arts subjects (Audit report, pp14-21). Documenting how students who are compelled to attend under-resourced secondary schools have few choices with regards to their education, the report recommends that the education system address the inequality of access and provide all secondary school students the choice of pursing either a STEM focused education or one in Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences. We support this recommendation of the report. The report, however, fails to connect how the inequality that prevails in the school system and the inability to guarantee a good basic education for all, in turn limits the impact that higher education can make when no intervention specifically addresses this problem. The report then suggests that the graduates that the current system of Arts Education produces are unemployable and emphasizes the need to reduce the numbers that opt for the Arts stream. Such a reduction of numbers was planned through the introduction of the technology stream. However, the technology stream itself has its own problems, is insufficiently resourced and has not been a success in reducing the numbers choosing the Arts stream. Unfortunately, there is no recognition in the report that most students are being taught within a severely under-funded and under-resourced Arts stream and that strengthening Arts education itself would be an option that would result in Arts graduates with a higher quality Arts education.
The report is inadequately informed of what Arts education encompasses and the current state of tertiary Arts education in the country.
What is Arts Education?
While acknowledging the need for the Arts to enrich society, the report suggests that as a “developing country”, we have to emphasize economic growth and suggests that we cannot afford to spend resources (that could be spent on Science Technology Engineering Mathematics (STEM) education) on Arts education. Making reference to “literary men, actors, musicians and cinematographers and artists” as necessary for a society, the report states that we, as a developing country, must have a greater emphasis on growing the economy. It is unfortunate that the report’s authors consider the country to be undeserving of investment in the Arts and culture until economic development is achieved and also dissociates the Arts from engagement with economic activity. The lack of greater government support for the Arts is probably a reflection of this sensibility. Unfortunately, such shortsighted positions inform the report and much of education policy today. A vibrant society where the Arts and culture can thrive should be an aspiration that we should cultivate and share.
Arts Faculties also provide degrees in the social sciences, such as sociology, psychology, economics and geography, and in applied or “professional” fields such as education, archeology, and library sciences, as well as humanities subjects such as history, philosophy and literature, and modern and classical languages. Nowhere does the report name the wide variety of subjects that are categorized under Arts education or recognize the importance of such subjects. Other than pointing out in one instance that developed countries use their system of education to create “skilled persons”, while we in Sri Lanka create “academic persons,” the report only recognizes Arts subjects insofar as they are not Science Mathematics or Technology subjects. The skills and perspectives provided by the Humanities and Social Sciences (Arts subjects) are essential to a holistic understanding of any social problem, such as poverty or education, or even any “technical” problem, such as water scarcity. The ability to understand the philosophical and ideological bases of such problems, and identify the social, cultural, and human consequences of proposed solutions, is provided by the skillset cultivated by an Arts education. In fact, this is the very reason that multidisciplinary perspectives are frequently called upon for policy research. It is important then that we recognize the contribution that a good quality Arts education can offer to society. We as a country are suffering today from a lack of attention to the perspectives that social science and humanities education can provide. This is also why those with little or no exposure to the above fields feel qualified to drive policy in various sectors that have substantial social consequences. This situation does not bode well for our future.
As indicated in the quotation above where the Sri Lankan system is accused of producing “academic persons” as opposed to skilled individuals, the report assumes that academically-oriented programmes are somehow antithetical to programmes that provide employment-oriented “skills.” Such a perspective mischaracterizes both the nature of academic engagement and the essence of job-oriented training. A strong academic programme that focuses on critical thought, substantive engagement with course material, independent learning, good writing, presentation and debate skills, will enable graduates to think independently, express themselves and work towards creating meaningful change in whatever surrounding they find themselves in, including their jobs. An effective programme of this nature would simultaneously result in the development of English skills, “soft skills”, and IT skills as part of the curriculum. The World Bank loan funded AHEAD programme, currently being implemented across the university system, has integrated elements of such a perspective and Bank loan supported initiatives are no longer insisting—as they did in earlier cycles– that we carry out stand-alone programmes to cultivate English, IT and “soft skills.”
The contention of the report as stated earlier is that Arts education is the subject area into which the largest numbers of the country’s students flock, and is also the repository of the country’s poorest students. The report then sweepingly suggests that arts programmes draw “weak” students and are themselves “weak” and are of little societal value. This seems to be the preferred policy position with regards to Arts Education. The report notes that the Technology Stream was introduced with the goal of reducing the number of Arts students to less than 25 percent and increasing the number of students pursuing Maths, Science and Technology. The report establishes, however, that the demand for Arts subjects among the student population has increased despite government efforts to decrease the number. The report’s lack of interest in understanding what positive elements of Arts education might be attracting the large student numbers (other than perhaps the ability to become a lawyer) and what elements of Arts education are worth supporting and developing, is quite telling of its general devaluing of Arts education.
The report provides little insight into the content of Arts programmes that are offered by the Sri Lankan university system and its assessment of the efficacy of the programmes is limited to employment numbers provided by the UGC Tracer Study of 2016/17. The report also states that no statistical information is available on unemployed graduates although insights from the Unemployed Graduates Union were obtained. Its critique of the programmes is based on two criteria – the number of programme revisions that have been reported and the introduction of new programmes of study. Outside of the above criteria, the study does not recognize the many differences among Arts degree programmes. For one, not all Arts programmes are the same across the country’s university system. There are internal and external degree programs, three-year general arts degree programmes following different subject combinations and Study Stream degree programmes that offer specialization within a three-year period, and four-year honours degree programmes involving a research component. While the subject areas covered by Arts programmes are also diverse, the content of programmes across the many universities differ as well. Thus, Arts students demonstrate a wide and disparate range of abilities and skills. Addressing Arts Education as a non-disaggregated whole is unhelpful when analyzing the skills and capabilities of Arts graduates and numbers that refer only to programme review and the introduction of new programmes does not adequately capture the status of those programmes. Disaggregating between Arts programmes is essential in order to recognize and develop the new and evolving programmes and provide support for the areas that require reforms.
Arts Faculties currently cater to a large number of students and relative to other faculties, their student body is more diverse and are likely to have differing and greater challenges and require greater support in transitioning to university education. Their student to staff ratios are larger, they tend to offer a large number of degree programmes that are delivered in different language media, and their per student funding is lesser than for other degree programmes. This creates a number of unique difficulties for arts faculties. These problems require systematic investigation in order for universities to provide the type of enriching education that an arts graduate requires.
These concerns that plague arts education cause difficulties in giving the arts graduate the type of education that they require and deserve. In the Commission’s report, these complex problems are not adequately presented or discussed.
Arts Education and Employment.
We recognize that some students who follow an arts education may have difficulties in finding work. As the report points out these difficulties stem partly from the immense social and economic disparities that influence student educational pathways and subsequent employment paths. The report suggests a number of solutions through which employment related problems that Arts students face may be addressed. These solutions proposed in the report require aligning educational paths with employment paths, through coordination among educational and employment providing institutions and greater funding for secondary and tertiary education. We pose, however three issues that the report has failed to address in making this case:
1. Framing recommendations with a rigorous analysis of the labour/job markets and their forecasts. The report neglects to include analyses of the job market or forecasts of the labour force. It does not address national policy to attract and create jobs, which are consistent with national trends in human capital. In short, the report does not link jobs and employment to broader policies to create good quality jobs that are secure and safe to all employees (see for instance, ILO, 2004). As a result, how the report construes where graduates will be placed once they graduate is unclear. Such an analysis should now be sensitive to changes caused by the Covid 19 pandemic, which likely hit youth and women particularly hard (ILO, 2020). Problems of the employment of arts graduates are especially salient to youth and women.
2. Justifying the linkages between employment and university education. The report rests on the assumption that students who follow a university education will become an “economic good”, meaning that their education will be transformed into some tangible, national, and tradable good. Yet the nature of this good is unclear, particularly considering that the labour market is in flux (see Blenkinsopp, 2011). For instance, with the rise in automation, jobs themselves are transforming in all sectors (see Oliver, 2015, Rothwell & Rothwell, 2016). These trends are likely to drastically reduce the number of jobs available and change how work is carried out. Skillsets, particularly those that are narrowly defined and context-specific, which are relevant and desired today, may have no importance in years to come. Thus, an analysis of jobs specific skills training, required of young people for employment in the future, should begin with an analysis of job markets of the future. Whether providing these skills should be the primary role of universities and whether the country has the jobs required for such trained individuals are also questions that will need to be addressed.
3. The report also rests on the assumption that learning activities that specifically target narrowly defined soft skills and skills in ICT and English language will result in the economic good mentioned in #2. This assumption has no basis. For instance, a strong humanities or social science education can provide invaluable skills in thinking critically (see Fahim & Masouleh, 2012) that are very much relevant to jobs. Within the study of job-related competencies, conceptual and thinking skills that are adaptable across job contexts and Reinforce a desire and ability to learn for oneself are particularly important (Snow & Snell, 1993). Cultivating these types of foundational skills require a curriculum that is built on a gradual and sustained process of developing them (see Fahim & Masouleh, 2012) rather than one-off courses that teach students a narrow skill set.
Education, Work and Economic Development
For most university graduates, employment means to be employed in the government sector. When graduates report unemployment, they do not necessarily mean they are not engaged in other income-generating activities or a private sector job. (One of the reasons for unemployment noted in the report is to be waiting for a government job.) Defining a “job” as a government job alone may be understood as part of a cultivated culture of patronage and entitlement. Such a position also draws from a realization that the working conditions, job security, and benefits of a government position far outweigh those in the private sector, regardless of claims to creativity, job satisfaction, higher pay, etc. Additionally, most private sector jobs are only available in and around urban areas. The report recognizes many of these issues and recommends raising awareness on the benefits of private sector jobs among undergraduates and urges the government to address the working conditions in the private sector.
The report points out that the majority of unemployed Arts graduates are women, but does not explore the gendered reasons as to why university educated women may be unemployed or opt out of employment. The Labour Demand Survey of 2017 provides insights on this matter. According to the Survey results, employers expressed negative attitudes towards hiring women owing to their “family commitments,” “security concerns”, and “maternity leave.” Employers’ reluctance to accommodate women’s unpaid care responsibilities and fear of sexual harassment and violence point to yet another societal malaise that is not reducible to a factor of university education alone. Not only are women overburdened with care work and at risk of violence in society, employers neither recognize nor provide support to women to work despite these challenges. Recent discussions on the unpaid care economy and women’s unaccounted labour at home are relevant here.
Many women opt out of formal employment or engage in informal work to accommodate the demands of care work in the home. Additionally, workplace sexual harassment and risk of the same when traveling home late after work are factors that contribute to women’s low labour force participation. These issues must be taken into account to arrive at a complete picture of graduate unemployment.
The audit report highlights the fact that we, as a “developing country”, must concentrate on economic advancement. However, there is no acknowledgement that one of the factors that have directly impacted the Sri Lankan economy and continues to do so has been ethno religious conflict. Over 30 years of war, and after the end of the war increasing numbers of organized violent attacks against Muslims, and the Easter Sunday bombings carried out by Muslims channelling the rhetoric of global Islamic terrorism to respond to local problems have destroyed lives and livelihoods and decimated the Sri Lankan economy. There is no analysis of how universities could provide a space to imagine alternatives to conflict and hostility and how such alternatives can be nurtured.
Unfortunately, education institutions have so far served to produce, reproduce and sustain Sinhala-Buddhist hegemonic narratives and to glorify ‘Sinhala-Buddhist’ culture at the expense of the stories and the culture of the country’s minority communities. These political efforts to divide and pit communities against each other encounter little or no ideological resistance. It is ironic that policy makers choose to see no connection between the country’s long history of ethnoreligious conflict and the system of education. Instead of playing a vital role in building trust in the post-war context among our communities, the education system has served to perpetuate structural violence along class, gender, ethnic and other lines. It is time that policy makers and political leaders discuss the manner in which education will help nurture a polity that can imagine collective engagement that is not overdetermined by conflict.
No doubt education has to cater to the economic needs of society, but the world has come a long way since ‘development’ was reduced to the ‘economy’. Contemporary approaches to development are much broader with far-reaching goals and meanings beyond the economy. Education should be a vehicle for achieving larger social goals through the development of creative capabilities and peaceful co-existence, which could, in turn, facilitate realizing economic goals within a society that is not plagued by violence.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Addressing the problems that plague Arts education in Universities, will strengthen not only Arts education in the University system but education in general. By framing the problem more widely, we propose the following:
The Education System:
1. The salutary goals that were envisioned when a free education system was introduced to the country still remain relevant. The social transformation that education continues to promise to countless Sri Lankan citizens is currently under severe strain. Therefore it is important that the challenges to the free education system be recognized and addressed in a manner that strengthens its foundational principles of universality and equality of access.
2. Broaden the understanding of the problems of the education system. Employability—narrowly defined– should not be the only framework from which reform of education should be approached. Education as a democratic endeavor must be recognized and questions must be raised as to whether the education system succeeds in strengthening democracy.
3. Ensure that education at both the secondary and tertiary levels is designed to overturn ethno-religious tensions and prejudices related to class, caste gender, gender identity and sexual orientation.
4. Provide solutions to address the inequalities in access to secondary education options, and minimize disparities in resources, facilities, and teachers.
Arts Education:
5. Provide arts faculties with the option of having foundation courses that will better equip students to perform well in degree programmes.
6. Have a better understanding of the different Arts degree programmes in the country, conduct a holistic analysis of the problems facing arts education and provide support when needed and reform where needed.
7. Increase spending on Arts Education. Recognize the contribution that Humanities and Social Sciences can make to society and provide support for such programmes.
8. Recognize and support the unique environments of the Arts Faculties as arguably consisting of the most diverse student bodies and serving the largest number of under privileged students.
9. Resist the formulation of one- size-fits-all policies for the improvement of Humanities and Social Science Education.
Technology Stream:
10. Ensure that students are guided into such streams through provision of services at both secondary and tertiary levels.
11. Provide trained teachers for technology education, revisit curricula, and improve infrastructure facilities.
Employment and employment markets:
12. Look into the job requirement of the country and the policies in place for job creation.
13. Ensure laws are in place to provide the necessary support services for women to enter the labour force.
14. Provide greater state support for the Creative Arts (as a job creation strategy that will strengthen the economy).
15. Ensure that the benefits and work conditions in the private sector match those of the public sector and remain attractive to university graduates
Features
Misinterpreting President Dissanayake on National Reconciliation
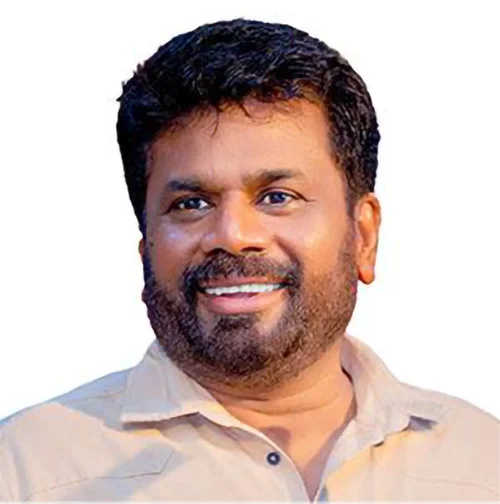

President Anura Kumara Dissanayake has been investing his political capital in going to the public to explain some of the most politically sensitive and controversial issues. At a time when easier political choices are available, the president is choosing the harder path of confronting ethnic suspicion and communal fears. There are three issues in particular on which the president’s words have generated strong reactions. These are first with regard to Buddhist pilgrims going to the north of the country with nationalist motivations. Second is the controversy relating to the expansion of the Tissa Raja Maha Viharaya, a recently constructed Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai which has become a flashpoint between local Tamil residents and Sinhala nationalist groups. Third is the decision not to give the war victory a central place in the Independence Day celebrations.
Even in the opposition, when his party held only three seats in parliament, Anura Kumara Dissanayake took his role as a public educator seriously. He used to deliver lengthy, well researched and easily digestible speeches in parliament. He continues this practice as president. It can be seen that his statements are primarily meant to elevate the thinking of the people and not to win votes the easy way. The easy way to win votes whether in Sri Lanka or elsewhere in the world is to rouse nationalist and racist sentiments and ride that wave. Sri Lanka’s post independence political history shows that narrow ethnic mobilisation has often produced short term electoral gains but long term national damage.
Sections of the opposition and segments of the general public have been critical of the president for taking these positions. They have claimed that the president is taking these positions in order to obtain more Tamil votes or to appease minority communities. The same may be said in reverse of those others who take contrary positions that they seek the Sinhala votes. These political actors who thrive on nationalist mobilisation have attempted to portray the president’s statements as an abandonment of the majority community. The president’s actions need to be understood within the larger framework of national reconciliation and long term national stability.
Reconciler’s Duty
When the president referred to Buddhist pilgrims from the south going to the north, he was not speaking about pilgrims visiting long established Buddhist heritage sites such as Nagadeepa or Kandarodai. His remarks were directed at a specific and highly contentious development, the recently built Buddhist temple in Kankesanturai and those built elsewhere in the recent past in the north and east. The temple in Kankesanturai did not emerge from the religious needs of a local Buddhist community as there is none in that area. It has been constructed on land that was formerly owned and used by Tamil civilians and which came under military occupation as a high security zone. What has made the issue of the temple particularly controversial is that it was established with the support of the security forces.
The controversy has deepened because the temple authorities have sought to expand the site from approximately one acre to nearly fourteen acres on the basis that there was a historic Buddhist temple in that area up to the colonial period. However, the Tamil residents of the area fear that expansion would further displace surrounding residents and consolidate a permanent Buddhist religious presence in the present period in an area where the local population is overwhelmingly Hindu. For many Tamils in Kankesanturai, the issue is not Buddhism as a religion but the use of religion as a vehicle for territorial assertion and demographic changes in a region that bore the brunt of the war. Likewise, there are other parts of the north and east where other temples or places of worship have been established by the military personnel in their camps during their war-time occupation and questions arise regarding the future when these camps are finally closed.
There are those who have actively organised large scale pilgrimages from the south to make the Tissa temple another important religious site. These pilgrimages are framed publicly as acts of devotion but are widely perceived locally as demonstrations of dominance. Each such visit heightens tension, provokes protest by Tamil residents, and risks confrontation. For communities that experienced mass displacement, military occupation and land loss, the symbolism of a state backed religious structure on contested land with the backing of the security forces is impossible to separate from memories of war and destruction. A president committed to reconciliation cannot remain silent in the face of such provocations, however uncomfortable it may be to challenge sections of the majority community.
High-minded leadership
The controversy regarding the president’s Independence Day speech has also generated strong debate. In that speech the president did not refer to the military victory over the LTTE and also did not use the term “war heroes” to describe soldiers. For many Sinhala nationalist groups, the absence of these references was seen as an attempt to diminish the sacrifices of the armed forces. The reality is that Independence Day means very different things to different communities. In the north and east the same day is marked by protest events and mourning and as a “Black Day”, symbolising the consolidation of a state they continue to experience as excluding them and not empathizing with the full extent of their losses.
By way of contrast, the president’s objective was to ensure that Independence Day could be observed as a day that belonged to all communities in the country. It is not correct to assume that the president takes these positions in order to appease minorities or secure electoral advantage. The president is only one year into his term and does not need to take politically risky positions for short term electoral gains. Indeed, the positions he has taken involve confronting powerful nationalist political forces that can mobilise significant opposition. He risks losing majority support for his statements. This itself indicates that the motivation is not electoral calculation.
President Dissanayake has recognized that Sri Lanka’s long term political stability and economic recovery depend on building trust among communities that once peacefully coexisted and then lived through decades of war. Political leadership is ultimately tested by the willingness to say what is necessary rather than what is politically expedient. The president’s recent interventions demonstrate rare national leadership and constitute an attempt to shift public discourse away from ethnic triumphalism and toward a more inclusive conception of nationhood. Reconciliation cannot take root if national ceremonies reinforce the perception of victory for one community and defeat for another especially in an internal conflict.
BY Jehan Perera
Features
Recovery of LTTE weapons

I have read a newspaper report that the Special Task Force of Sri Lanka Police, with help of Military Intelligence, recovered three buried yet well-preserved 84mm Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers used by the LTTE, in the Kudumbimalai area, Batticaloa.
These deadly weapons were used by the LTTE SEA TIGER WING to attack the Sri Lanka Navy ships and craft in 1990s. The first incident was in February 1997, off Iranativu island, in the Gulf of Mannar.
Admiral Cecil Tissera took over as Commander of the Navy on 27 January, 1997, from Admiral Mohan Samarasekara.
The fight against the LTTE was intensified from 1996 and the SLN was using her Vanguard of the Navy, Fast Attack Craft Squadron, to destroy the LTTE’s littoral fighting capabilities. Frequent confrontations against the LTTE Sea Tiger boats were reported off Mullaitivu, Point Pedro and Velvetiturai areas, where SLN units became victorious in most of these sea battles, except in a few incidents where the SLN lost Fast Attack Craft.

Carl Gustaf recoilless rocket launchers
The intelligence reports confirmed that the LTTE Sea Tigers was using new recoilless rocket launchers against aluminium-hull FACs, and they were deadly at close quarter sea battles, but the exact type of this weapon was not disclosed.
The following incident, which occurred in February 1997, helped confirm the weapon was Carl Gustaf 84 mm Recoilless gun!
DATE: 09TH FEBRUARY, 1997, morning 0600 hrs.
LOCATION: OFF IRANATHIVE.
FACs: P 460 ISRAEL BUILT, COMMANDED BY CDR MANOJ JAYESOORIYA
P 452 CDL BUILT, COMMANDED BY LCDR PM WICKRAMASINGHE (ON TEMPORARY COMMAND. PROPER OIC LCDR N HEENATIGALA)
OPERATED FROM KKS.
CONFRONTED WITH LTTE ATTACK CRAFT POWERED WITH FOUR 250 HP OUT BOARD MOTORS.
TARGET WAS DESTROYED AND ONE LTTE MEMBER WAS CAPTURED.
LEADING MARINE ENGINEERING MECHANIC OF THE FAC CAME UP TO THE BRIDGE CARRYING A PROJECTILE WHICH WAS FIRED BY THE LTTE BOAT, DURING CONFRONTATION, WHICH PENETRATED THROUGH THE FAC’s HULL, AND ENTERED THE OICs CABIN (BETWEEN THE TWO BUNKS) AND HIT THE AUXILIARY ENGINE ROOM DOOR AND HAD FALLEN DOWN WITHOUT EXPLODING. THE ENGINE ROOM DOOR WAS HEAVILY DAMAGED LOOSING THE WATER TIGHT INTEGRITY OF THE FAC.
THE PROJECTILE WAS LATER HANDED OVER TO THE NAVAL WEAPONS EXPERTS WHEN THE FACs RETURNED TO KKS. INVESTIGATIONS REVEALED THE WEAPON USED BY THE ENEMY WAS 84 mm CARL GUSTAF SHOULDER-FIRED RECOILLESS GUN AND THIS PROJECTILE WAS AN ILLUMINATER BOMB OF ONE MILLION CANDLE POWER. BUT THE ATTACKERS HAS FAILED TO REMOVE THE SAFETY PIN, THEREFORE THE BOMB WAS NOT ACTIVATED.

Sea Tigers
Carl Gustaf 84 mm recoilless gun was named after Carl Gustaf Stads Gevärsfaktori, which, initially, produced it. Sweden later developed the 84mm shoulder-fired recoilless gun by the Royal Swedish Army Materiel Administration during the second half of 1940s as a crew served man- portable infantry support gun for close range multi-role anti-armour, anti-personnel, battle field illumination, smoke screening and marking fire.
It is confirmed in Wikipedia that Carl Gustaf Recoilless shoulder-fired guns were used by the only non-state actor in the world – the LTTE – during the final Eelam War.
It is extremely important to check the batch numbers of the recently recovered three launchers to find out where they were produced and other details like how they ended up in Batticaloa, Sri Lanka?
 By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
By Admiral Ravindra C. Wijegunaratne
WV, RWP and Bar, RSP, VSV, USP, NI (M) (Pakistan), ndc, psn, Bsc (Hons) (War Studies) (Karachi) MPhil (Madras)
Former Navy Commander and Former Chief of Defence Staff
Former Chairman, Trincomalee Petroleum Terminals Ltd
Former Managing Director Ceylon Petroleum Corporation
Former High Commissioner to Pakistan
Features
Yellow Beatz … a style similar to K-pop!
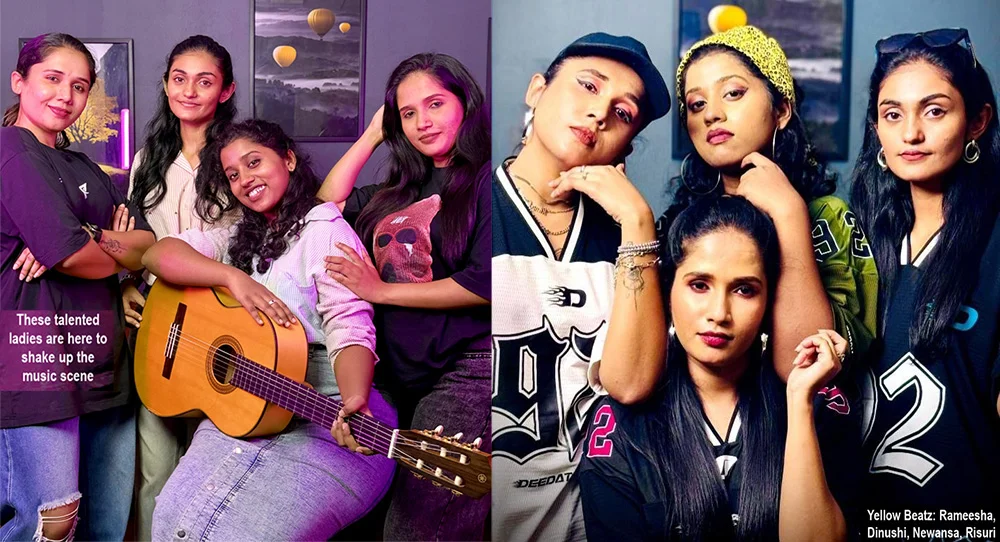
 Yes, get ready to vibe with Yellow Beatz, Sri Lanka’s awesome girl group, keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-pop!
Yes, get ready to vibe with Yellow Beatz, Sri Lanka’s awesome girl group, keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-pop!
With high-energy beats and infectious hooks, these talented ladies are here to shake up the music scene.
Think bold moves, catchy hooks, and, of course, spicy versions of old Sinhala hits, and Yellow Beatz is the package you won’t want to miss!
According to a spokesman for the group, Yellow Beatz became a reality during the Covid period … when everyone was stuck at home, in lockdown.
“First we interviewed girls, online, and selected a team that blended well, as four voices, and then started rehearsals. One of the cover songs we recorded, during those early rehearsals, unexpectedly went viral on Facebook. From that moment onward, we continued doing cover songs, and we received a huge response. Through that, we were able to bring back some beautiful Sri Lankan musical creations that were being forgotten, and introduce them to the new generation.”
The team members, I am told, have strong musical skills and with proper training their goal is to become a vocal group recognised around the world.
Believe me, their goal, they say, is not only to take Sri Lanka’s name forward, in the music scene, but to bring home a Grammy Award, as well.
“We truly believe we can achieve this with the love and support of everyone in Sri Lanka.”
The year 2026 is very special for Yellow Beatz as they have received an exceptional opportunity to represent Sri Lanka at the World Championships of Performing Arts in the USA.
Under the guidance of Chris Raththara, the Director for Sri Lanka, and with the blessings of all Sri Lankans, the girls have a great hope that they can win this milestone.
“We believe this will be a moment of great value for us as Yellow Beatz, and also for all Sri Lankans, and it will be an important inspiration for the future of our country.”
Along with all the preparation for the event in the USA, they went on to say they also need to manage their performances, original song recordings, and everything related.

The year 2026 is very special for Yellow Beatz
“We have strong confidence in ourselves and in our sincere intentions, because we are a team that studies music deeply, researches within the field, and works to take the uniqueness of Sri Lankan identity to the world.”
At present, they gather at the Voices Lab Academy, twice a week, for new creations and concert rehearsals.
This project was created by Buddhika Dayarathne who is currently working as a Pop Vocal lecturer at SLTC Campus. Voice Lab Academy is also his own private music academy and Yellow Beatz was formed through that platform.
Buddhika is keen to take Sri Lankan music to the world with a style similar to K-Pop and Yellow Beatz began as a result of that vision. With that same aim, we all work together as one team.
“Although it was a little challenging for the four of us girls to work together at first, we have united for our goal and continue to work very flexibly and with dedication. Our parents and families also give their continuous blessings and support for this project,” Rameesha, Dinushi, Newansa and Risuri said.
Last year, Yellow Beatz released their first original song, ‘Ihirila’ , and with everything happening this year, they are also preparing for their first album.
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check
-

 Editorial6 days ago
Editorial6 days agoAll’s not well that ends well?












