Features
More on jungle treks: Lahugala and bold leopards

BY H A I Katugaha
(Continued from last week)
One morning in the 1950’s we had gone across into Yala Block 2 and our destination was Walaskema in search of the famous crossed tusker, so named because of the crossing of the tusks in front. We had Block 2 all to ourselves. Parking the jeep, we began our walk to Walaskema. There were four of us in the party, namely Uncle Sam, Upali, our tracker and myself.
We saw a leopard sitting under a tree. He got up and started walking towards us. This was most unusual. We shouted at him but he took no notice at all. He growled at us and kept getting closer. Shouting at him we walked backwards and even threw stones at him. One thrown by the tracker hit him on his head, but he kept on coming.
Having reached the jeep, Upali raced the engine and sped towards him. The leopard then ran off into the jungle. Leopards usually run off at the sight of man, and the difficulty is to get close to one. Uncle Sam was of the opinion that this one may well have been used to humans since the Kataragama pilgrims passed this way every year. Maybe he even had a taste of human flesh by eating the corpse of a pilgrim that had died during the walk across Kumbukkan Oya to Menik Ganga. It was a large male animal in the prime of his life.
We reached Walaskema, which was a water-hole, and though we waited till evening the famous tusker did not come to drink water. On our way back we did see a herd of elephants across the Pilinnawa plains.
Years later while camping out at Kosgasmankada in Yala Block 1, one night I noticed some movement under one of the lanterns that we had hung around the camp to keep animals away. Using my torch I discovered that it was a leopard that sat right under the lantern and watched our camp. Soon several torches were focused on it and we had a good look at this fine male leopard. One member of our party then turned the vehicle and put on the headlights. There he was in all his glory watching us with apparent delight.
Next morning we reported this unusual behavior to the park office and were told that this was a bold leopard that had even attacked a labourer attached to the department while walking along at the campsite. The rule is that a leopard will run off at the sight of man unless man has wounded him. It is always best to remember that there are exceptions to every rule.
Land of the gentle giants
At dawn, in the early 1960’s, I lay stretched out on a mat in the verandah of the old Irrigation Department bungalow at Lahugala. A regular swish-swish close by informed me that an elephant, perhaps two, were feeding on the luscious beru grass close to the sluice. It was still very dark. The first vocalists for the morning were a pair of magpies. Their whistling calls were welcome indeed. Next a shama gave vent to his repertoire of vocal renderings. Then the pair of brown fish owls that was always to be found near the sluice finished their serenade with a short burst of hoo hoo.
As darkness gave way to light that misty morning, I watched the dark shape of an elephant slowly moving up to the rock in front of the bungalow. He stood still, probably enjoying the cool breeze that was blowing across the tank. After about 15 minutes he came down and walked towards the well.
Sammy, the Department’s watcher at the bungalow, kindly brought me a hot cup of tea and whispered, “Sir, be careful when you go for a wash, there is an elephant by the well.” I thanked him for his concern.
By the time my friends and I finished our tea, the elephant left the well and moved off into the jungle to our right. We could now see that there were two elephants feeding by the sluice. About 7 am they slowly walked up the bend of the tank and faded away to the left of us.
Across the tank, felled logs of the majestic trees that they once were, stood out in the early morning sun. It happened to be the depot of the State Timber Corporation and quite an eyesore in such a wonderful setting. Birds that were resting by the tank, such as painted storks, pelicans, teal, open-billed storks and a few white-necked storks, took off to look for breakfast. Four adjutant storks began their stately walk in search of food.
It was a typical morning at Lahugala. As we walked up to the rock a solitary pied kingfisher hovered momentarily, dived and came up with a fish. He flew to his perch, flicked the fish up and expertly swallowed it head first. The purple herons and the coots were active in the grass, while the beautiful jacanas were flitting over the lotus leaves looking for food.

Lahugala was then only a forest reserve and not a national park. The tank was managed by the Irrigation Department and Sammy was its watcher that looked after the sluice. Later Lahugala became an elephant reserve. Elephants were the chief attraction and they were to be seen throughout the year, but during the dry season from July to September, they congregated in large numbers. During this period, the herds gathered here for water and for the beru grass that they loved so much. There was always a resident population of elephants numbering about twenty. It was not till the 1970’s that it finally became a national park. Though it was only five square miles in extent it was a haven for elephants.
That morning we got on our scooters and went to the village for breakfast. Coming back for a bath in the tank was always refreshing. Our lunch over we did have a short snooze, leaving Sammy on the lookout for elephants, It was not till 2 pm that the elephants began to come to the tank. The first to arrive were solitary bulls, six of whom arrived from different spots and waded into the tank. That evening the herds came late, and by 5.30 pm there were over 50 elephants out in the tank. Depending on where the herds were, we walked up to the nearest tree and observed them, feeling quite safe. (Walking in the park was allowed in those days.)
One afternoon, Mr.Peter Jayawardena, who was the Wildlife Department’s ranger stationed at Lahugala, took us for a walk along the bund. Hearing a noise he led us into the jungle. There in a clearing were three elephants lying flat and sleeping. The noise that we heard was their snoring. They were soon joined by another that came up to them, laid himself down and then slept. After a while Mr. Jayawardena clapped. The four elephants were up instantly and crashed away into the jungle. It was amazing to see such large animals get up and run so quickly. The jungle was soon silent.
At the time Lahugala was an elephant reserve, and the Wildlife and Nature Protection Society took the Irrigation Department’s old Bungalow on lease. It was renovated and made comfortable. The late Mr. Noel de Costa was responsible for getting the place into a satisfactory condition. Thereafter we were able to book the bungalow and stay in it in comfort. We had only to take our food and bedding with us.
During those days it was a common sight to see people walk into the jungle with guns and many dogs at their heel. Gunshots were heard every night. Venison was freely available at the bazaar. Poaching was rampant.
It has been my good fortune to see two leopards at Lahugala. One was on the road leading to the bungalow late one evening when we were returning from Kithulana. The other walked past the bungalow one night just as we were about to retire for the night, A bear came along the road one night and hooted, and we watched him by moonlight. Had he not made a sound we would never have seen him. Deer and wild boar were not seen in those early days, and no doubt poaching was responsible for this scarcity. Every night we heard gunshots..
Lahugala has always been a bird watcher’s paradise. The tank is a fine rendezvous for storks, herons, waders, and other water birds. The surrounding jungle abounds with birds. A pair of grey-headed fishing eagles had a nest on a tall tree close to the sluice. They carefully tended their nest every year. A pair of brown fish owls nested close by. Many raptorials were seen over the tank at all times. I have seen one black-necked stork in the 1970’s and several adjutant storks. The thrill was to spot the beautiful red-faced malkoha or the racquet-tailed drongo. On a short walk along the track leading to Heda Oya, one would invariably see the red-faced malkoha. In fact we named it Malkoha Lane. It was not uncommon to see them in groups of four to six.
It was during the time I was at Badulla that I was able to really explore Lahugala and its surroundings. One afternoon there were two bull elephants feeding by the sluice. Getting close to them, keeping behind the bund, I took photographs, but one of them suddenly charged. He could not have seen me and the wind was in my favour. I ducked down on the blind side of the bund and lay flat among some large granite blocks that were thankfully there. The bull elephant came up the bund and to my relief ran along it. Had I run in panic on that day I would not be writing this article.
I picked up my field glasses and went back to see what his problem was, this time from a very safe distance. He had suppurating gunshot wounds on both his hind legs, and his left ear was torn. Many other swellings on his body and head only proved how many times he had been shot at. Naturally he hated man. I informed the Wildlife and Nature Protection Society of this troublesome bull elephant, so that they could inform other occupants who came to this place to be careful of this animal.
Several months later I was at Lahugala with my family. Late one evening we met the elephant on the main road. A herd was feeding below the culvert and he was coming along to join the group. I was able to take a picture of him as he was crossing the culvert. While we were watching the herd I noticed that he was quickly moving parallel to us. and was trying to come in front of us. We moved ahead and waited for him. Sure enough he came to the road and immediately charged us. This time we were in a jeep and had no difficulty in avoiding his aggressive behaviour. He charged us three times on that day.
This bull elephant became quite a menace. He would wait quietly by the road and suddenly charge at any passing vehicle. Buses were his favourite targets. Three months later I was informed that he was shot. I drove down to verify if it was the same animal. It was truly the same troublesome bull, which was shot and had fallen in a chena close to Kithulana Tank. Birds were picking up dead maggots from his wounds. He had 23 wounds on the left side of his body and eight on his head. Finally he was at rest.
Lahugala was next declared a national park. The area began to be patrolled and it was at last getting the protection that it so richly deserved. It was in the late 1970’s that I saw the first herd of deer come out to feed. Wild boar soon made their presence felt.
One morning while I was seated on the rock, I met Appuhamy who came with a katty (a cutting blade with a long handle) on his ample shoulder. Having heard that I had come all the way to watch elephants, he took me to his chena, which was close to the Sengamuwa tank. To my horror I saw that his entire chena was devastated, having been trampled by a large number of elephants that had passed through. All his labour was lost in one night.
“You will see them at Lahugala today.” he said sadly. I gave him most of the cash I had with me and asked him about compensation. “Sir, I will get my money but I will have to give bribes in return; otherwise it will take months, perhaps even a year.” It is one thing for us to talk of conservation of the elephant from our homes and offices; while it is quite another matter for the poor cultivator. I told him it was a known fact that elephants come to Lahugala during that time of the year.
“True Sir, I would have harvested my crop by now, but the rains were delayed and so I planted late.” As I sat on the rock that evening and watched elephants pouring out of the jungle to my right, Appuhamy’s saying that I would see elephants at Lahugala that day kept ringing in my ears. As many as 186 elephants with four tuskers came to the tank. A herd of over a hundred elephants would have walked across his cultivation.
The conditions at the park improved rapidly, thanks to a dedicated staff that was stationed there. Being a small park it was easy to patrol. Poaching decreased. We began to see small herds of deer grazing close to the tank. I even saw a few sambhur.
There are many places of historical interest that one could visit while staying at Lahugala. One such place is Habutagala, where many ancient ruins, which include a forty-foot reclining statue of Lord Buddha in a cave, are found. Treasure hunters have dug into the statue. There is a small dagoba and several pillars to be seen. The most interesting features are Lord Buddha’s footprint carved in stone and an ancient stone inscription. These ruins belong to the Ruhunu period. Northern terrorists have attacked the village of Hulanuge twice.
Magul Maha Viharaya too is worthy of a visit. Situated close to Lahugala bazaar, it has several stone pillars and foundations. During the 1970’s, a unique moonstone was unearthed at this spot. It was in a fine state of preservation. Four of the elephants in the row of these animals carved on stone were dressed and had a rider on each. No other moonstone yet discovered anywhere in the country had this feature. Here again we find a small dagoba, a shrine room and a foundation of some structure with beautifully carved lions round its base.
More on jungle treks:…
Ancient stone inscriptions can also be seen. When conservation is completed some more interesting finds are likely to be found at this place.
Nilagiri Maha Seya is still covered in jungle. One has to cross Heda Oya and travel south along a jungle path to get there. We were warned to be extra careful and to make a loud noise when walking along, as there was a reputation for the presence of bears, in addition to the ever-present elephants. The walk was rewarding. The jungle was cool and had plenty of bird life to keep us occupied. My late brother, Upali, and Dr. Mahi Kottegoda accompanied me on all archaeological and nature-watching trips to the area. Kotte, as we called him, was an ardent bird watcher.
Nilagiri Maha Seya was in complete ruin. It was huge, with massive trees growing even at the summit. We were told that it was much bigger than the famous Tissamaharama dagoba. A large cylindrical stone kotha (crown of a Buddhist dagoba) was seen fallen at the very top of the dagoba, which resembled a hill covered in jungle.
A beautifully carved Bodhisatva statue is found at Mudu Maha Viharaya at Panama. This carving is in crystalline limestone and is really well done.
Lahugala became more and more popular. The Society bungalow was almost always occupied. Deer and wild boar were seen every day. Elephants were the main draw. One could see them every day of the year. A resident population of about 12 to 20 elephants never failed to appear. During the drought the numbers increased to about a hundred to 200 elephants. If we did not see them at Lahugala, we found them at Kithulana or Sengamuwa tanks.
Arugam Bay is only 12 miles away. It was a common practice to go there for the morning sea bath and bring back seafood for lunch. Then, followed by a well-earned siesta, we would wait for the elephants in the evening.
At ten past five, trumpeting announced the arrival of the herds as 32 elephants of different sizes ran to the water. They spread out in a line, had their drink and ran back to the jungle. They did not feed. It was obvious to us that they had arrived after a long walk. While we were wondering what had disturbed them, a large female, obviously the matriarch, led the 32 back to water. They were followed by over 80 more, who came out nearly in single file and waded into the tank. We counted them as they came out. We were seated on the rock in front of the bungalow.
Our friend Sammy whispered in my ear that more were coming. Sure enough another group came out to our left and walked over the bund to get into the tank. There were over 40 in this group. The two groups mingled freely and we saw a line of elephants across the Lahugala tank, a fabulous sight indeed. The bull elephants kept moving from one group to another testing the females for receptivity. One young female squealed and ran away from a bull. A larger one, probably the mother, came running to the bull and began stroking him around his ears. The bull immediately turned and began testing her.
We next noticed a huge bull elephant, which was the biggest in the gathering, coming along the bund. He made straight to the herds. Two smaller bulls took to their heels and left the herd to the big bull. Later in the evening when the elephants were leaving the tank, he was there by our rock with two female elephants. Yes, he was ready for a night of love.
It has been my good fortune to see six different tuskers at Lahugala. Two were really big ones, but sadly this gathering of over a 100 had none. I have observed mating of elephants at Lahugala on three occasions, too far for effective photography.
Up to about 1985 there was peace and tranquillity, then the terrorists began to attack the humble jungle villages. Soon the bungalow, the office of the Wildlife Department and the staff quarters were torched. The army soon moved in. One could still go past Lahugala on the way to the east coast at one’s own risk. The area was considered risky, and no one would dare to stay in the area.
The army is there and elephants still come to the tank. The small national park remains in mute silence. The deer and wild boar are no longer seen in daylight. Even elephants have been shot at. We can only hope that the interim cessation of hostilities will lead to permanent peace once again and we would be able to visit these places to enjoy what nature has bestowed so generously.
Reference: Trimen, Henry (1898). A hand-book to the flora of Ceylon, vol 3, p 216, Dulau & Co, London.
(Concluded)
(Excerpted from Jungle Journeys in Sri Lanka edited by CG Uragoda)
Features
Ranking public services with AI — A roadmap to reviving institutions like SriLankan Airlines

Efficacy measures an organisation’s capacity to achieve its mission and intended outcomes under planned or optimal conditions. It differs from efficiency, which focuses on achieving objectives with minimal resources, and effectiveness, which evaluates results in real-world conditions. Today, modern AI tools, using publicly available data, enable objective assessment of the efficacy of Sri Lanka’s government institutions.
Among key public bodies, the Supreme Court of Sri Lanka emerges as the most efficacious, outperforming the Department of Inland Revenue, Sri Lanka Customs, the Election Commission, and Parliament. In the financial and regulatory sector, the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) ranks highest, ahead of the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Public Utilities Commission, the Telecommunications Regulatory Commission, the Insurance Regulatory Commission, and the Sri Lanka Standards Institution.
Among state-owned enterprises, the Sri Lanka Ports Authority (SLPA) leads in efficacy, followed by Bank of Ceylon and People’s Bank. Other institutions assessed included the State Pharmaceuticals Corporation, the National Water Supply and Drainage Board, the Ceylon Electricity Board, the Ceylon Petroleum Corporation, and the Sri Lanka Transport Board. At the lower end of the spectrum were Lanka Sathosa and Sri Lankan Airlines, highlighting a critical challenge for the national economy.
Sri Lankan Airlines, consistently ranked at the bottom, has long been a financial drain. Despite successive governments’ reform attempts, sustainable solutions remain elusive.
Globally, the most profitable airlines operate as highly integrated, technology-enabled ecosystems rather than as fragmented departments. Operations, finance, fleet management, route planning, engineering, marketing, and customer service are closely coordinated, sharing real-time data to maximise efficiency, safety, and profitability.
The challenge for Sri Lankan Airlines is structural. Its operations are fragmented, overly hierarchical, and poorly aligned. Simply replacing the CEO or senior leadership will not address these deep-seated weaknesses. What the airline needs is a cohesive, integrated organisational ecosystem that leverages technology for cross-functional planning and real-time decision-making.
The government must urgently consider restructuring Sri Lankan Airlines to encourage:
=Joint planning across operational divisions
=Data-driven, evidence-based decision-making
=Continuous cross-functional consultation
=Collaborative strategic decisions on route rationalisation, fleet renewal, partnerships, and cost management, rather than exclusive top-down mandates
Sustainable reform requires systemic change. Without modernised organisational structures, stronger accountability, and aligned incentives across divisions, financial recovery will remain out of reach. An integrated, performance-oriented model offers the most realistic path to operational efficiency and long-term viability.
Reforming loss-making institutions like Sri Lankan Airlines is not merely a matter of leadership change — it is a structural overhaul essential to ensuring these entities contribute productively to the national economy rather than remain perpetual burdens.
By Chula Goonasekera – Citizen Analyst
Features
Why Pi Day?

International Day of Mathematics falls tomorrow
The approximate value of Pi (π) is 3.14 in mathematics. Therefore, the day 14 March is celebrated as the Pi Day. In 2019, UNESCO proclaimed 14 March as the International Day of Mathematics.
Ancient Babylonians and Egyptians figured out that the circumference of a circle is slightly more than three times its diameter. But they could not come up with an exact value for this ratio although they knew that it is a constant. This constant was later named as π which is a letter in the Greek alphabet.
It was the Greek mathematician Archimedes (250 BC) who was able to find an upper bound and a lower bound for this constant. He drew a circle of diameter one unit and drew hexagons inside and outside the circle such that the sides of each hexagon touch the sides of the circle. In mathematics the circle passing through all vertices of a polygon is called a ‘circumcircle’ and the largest circle that fits inside a polygon tangent to all its sides is called an ‘incircle’. The total length of the smaller hexagon then becomes the lower bound of π and the length of the hexagon outside the circle is the upper bound. He realised that by increasing the number of sides of the polygon can make the bounds get closer to the value of Pi and increased the number of sides to 12,24,48 and 60. He argued that by increasing the number of sides will ultimately result in obtaining the original circle, thereby laying the foundation for the theory of limits. He ended up with the lower bound as 22/7 and the upper bound 223/71. He could not continue his research as his hometown Syracuse was invaded by Romans and was killed by one of the soldiers. His last words were ‘do not disturb my circles’, perhaps a reference to his continuing efforts to find the value of π to a greater accuracy.
Archimedes can be considered as the father of geometry. His contributions revolutionised geometry and his methods anticipated integral calculus. He invented the pulley and the hydraulic screw for drawing water from a well. He also discovered the law of hydrostatics. He formulated the law of levers which states that a smaller weight placed farther from a pivot can balance a much heavier weight closer to it. He famously said “Give me a lever long enough and a place to stand and I will move the earth”.
Mathematicians have found many expressions for π as a sum of infinite series that converge to its value. One such famous series is the Leibniz Series found in 1674 by the German mathematician Gottfried Leibniz, which is given below.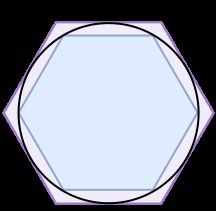
π = 4 ( 1 – 1/3 + 1/5 – 1/7 + 1/9 – ………….)
The Indian mathematical genius Ramanujan came up with a magnificent formula in 1910. The short form of the formula is as follows.
π = 9801/(1103 √8)
For practical applications an approximation is sufficient. Even NASA uses only the approximation 3.141592653589793 for its interplanetary navigation calculations.
It is not just an interesting and curious number. It is used for calculations in navigation, encryption, space exploration, video game development and even in medicine. As π is fundamental to spherical geometry, it is at the heart of positioning systems in GPS navigations. It also contributes significantly to cybersecurity. As it is an irrational number it is an excellent foundation for generating randomness required in encryption and securing communications. In the medical field, it helps to calculate blood flow rates and pressure differentials. In diagnostic tools such as CT scans and MRI, pi is an important component in mathematical algorithms and signal processing techniques.
This elegant, never-ending number demonstrates how mathematics transforms into practical applications that shape our world. The possibilities of what it can do are infinite as the number itself. It has become a symbol of beauty and complexity in mathematics. “It matters little who first arrives at an idea, rather what is significant is how far that idea can go.” said Sophie Germain.
Mathematics fans are intrigued by this irrational number and attempt to calculate it as far as they can. In March 2022, Emma Haruka Iwao of Japan calculated it to 100 trillion decimal places in Google Cloud. It had taken 157 days. The Guinness World Record for reciting the number from memory is held by Rajveer Meena of India for 70000 decimal places over 10 hours.
Happy Pi Day!
The author is a senior examiner of the International Baccalaureate in the UK and an educational consultant at the Overseas School of Colombo.
by R N A de Silva
Features
Sheer rise of Realpolitik making the world see the brink

 The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
The recent humanly costly torpedoing of an Iranian naval vessel in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone by a US submarine has raised a number of issues of great importance to international political discourse and law that call for elucidation. It is best that enlightened commentary is brought to bear in such discussions because at present misleading and uninformed speculation on questions arising from the incident are being aired by particularly jingoistic politicians of Sri Lanka’s South which could prove deleterious.
As matters stand, there seems to be no credible evidence that the Indian state was aware of the impending torpedoing of the Iranian vessel but these acerbic-tongued politicians of Sri Lanka’s South would have the local public believe that the tragedy was triggered with India’s connivance. Likewise, India is accused of ‘embroiling’ Sri Lanka in the incident on account of seemingly having prior knowledge of it and not warning Sri Lanka about the impending disaster.
It is plain that a process is once again afoot to raise anti-India hysteria in Sri Lanka. An obligation is cast on the Sri Lankan government to ensure that incendiary speculation of the above kind is defeated and India-Sri Lanka relations are prevented from being in any way harmed. Proactive measures are needed by the Sri Lankan government and well meaning quarters to ensure that public discourse in such matters have a factual and rational basis. ‘Knowledge gaps’ could prove hazardous.
Meanwhile, there could be no doubt that Sri Lanka’s sovereignty was violated by the US because the sinking of the Iranian vessel took place in Sri Lanka’s Exclusive Economic Zone. While there is no international decrying of the incident, and this is to be regretted, Sri Lanka’s helplessness and small player status would enable the US to ‘get away with it’.
Could anything be done by the international community to hold the US to account over the act of lawlessness in question? None is the answer at present. This is because in the current ‘Global Disorder’ major powers could commit the gravest international irregularities with impunity. As the threadbare cliché declares, ‘Might is Right’….. or so it seems.
Unfortunately, the UN could only merely verbally denounce any violations of International Law by the world’s foremost powers. It cannot use countervailing force against violators of the law, for example, on account of the divided nature of the UN Security Council, whose permanent members have shown incapability of seeing eye-to-eye on grave matters relating to International Law and order over the decades.
The foregoing considerations could force the conclusion on uncritical sections that Political Realism or Realpolitik has won out in the end. A basic premise of the school of thought known as Political Realism is that power or force wielded by states and international actors determine the shape, direction and substance of international relations. This school stands in marked contrast to political idealists who essentially proclaim that moral norms and values determine the nature of local and international politics.
While, British political scientist Thomas Hobbes, for instance, was a proponent of Political Realism, political idealism has its roots in the teachings of Socrates, Plato and latterly Friedrich Hegel of Germany, to name just few such notables.
On the face of it, therefore, there is no getting way from the conclusion that coercive force is the deciding factor in international politics. If this were not so, US President Donald Trump in collaboration with Israeli Rightist Premier Benjamin Natanyahu could not have wielded the ‘big stick’, so to speak, on Iran, killed its Supreme Head of State, terrorized the Iranian public and gone ‘scot-free’. That is, currently, the US’ impunity seems to be limitless.
Moreover, the evidence is that the Western bloc is reuniting in the face of Iran’s threats to stymie the flow of oil from West Asia to the rest of the world. The recent G7 summit witnessed a coming together of the foremost powers of the global North to ensure that the West does not suffer grave negative consequences from any future blocking of western oil supplies.
Meanwhile, Israel is having a ‘free run’ of the Middle East, so to speak, picking out perceived adversarial powers, such as Lebanon, and militarily neutralizing them; once again with impunity. On the other hand, Iran has been bringing under assault, with no questions asked, Gulf states that are seen as allying with the US and Israel. West Asia is facing a compounded crisis and International Law seems to be helplessly silent.
Wittingly or unwittingly, matters at the heart of International Law and peace are being obfuscated by some pro-Trump administration commentators meanwhile. For example, retired US Navy Captain Brent Sadler has cited Article 51 of the UN Charter, which provides for the right to self or collective self-defence of UN member states in the face of armed attacks, as justifying the US sinking of the Iranian vessel (See page 2 of The Island of March 10, 2026). But the Article makes it clear that such measures could be resorted to by UN members only ‘ if an armed attack occurs’ against them and under no other circumstances. But no such thing happened in the incident in question and the US acted under a sheer threat perception.
Clearly, the US has violated the Article through its action and has once again demonstrated its tendency to arbitrarily use military might. The general drift of Sadler’s thinking is that in the face of pressing national priorities, obligations of a state under International Law could be side-stepped. This is a sure recipe for international anarchy because in such a policy environment states could pursue their national interests, irrespective of their merits, disregarding in the process their obligations towards the international community.
Moreover, Article 51 repeatedly reiterates the authority of the UN Security Council and the obligation of those states that act in self-defence to report to the Council and be guided by it. Sadler, therefore, could be said to have cited the Article very selectively, whereas, right along member states’ commitments to the UNSC are stressed.
However, it is beyond doubt that international anarchy has strengthened its grip over the world. While the US set destabilizing precedents after the crumbling of the Cold War that paved the way for the current anarchic situation, Russia further aggravated these degenerative trends through its invasion of Ukraine. Stepping back from anarchy has thus emerged as the prime challenge for the world community.
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoPeradeniya Uni issues alert over leopards in its premises
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoRepatriation of Iranian naval personnel Sri Lanka’s call: Washington
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoWife raises alarm over Sallay’s detention under PTA
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoWinds of Change:Geopolitics at the crossroads of South and Southeast Asia
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoProf. Dunusinghe warns Lanka at serious risk due to ME war
-

 Sports3 days ago
Sports3 days agoRoyal start favourites in historic Battle of the Blues
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoHeat Index at ‘Caution Level’ in the Sabaragamuwa province and, Colombo, Gampaha, Kurunegala, Anuradhapura, Vavuniya, Hambanthota and Monaragala districts
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoThe final voyage of the Iranian warship sunk by the US




















