Midweek Review
Genealogy of Concept and Genesis of 13th Amendment-1

By Prof. Gamini Keerawella
Those who oppose devolution of power are up in arms now against the 13th Amendment, believing that the Provincial Council system has created a political space for the sub-national groups in the North and East to share power at the regional level. They allege that the 13th Amendment was an externally engineered move, and the Provincial Council system is a parasitic organ planted in the body politic of Sri Lanka by India and, therefore, they should be abolished without delay.
When one traces the chain of dramatic events leading to the 13th Amendment, it is clear that the immediate compulsion that forced President J.R. Jayewardene to present the 13th Amendment to the Parliament was India’s coercive diplomacy against Sri Lanka, which was known as ‘Parippu Diplomacy.’ However, the concept of devolution of power and the idea of Provincial Councils as a unit of devolution had been at the centre of political discourse well before the Indo-Sri Lanka Peace accord, at least from the 1920s. The Provincial Councils did not come from the blue sky with the Indian dhal cannon in 1987. The concept of devolution had surfaced again and again in the post independent political discourse in the course of sporadic attempts to accommodate political interests of sub-national groups. However, the manner in which the Provincial Council system was established in 1987 and the presence of the IPKF destroyed the legitimacy of the provincial council system at its inception. It does not negate the validity of devolution of power as a devise of unity in a fractured society. This essay intends to debunk certain misperceptions relating to the origins of the Provincial Council system by tracing the genealogy of the political discourse on devolution of power embodied in the 13th Amendment.
The conceptual origins of the Provincial Councils could be traced back to the Donoughmore Report in 1928. Conceptualizing it within the framework of local government, it presented a proposal to establish Provincial Councils to delegate certain administrative functions of the Central Government. More important is the rationale presented by the Donoughmore Commission for Provincial Council in 1928.
The argument in favour of the establishment of a Provincial Council in each Province is that such a scheme might result in a large part of administrative work now carried out in the Legislative Council coming into the hands of persons permanently resided in the country districts and thus more directly in contact with their needs; in the relief of the departments of the central government of much detailed work and in their being thereby set free to consider and advise on the larger affairs of the country: in the special views of the different races predominant in the different part of the Island having effects in the administration of these parts; in members of growing body of politically-minded persons in the country being placed in an honourable position to render real assistance in administration.
The Commission recommended that the new department without delay should explore the possibility of establishing Provincial Councils. Further it proposed that ‘an experiment with a council of this nature may be made in a more highly developed province within the next few years, and if that should prove successful, the system rapidly extended throughout the island’. The Issue of Provincial Councils came to discussion at the State Council in 1940 when R.S.S. Gunawardena proposed a motion on 10 July 1940. The The motion declared, “This Council is of the opinion that immediate effects should be given to the recommendation of the Donoughmore Commission with regard to the establishment of Provincial Councils”. Following the Motion, S.W. R.D. Bandaranaike as the Minister of Local Administration placed a detailed report of the Executive Committee of Local Administration on Provincial Councils before the State Council. It identified functions of proposed Provincial Councils in three main classes: supervisory, direct executive and advisory. The proposal was soon overtaken by other developments relating to the transfer of power and the issue of representation. Referring to the Provincial Councils, S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike stated in December 1947 during the Budget Debate that: “I do not think I shall be able to introduce the Bill relating to Provincial Councils before January next year. The Bill is ready, but as it impinges on the functions of my colleagues in the Cabinet, I have to obtain their consent to all the implications of the Bill before I can introduce it in this House”. It is important to note that even in the 1940s the Tamil leadership had not taken the issue of Regional Councils and devolution of power to regions into their hands.
When the transfer of power to Sri Lanka was in sight after the 1943 Declaration, the issue of how to reconcile the competing claims to present a constitutional arrangement satisfactory to all stakeholders came to the forefront. The 1943 Declaration requested the Board of Ministers to proceed with the framing of their constitutional proposals. At the same tine it emphasized that the proposals should obtain a three-fourth majority. One of the key issues that cropped up in this process was the basis of representation. Both, the purely population basis as well as communal representation were found to be not acceptable. Accordingly, the method of one seat for every 75,000 of population and one seat for every 1,000 square miles of territory in each province was worked out. It was at this point the British Government appointed the Soulbury Commission. The Tamil Congress under G.G. Ponnambalam was not prepared to accept the Ministers’ proposals and presented their own instead. After the experiences of the Donoughmore Constitution, the main Tamil leadership insisted on balanced representation, i.e. fifty percent of the seats for minorities including ‘Ceylon Indians’ – term used then to identify the Tamils of Indian origin. As I. D. S. Weerawardena pointed out when the Ministers drafted their proposals they pledged to give some weightage to all the minorities. S.W.R.D. Bandaranaike offered a scheme of 60:40 as a basis of representation. The proposals of the BOM were accepted by the Soulbury Commission and incorporated into the new constitution. In I. D.S. Weerawardena’s words, “From the point of view of the minorities, the new Constitution of Ceylon was the point of balance among the various conflicting communal claims”. Ultimately, the Tamil Congress of G.G. Ponnambalam agreed to settle for the unitary form of constitution with balanced representation based on 60:40 formula negotiated by S.W.R.D. Bandaranaike on behalf of the Ceylon National Congress. The one of very first acts of the rulers of Independent Sri Lanka disrupted this balance setup by the Soulbury Constitution ‘among the various conflicting communal claims’. The Citizenship Acts of 1948 and 1949 changed the political scenarios. This move not only made the earlier formula of distributing seats to provinces meaningless but also created an unresolved issue between Sri Lanka and India, leaving room for India to intervene. “The Soulbury Constitution received minority support (without which it could not have been implemented) because it arranged to enable the minorities to win a certain number of seats. The Ceylon Indians were among these minorities. To deny them the vote is to deny them the seats. One moral undertaken has been done away with. To deny the vote to Ceylon Indian is also to reduce the total number of seats available to all minorities. That is a broken pledge to all minorities…. The moral basis of the Soulbury Constitution has been wiped away. To attempt to prove the constitutionality of the position is not to attempt to prove its justice”.
 Its implications for the new political environment as well as for Tamil political circles were far reaching. Within the Ceylon Tamil Congress a group led by S.J.V. Chelvanayakam left the party to form the Federal Party on a regional agenda. At first, however, the regional agenda put forward by the Federal Party did not have any serious impact on Tamil politics and in the 1952 general elections the regional agenda was clearly rejected by substantial margins in the North and East in favour of the Ceylon Tamil Congress candidates. This situation rapidly changed in the period 1952-1956.
Its implications for the new political environment as well as for Tamil political circles were far reaching. Within the Ceylon Tamil Congress a group led by S.J.V. Chelvanayakam left the party to form the Federal Party on a regional agenda. At first, however, the regional agenda put forward by the Federal Party did not have any serious impact on Tamil politics and in the 1952 general elections the regional agenda was clearly rejected by substantial margins in the North and East in favour of the Ceylon Tamil Congress candidates. This situation rapidly changed in the period 1952-1956.
In 1955 the Commission of Local Government was appointed with N.K. Choksy as its Chairman. In its report the commission admitted that there was a strong support in favour of the establishment of Regional Councils in the country. However, the Commission strongly presented the case in favour of the Provincial Committees and not Regional Councils.
The phenomenon of regional councils based on existing provinces came into political discourse once again in the history of post-Independence Sri Lanka in 1957, with the Bandaranaike-Chelvanayakam Pact, three decades prior to the 13th Amendment. Part –B of the Pact contained the Joint Statement on Regional Councils. According to the provisions of the agreement regional areas were to be defined in the Bill and the Northern Province was to form a regional area but the Eastern Province was to be divided into two or more regional areas.
Provision was to be made in the Bill to enable two or more regions to amalgamate beyond the provincial limits and for one region to divide itself subject to ratification by Parliament. Parliament was to delegate powers and specify them in the Act. The Central government would provide block grant to the Regional Councils. At the same time, the Regional Councils would have powers of taxation and borrowing.
The unilateral abrogation of the B-C Pact in the face of articulate small group of political activists belied an early opportunity of accommodating the interests of sub-national groups. Bandaranaike did not address the broader constituency over the heads of these elements using his mass appeal to save the B.C. pact. In the face of a lack of support within the government quarters itself, Bandaranaike did not have courage to confront the anti-Pact forces. What happened to the B-C Pact is now well known. However, the political dynamics of post-colonial Sri Lanka linked with multi-ethnic social reality did not allow burying the basic principles embodied in the B-C Pact and they conjured up again and again in different garb.
The UNP, which took to the streets in opposing the B-C Pact was forced to come to terms with the Federal Party in 1965. The Senanayake-Chelvanayakam Agreement of 1965 covered three issues: the language rights of the Tamil people, granting of land in colonization schemes and regional devolution of power. According to Article 3 of the Agreement, “Action will be taken to establish District Councils in Ceylon vested with powers over subjects to be mutually agreed upon between the two leaders. It was agreed, however, that the Government should have power under the law to give directions to such Councils under the national interests”.
The main Left parties (the CP and the LSSP) who were the champions of equal language rights in their good old days now joined hands with the SLFP to oppose the Tamil Language (Special Provisions) Regulations. In the light of the antipathy created by the opposition in the country, the UNP-led coalition government was faltering in presenting District Councils provisions to the Parliament. Ultimately a White Paper on proposals for the establishment of District Councils under the control of the central government was presented to the Parliament in 1968. The SLFP boycott the debate at the Parliament and campaigned against it outside. In view of a possible backlash on the part of the Government caucus itself, Prime Minister Senanayake decided not to go ahead with the White Paper.
It is important to note that Mrs. Bandaranaike also had to grapple with the issue of regional devolution of power. S.J.V. Chelvanayakam resigned his seat in protest following the adoption of the first Republican Constitution. After much delay the UNF government decided to have s bye-election in1975. The United Front decided to field V. Ponnambalam, a veteran Communist Party member against Chelvanayakam. Despite the unfavourable political climate in the country in general and in the region in particular, V. Ponnambalam fared comparatively well (9457) vis-à-vis Chelvanayakam (25,927). After the bye-election, V. Ponnambalm resigned from the C.P. It was later revealed that Ms Bandaranaike had promised V. Ponnambalam that a statement will be issued before the Election Day promising regional devolution. Santasilan Kadirgamar refers to the book Senthamilar Ahuvom written by V. Ponnambalam in which he reasoned out why he resigned from the C.P. According to Kadirgamer, “he revealed how he and the Tamil supporters of the left movement who had worked hard at the 1975 bye-elections had been severely let down. The United Front had given him the assurance that 48 hours before the poll the Kankesanturai electorate would be flooded with pamphlets promising a substantial degree of autonomy to the North and East, that would gone beyond the abrogated Bandranaike-Chelvanayakam Pact of 1957. At the last minute the SLFP high command went back on this promise and the CP leadership succumbed to this betrayal”. (To be concluded)
Midweek Review
House erupts over Met Chief’s 12 Nov unheeded warning about cyclone Ditwah
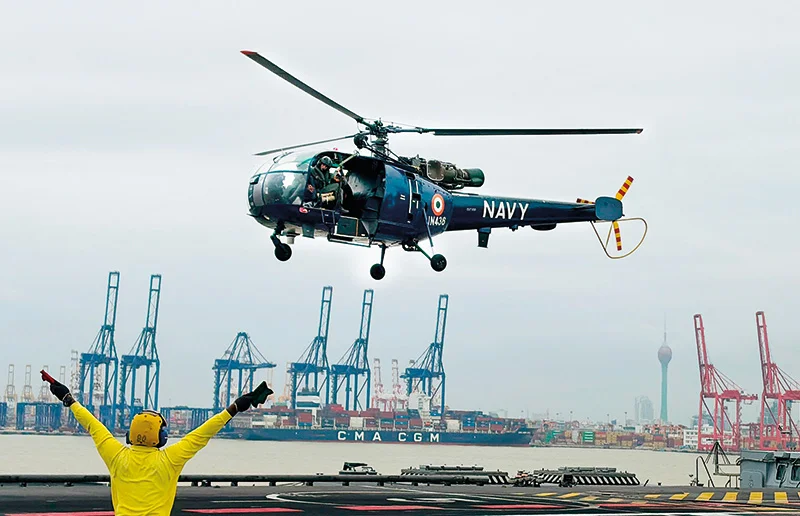

Pakistan arranged a series of C-130 humanitarian flights to transport the Urban Search and Rescue (USAR) team, fully equipped field hospitals, and approximately 100 tons of relief assistance. Pakistan, whose assistance during the war prevented the breaking up of Sri Lanka, also directed a Pakistan Navy Ship (PNS), that was here to participate in the International Fleet Review to mark Sri Lanka Navy’s 75th anniversary, to engage in humanitarian operations. The Pakistan High Commission here said that the vessel’s onboard helicopter was deployed for relief and rescue missions, in coordination with Sri Lankan Forces, extending crucial aerial support to affected areas. (At the time this edition went to press, Pakistan hasn’t been able to dispatch the aid aircraft due to India not granting sufficient time to carry out the movement, Pakistan HC in Colombo alleged. India earlier said that approval has been granted for Pakistan to fly over India)
The year 2025 ends with devastating loss of lives and property, both private and public, as a result of floods and landslides triggered by Cyclone Ditwah.
Social media erupted over accusations that the National People’s Power (NPP)government failed to issue a proper warning, in spite of the Director General of the Meteorology Department, Athula Karunanayaka, declaring the impending unprecedented danger.
Karunanayaka made the deadly prediction on 12 November on ‘Big Focus.’ He said so responding to ‘Big Focus’ presenter Kalindu Karunaratne.
Karunanayake didn’t mince his words when he warned of the impending catastrophe. The top official warned that the situation could take a turn for the worse on or after 14 November. Declaring that the threat could progress rapidly though it may not happen on 14 November, Katunanayake said at that moment he wouldn’t call the development a cyclone.
Cyclone Ditwah made landfall on 27 November, two weeks after DG Karunanayake’s warning.
Some compared the alleged lapse with the failure on the part of the Yahapalana administration to thwart the 2019 Easter Sunday carnage, though the powers that be received actionable intelligence.
The nearly one-hour long programme entirely dealt with the developing weather situation. The Director General of the Disaster Management Centre (DMC), Major General (retd.) Sampath Kotuwegoda, and scientist Imaya Ariyarathna of the National Building Research Organisation (NBRO) joined the discussion.
What really prompted ‘Big Focus’ to invite them for a discussion on weather at a time when much more interesting developments were taking place, with a section of the Opposition planning the Nugegoda protest. Let me emphasise that the Meteorology Department comes under the purview of the Ministry of Defence (MoD) and it works closely with the DMC. President Anura Kumara Dissanayake is the Minister of Defence, while his deputy is Major General (retd.) Aruna Jayasekera. The Secretary to the MoD is celebrated helicopter gunship pilot, Air Vice Marshal (retd.) Sampath Thuyakontha.
It would be pertinent to ask whether the Meteorology Department alerted the Defence Ministry, in writing, regarding the impending threat. Had DG Karunanayake been so sure of the developing threat shouldn’t he have advised the government immediately? In addition to DG Karunanayake, it would be necessary to inquire into the DMC’s response and that of NBRO as both organisations had been represented at the discussion.
In fact, the Metrology Chief should have advised the government of the developing situation before he appeared on ‘Big Focus.’ What did the Metrology Department, the DMC and NBRO do over the next 10 days before Cyclone Ditwah ravaged Sri Lanka?
Instead of demanding a Parliamentary Select Committee (PSC) to ascertain the overall failure of those responsible to act on available data, the main Opposition Samagi Jana Balawegaya (SJB) pursued a politically motivated agenda. Finally, the SJB forcefully raised the issues at hand in Parliament on 01 December. The government struggled to cope up with Opposition accusations.
A section of the Opposition sought to take political advantage of the developing crisis by demanding the cancellation of a national programme called the ‘Sri Lankan Day’, meant to foster unity and understanding among the country’s diverse communities and utilisation of the funds, allocated for that project, to provide urgently required assistance for the needy.
Buddhasasana, Religious and Cultural Affairs Ministry has been tasked with implementing that programme, which is scheduled to take place on 12, 13, and 14 December, 2025. The Opposition should have pressed both the government and DG Meteorology as to how specific warnings weren’t issued at least in the wake of the ‘Big Focus’ disclosure.
Political conspiracy

Sampath Kotuwegoda / Athula Karunanayaka
Lawyer and political commentator Nayana Tharanga Gamage lambasted Derana over repeating that segment of the programnme where DG Karunanayake issued the warning. Gamage found fault with the television channel for its reportage while raising the possibility of that channel propagating anti-NPP government propaganda for the benefit of Derana Chief. Gamage was referring to Sarvajana Balaya leader and its only MP Dilith Jayaweera (National List).
Referring to previous instances of the media exploiting crisis situations, Attorney-at-Law Gamage, in his regular social media comment that always addressed issues, lambasted Derana for its reportage of Cyclone Ditwah.
However, the failure on the part of the SJB, and those who organised the Nugegoda rally, to take up vigorously the disclosure made on ‘Big Focus,’ is quite disappointing. All three institutions that had been represented at the discussion with Kalindu Karunaratne owed an explanation and apology as to why absolutely no action was taken until Cyclone Ditwah struck Sri Lanka.
Had the JVP-led NPP represented parliamentary Opposition, that party would have definitely raised the issue. Even if the irresponsible Opposition so far failed to take up this issue, it would be the responsibility of the government to explain the developments since 12 November.
But even if prior warnings had been issued in the wake of ‘Big Focus’ declaration, the destruction caused to infrastructure and houses/buildings couldn’t have been averted but it could have been minimised and certainly many lives could have been saved. Experts say the impact could have been minimised if the authorities had lowered the water levels in the reservoirs, systematically, much earlier as they had been forewarned of the coming monster storm, instead of suddenly releasing vast quantities of water when things were too late, which caused devastating floods downstream. At the time of writing this, the death toll had passed 800 with bodies of over 400 men, women and children yet unaccounted for, and they may never be found.
The number of deaths caused by Cyclone Ditwah is much more than from the Easter Sunday carnage. Multiple attacks, blamed on the National Thowheeth Jaamath (NTJ), claimed the lives of approximately 270 people, andabout 500 received injuries.
Economic fallout of the devastation caused by Cyclone Ditwah has to be ascertained. The national economy, still struggling to cope up with the disgraceful financial status, may experience intensified pressure as the government had no option but to review its overall strategy. The impact on tourism would be devastating as happened in the wake of 2019 Easter Sunday carnage and those who are responsible for managing the economy would be compelled to rethink their economic strategy.
Both the government and the Opposition would have to sink their differences and work together to overcome the developing crisis. The devastation is so huge a reappraisal of budget expenditure, too, may be necessary without delay. Whatever the ruling party politicians may say, it would be prudent to reexamine the arrangement with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) as well as the World Bank and other lending bodies as to how the 2028 deadline for the resumption of debt repayment can be met.
The reportage of the post-Cyclone Ditwah situation primarily focused on rescue efforts and providing of relief. The long-term impact of the devastation caused seemed to have been conveniently forgotten.
The government should realise that its overwhelming 2/3 majority in Parliament does not mean anything. In fact, the re-building of public infrastructure and private property would pose such an intimidating challenge, the NPP, perhaps, may have to change its priorities and think of short, medium and long-term plans to revive the national economy, especially the agriculture sector, which received a body blow as never before.
The urgent need to examine the devastating impact of the disruption of overland main roads, leading to/from the upcountry region, cannot be overemphasised. Unfortunately, the powers that be seemed to be interested in the basic coverage of the post-Cyclone Ditwah developments.
It would be interesting to know whether the Meteorology Department alerted the Examination Department regarding the developing situation before or after the ‘Big Focus’ discussion or never bothered to do so before Cyclone Ditwah swooped down on Sri Lanka. The failure on the part of the Meteorology Department to do so cannot be pardoned under any circumstances. The DMC is also equally responsible for the lapse as its head, Major General (retd.) Kotuwegoda, had been part of the ‘Big Focus’ panel.
The Advance Level examination commenced on 10 November, two days before the Meteorology Department issued a warning. Regardless of assurances given by the Examination Department, the government would find it extremely difficult to re-schedule the examination which was earlier scheduled to be completed on 05 December. Let us hope Advance Level candidates weren’t among the dead and those disappeared.
Operation Sagar Bandhu
In line with India’s ‘Neighbourhood First Policy’ New Delhi acted swiftly and decisively in the wake of Cyclone Ditwah strike.
Aircraft carrier INS Vikrant and INS Udaygiri — the second ship of Project 17A’s stealth frigates that arrived in Colombo to participate in the International Fleet Review (IFR) to mark Sri Lanka Navy’s 75tth anniversary that was to be held on 30 November brought in urgently needed supplies for Sri Lankan victims. India seemed to have been aware of the developing threat and brought in essential items which were handed over to Sri Lanka. The vessels that were sent here to participate in the IFR, according to a press release issued by the Indian High Commission in Colombo, carried 4.5 tons of dry rations and 2 tons of fresh rations, consisting of staple foods, packaged and ready-to-eat items, dairy and bakery products, beverages, and other nutritional essentials to meet urgent household needs. In addition, the vessels delivered other essential survival items.
Chetak helicopters were launched from INS Vikrant to airlift those who had been marooned while Mi 17 helicopters of Indian Air Force (IAF) conducted search and rescue operations over the last weekend near the inaccessible Kotmale area, saving stranded persons, including pregnant women, infants, and those critically injured. The IHC declared that those who had been rescued consisted of Sri Lankans, Indians, Germans, Slovenians, British, South Africans, Polish and people from Belarus, Iran, Australia, Pakistan and Bangladesh. Further, the helicopters also airlifted critical casualties to Colombo as well as carrying Sri Lankan Army personnel to landslide affected regions.
Obviously, Sri Lanka couldn’t have faced the dire situation without Indian assistance. The Indian response is very much similar to the action during the economic crisis here a few years back. It would be also interesting to examine whether against the backdrop of the scheduled IFR, Navy Headquarters sought clarification from the Meteorology Department regarding the 12 November Cyclone warning. The Navy couldn’t go ahead with the IFR with the participation of eight warships from seven countries.
Two IAF aircraft, a C-130J and an IL-76, brought in approximately 21 tonnes of relief supplies, along with 80 personnel from the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF). They were deployed in Puttalam and Badulla, two of the worst-affected regions. Subsquently, India sent more assistance, both in the form of men and material. We should also be grateful for assistance provided by India, China, Japan, the US, Australia, UK, New Zealand and others but New Delhi cannot absolve itself of the responsibility for causing terrorism here.
Tragedy
During relief missions on Sunday (30), SLAF lost a pilot, Wing Commander Nirmal Siyambalapitiya, when he was forced to make an emergency landing near the Lunuwila bridge. Siyambalapitiya, with over 3,000 flying hours during his distinguished service, succumbed to his injuries, and had been in command of the Bell 212 altogether carrying five personnel, including a co-pilot.
Against the backdrop of the Commander of the Air Force, Air Marshal Bandu Edirisinghe, ordering the setting up of a board of inquiry to investigate the incident, the government cannot ignore the need to probe the failure to act in spite of the Met Department issuing warnings.
Five SLN personnel, attached to the Chalai detachment, in the Vettilaikerni sector, also died, on Sunday, when they were caught in flood waters.
In spite of the setbacks, the war-winning armed forces sustained relief and rescue efforts in virtually all affected areas. The social media comments on the role played by the armed forces reminded the country again and again how the public are divided over the government’s approach.
Let me be clear, regardless of the issuance of an early warning, floods and landslides were certain to cause catastrophe but some lives could have been saved and household items, and vehicles, moved to safety. The government is accountable for the failure to act on the basis of the Meteorology Department’s assessment.
Some social media posts reminded me of the alleged Helping Hambantota financial scam perpetrated after the 2004 tsunami. International funds that had been sent to the then Prime Minister Mahinda Rajapaksa’s official account were allegedly transferred to a privately-run scheme. That had been a major issue at the 2005 presidential election won by Mahinda Rajapaksa.
Helping the Hambantota scheme caused Mahinda Rajapaksa immense harm. The Criminal Investigation Department (CID) sought permission from the courts to investigate the accounts alleging that there was a breach of trust concerning nearly 83 million Sri Lankan rupees (approx. 820,000 US dollars).
Deputy Solicitor General, Palitha Fernando, who represented the Attorney General, told court that the CID was directed to initiate an investigation after a complaint made by United National Party (UNP) parliamentarian Kabir Hashim.
This transpired when a fundamental rights petition by Mahinda Rajapaksa against the probe by the CID was taken into consideration by the Supreme Court. The then Chief Justice Sarath Nanda Silva is on record as having said the CID seemed to have worked under political influence as there was no written evidence against the then Prime Minister, Mahinda Rajapaksa.
The CJ said President Rajapaksa had to seek legal assistance due to “inappropriate” action by the Criminal Investigation Department (CID). Years later Sarath Nanda Silva changed his stand on this particular case.
The bottom line is the latest calamity has weakened Sri Lanka further. That is the undeniable truth. Whatever the politicians say Sri Lanka faces an uphill task in pursuing economic recovery.
The government may be compelled to cancel a controversial deal to procure over 1,700 diesel double cabs in violation of laid down procedures. We wonder why the government at least did not make any attempt to procure electric vehicles for the government fleet as it would have at least helped to lessen air pollution that many areas of the country has been enveloped in for some time. It would even save the money that would have been spent on costly diesel and engine oil. Perhaps, in economic terms, the devastation caused by Cyclone Ditwah is definitely far worse than the 2019 Easter Sunday attacks. The cost of infrastructure losses is yet to be estimated and appropriate measures taken to restore them. The task seems to be overwhelming, especially against the backdrop of interested parties seeking to take advantage of the calamity.
Maybe we should ask our powerful friends in the West, like the USA, to postpone sending attack helicopters and military transport planes as we are not in any war with any other country, but instead to send us things like medicines that our hospitals are gravely short of. Definitely when we can hardly stand up on our own feet how can we afford to get into scrapes started by others?
Midweek Review
Climate Change, new technology and the future of the world: A turning point for humanity

Climate change is no longer a distant scientific concern; it is now the most urgent global crisis shaping economies, politics, and the daily lives of billions. Around the world, rising temperatures, unpredictable weather patterns, and environmental degradation continue to intensify. At the same time, rapid technological innovation from artificial intelligence to renewable energy systems is transforming how societies respond to this crisis. Nations stand at a historic crossroads, and the choices made in this decade will determine the fate of future generations.
Recent global climate summits, including the United Nations Climate Change Conferences (commonly known as COP meetings), have repeatedly stressed that the world must limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Leaders have emphasised rapid decarbonisation, accelerated renewable energy adoption, climate finance for vulnerable nations, and stronger commitments to phase down fossil fuels. While progress has been uneven, these summits have highlighted the dual necessity of environmental responsibility and technological innovation. The message is simple: the world cannot avoid catastrophic heating unless governments, industries and citizens work together guided by science and strengthened by emerging technologies.
Sri Lanka, like many developing nations, stands at the frontline of climate vulnerability. Rising temperatures, severe droughts, floods, landslides, coastal erosion and saltwater intrusion are already affecting agriculture, urban infrastructure, fishing communities, and rural livelihoods. The country’s climatic shifts from prolonged dry spells in the North and East to intensified monsoons in the South and Central highlands reflect broader global patterns. For Sri Lanka, climate change is not an abstract scientific debate; it is a lived reality. The nation’s current experience underscores why strong climate policies and technological investment are essential.
Renewable energy is one of the most transformative tools in the global fight against climate change. Solar and wind power have become increasingly affordable, enabling nations to reduce dependence on fossil fuels. In Sri Lanka, the government has announced long-term plans to increase renewable energy to a major share of the national grid. Projects such as solar rooftop systems, rural micro-grids, large-scale wind farms in Mannar, and community-based energy initiatives are already part of the national strategy. These efforts align with global summit commitments that call for tripling renewable energy capacity worldwide by 2030. As the cost of renewable technology decreases, the possibility of a cleaner, energy secure future becomes more achievable.
Artificial intelligence is another powerful tool reshaping the world’s climate response. AI-driven forecasting models now help predict extreme weather events more accurately, allowing countries to prepare for floods, cyclones, droughts, and storm surges. In Sri Lanka, meteorological agencies increasingly rely on digital modelling to monitor monsoon behaviour, track ocean patterns, and issue early warnings. These systems have saved lives and minimised damage, especially in flood prone districts such as Gampaha, Kalutara and Ratnapura. At a global level, AI is also used to assess emissions, monitor deforestation, optimise farming, and manage energy distribution. As climate impacts grow more complex, digital intelligence will play an even greater role.
Technological innovation is transforming agriculture, a sector deeply affected by climate volatility. Around the world, scientists are developing drought resistant crops, precision irrigation systems, and satellite-based soil monitoring tools. Sri Lanka, where agriculture employs a significant portion of the population, is already experiencing challenges: reduced rainfall in the dry zone, declining groundwater levels, and pest outbreaks linked to warmer temperatures. New technologies notably drip-irrigation, greenhouse cultivation, and solar-powered water management are gradually being introduced to help farmers adapt. International climate agreements emphasise supporting such adaptation strategies, especially for vulnerable nations. With proper investment and training, Sri Lankan farmers can overcome many of the climate driven threats to food security.
Transportation is another key sector undergoing rapid transformation. Globally, electric vehicles (EVs), hydrogen powered transport, and smart public transit systems are gaining momentum. Many countries have pledged, under climate summit declarations, to phase out petrol and diesel vehicles by mid-century. Sri Lanka has shown growing interest in sustainable mobility, with the rising popularity of electric cars, three-wheelers, and commuter buses. Charging stations are slowly emerging, and policy frameworks are being considered to encourage cleaner transport solutions. While progress remains gradual due to economic constraints, the broader global trend signals that the future of mobility will be electric and digitally managed.
One of the most pressing concerns for the future is the rise of climate induced migration. As sea levels rise and extreme weather intensifies, millions around the world face displacement. Small island nations, South Asian coastal regions, and rural farming communities are particularly vulnerable. In Sri Lanka, coastal erosion from Negombo to Jaffna and from Hambantota to Kalmunai poses a serious threat. Saltwater intrusion is already affecting freshwater supplies and agriculture in areas such as Puttalam, Jaffna and Batticaloa. Global climate summit decisions repeatedly call for stronger adaptation funds, coastal protection strategies, and international support for countries confronting such challenges. Ensuring that vulnerable communities are protected will require both technological solutions and sustained political will.
At the heart of climate action lies public awareness. Across the world, young people have become powerful advocates for environmental protection. Climate activism, amplified by social media, has gained unprecedented momentum. In Sri Lanka too, university students, environmental groups, and civil organisations continue to push for stronger climate commitments, better waste management, and protection of natural resources. Their voices reflect a global shift in consciousness, where sustainability is increasingly viewed as essential rather than optional. Digital platforms have played a vital role, enabling activists to educate communities, mobilise support, and hold institutions accountable.
The economic landscape is also changing. Sustainability is now a competitive advantage for businesses. Organisations adopting green technologies, ethical sourcing, and energy-efficient operations are gaining consumer trust and long-term resilience. Global climate summits encourage private-sector participation in climate finance and green investment. In Sri Lanka, sectors such as tourism, manufacturing, agriculture, and energy are exploring new strategies to reduce emissions and strengthen environmental stewardship. Green jobs ranging from solar panel installation to environmental engineering are expanding, offering new opportunities for youth and professionals.
Yet challenges remain. Many developing nations struggle to access cutting edge technology due to limited financial resources. Infrastructure gaps, policy barriers, and economic instability can hinder the adoption of renewable and digital solutions. Sri Lanka’s own economic crisis has slowed the implementation of several climate related projects. Global climate summits have repeatedly emphasized that richer nations must provide climate finance grants, loans, and technology transfers to support vulnerable countries. While some progress has been made, funds often fall short of what is required. Without equitable support, the technological divide could worsen existing inequalities.
As the world looks ahead, the future depends on how effectively humanity can balance technological progress with environmental responsibility. The next decade will be critical. Decisions on energy, land use, industrial development, and digital systems will shape the planet’s stability for centuries. Despite the challenges, there is reason for cautious optimism. History shows that societies are capable of remarkable transformation when confronted with crisis. The rapid rise of renewable energy, global climate agreements, technological innovation, and growing environmental awareness all point toward the possibility of a greener, more resilient future.
For Sri Lanka, the path forward involves strengthening climate adaptation, expanding renewable energy, modernizing agriculture, protecting biodiversity, and ensuring that technology serves communities rather than deepening inequality. Collaboration between government, private sector, universities, and local communities will be essential. At the global level, summits like COP remind the world that climate change cannot be solved by one nation alone. It requires shared responsibility, scientific cooperation, and a commitment to fairness.
Ultimately, the story of climate change and technology is about humanity’s ability to adapt, innovate, and imagine a better future. The window for action is narrowing, but it remains open. The future of the planet and of nations like Sri Lanka depends on the choices made today. With wisdom, courage, and technological vision, the world can still steer toward a safer, cleaner, and more sustainable tomorrow.
Finally, Sri Lanka faces growing climate threats from floods and droughts to coastal erosion and crop losses mirroring global environmental changes. While new technologies and global climate agreements offer solutions, urgent national action is essential. Sri Lanka must strengthen early-warning systems, expand renewable energy, protect coastal zones, and modernize agriculture with climate-smart methods. Reforestation, watershed protection, and stricter land-use regulations are vital to reducing disaster risks. Improved climate education, stronger environmental laws, and sustained community involvement will help build resilience. With coordinated policy, technology, and public commitment, Sri Lanka can face future climate challenges with greater security and sustainability.
by Milinda Mayadunna
Midweek Review
UNP finally admits MR saved country from terrorism

Former UNP Minister Harin Fernando publicly declared for the first time that Mahinda Rajapaksa led the country, ignoring all those pundit nay sayers and brought the war against the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) to a successful end. The ex-parliamentarian also emphasised that Ranil Wickremesinghe restored the collapsed national economy. The UNPer was referring to the crushing of the LTTE militarily in May 2009 and Wickremesinghe completing the remainder of the ousted President Gotabaya Rajapaksa’s 5-year term won at the Nov 2019 presidential election.
Fernando said so addressing ‘Maha Jana Handa’ organised at the Nugegoda Ananda Samarakoon Open Air Theatre last Friday (21). Unfortunately, Fernando’s leader Ranil Wickremesinghe who actually proposed a high-profile joint Opposition campaign against the Jathika Jana Balawegaya (JJB) government and the war winning President Mahinda Rajapaksa conveniently skipped the Nugegoda rally. That, however proved how fed up the masses are with the current dispensation for breaking virtually all their promises by turning right, but nothing to show for it, after signaling left for so long promising a mythical revolutionary state, while causing so much death and destruction along the way with two abortive uprisings. Masses came in record numbers to the Nugegoda rally despite it being led by relative minnows in the opposition.
Wickremesinghe certainly owed an explanation regarding his absence as it was, he who proposed 1,000 meetings against the NPP/JVP government, at the UNP’s 79th convention held on Sept 20, this year at Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte. It was themed ‘Let’s Stand Together.’
The UNP hitherto never publicly acknowledged the fact that Mahinda Rajapaksa’s bold leadership ensured Sri Lanka’s triumph over the separatist terrorist LTTE. The significance of Fernando’s declaration was lost in political rhetoric as speakers challenged President Anura Kumara Dissanayake (AKD). SLPP National List MP and National Organizer Namal Rajapaksa vowed to topple the NPP at the first given opportunity unless AKD fulfilled promises made in the run-up to 2024 presidential election.
Among notable absentees was SLPP founder and former renowned political strategist Basil Rajapaksa. The nonattendance of the main Opposition Samagi Jana Balawegaya (SJB) leader Sajith Premadasa, who is also the Opposition Leader, as well as all constituent members of the SJB underscored the overall weakness of the initiative. The failure on the part of ‘Maha Jana Handa’ organisers to reach a consensus with the SJB regarding a tangible plan of action cannot be overemphasised.
Former Prime Minister and MEP leader Dinesh Gunawardena who backed Ranil Wickremesinghe candidature at the last presidential election also skipped the Nugegoda rally.
The SJB with 40 MPs is the second largest political party in the current parliament. Therefore, the SJB’s absence made the whole effort meaningless symbolically, but the enthusiasm of the massive crowd that converged there, despite all types of impediments put in their way, without doubt once again showed the growing unpopularity of the current dispensation. The SJB is very much unlikely to change its stand regarding participation in the current initiative unless an agreement with the UNP could be finalised. The SJB wouldn’t under any circumstances throw its weight behind any political initiative that failed to acknowledge the situation on the ground.
But the groundswell of disappointment with the JVP led government for having betrayed many of their longstanding ideals and also failing to deliver many of their election promises, may result in even SJB being overlooked by masses for other alternatives.
The UNP doesn’t represent the current parliament whereas Ranil Wickremesinghe backed New Democratic Front (NDF) at the last parliamentary election secured five seats, including two National List slots. The NDF group consists of Chamara Sampath Dassanayake, Anuradha Jayaratne, Rohitha Abeygunawardena, Ravi Karunanayake (NL) and Faizer Musthapha (NL). Of them, only Dassanayake joined the rally where he was one of the main speakers.
Namal Rajapaksa’s SLPP parliamentary group consists of just three MPs, hence the urgent need to bring the SJB into the fold. But that wouldn’t be possible unless ‘Maha Jana Handa’ recognised the SJB’s standing among opposition political parties and groups.
Harin Fernando, tasked by Wickremesinghe to organise countrywide meetings in his fiery speech appealed to the SJB while lambasting the Janatha Vimukthi Peremuna (JVP) for ruination of the country. Let me discuss Fernando’s declaration regarding Mahinda Rajapaksas bringing what the UNP dubbed an unwinnable war to an end and how that party pursued a despicable political strategy at the expense of post-war Sri Lanka.
A relentless offensive

Harin Fernando / Ranil Wickremesinghe
The UNP never believed in battle-field victory over the LTTE. Wickremesinghe operated on the assumption that the LTTE could reverse the ground situation with a devastating counter offensive on the Vanni front. That had been the general opinion among the Western and Indian diplomatic community here and the Tamil speaking community living outside the Northern Province. But those who lived in the North knew that there hadn’t been a similar multi-pronged ground offensive before.
But still the UNP felt that the LTTE could deliver a massive blow on the Vanni front and cause irreparable damage to the war effort. The LTTE’s last desperate bid to regain the initiative went awry in February 2009 and two months later the Army delivered a knockout blow to the enemy at Anandapuram. That was the end of their once formidable conventional military capacity. The destruction of the LTTE floating arsenals on the high seas during 2006-2007 period by Vice Admiral Wasantha Karannagoda’s Navy and the strategic air campaign conducted by the SLAF under AM Roshan Gunetilleke’s leadership facilitated the overall campaign.
Against the backdrop of Harin Fernando’s long-overdue admission, it would be pertinent to mention that President Mahinda Rajapaksa refused to heed combined UK (David Miliband)-French (David Kouchner) demand to halt the offensive. That bid to throw a lifeline to the LTTE was made in late April 2009 as the ground forces were engaged in their final push to break the back of the LTTE as they were cornered into an ever-decreasing patch of land. That courageous decision ensured Sri Lanka’s triumph over terrorism that plagued the country since 1983.
When David Miliband and Bernard Kouchner met President Rajapaksa at Chandrikawewa, the younger man is reported to have brazenly told President Rajapaksa, “Mr. President we want you to agree to a ceasefire. We cannot be passive spectators. There has to be a lull in the fighting.”
President Rajapaksa’s response was: “Secretary Miliband, I want to tell you we are no longer a colony. Empirical experience has shown that ceasefires only prolong the war. It would be a gross betrayal of our country to permit the Tigers to recuperate and return to war – as they have done on countless occasions.”
Historian and the creator of Thuppahi’s blog Michael Roberts revealed the exchange on the basis of what the then Foreign Secretary Palitha Kohana and International Trade Minister Prof. G. L. Peiris had told him (https://thuppahis.com/2018/07/02/how-mahinda-rajapaksa-rebuffed-david-miliband/).
Any other leader would have succumbed to that kind of big power pressure against the backdrop of the US sending a military team here to explore the possibility of evacuating terrorist leader Velupillai Prabhakaran, his family and top lieutenants.
The UNP remained silent about the joint UK-French attempt. Wickremesinghe who always boasts of his close connections with western governments may have been aware of the UK-French bid. Had Wickremesinghe intervened on behalf of the country/armed forces and issued a statement opposing a European backed ceasefire at that time he and the UNP could have saved face. Unfortunately, he played politics with the issue much to their own detriment.
Wickremesinghe went a step further, he joined hands with the Tamils National Alliance (TNA) that represented the LTTE’s interests both in and outside parliament (2001 to 2009) and the JVP to field war winning Army Commander at the 2010 presidential election. In hindsight that decision caused a ripple effect and contributed to the overall deterioration of the political party system.
Harin Fernando’s praise of Mahinda Rajapaksa wouldn’t absolve his party of treacherous betrayal of the victorious armed forces as well as the then political leadership at the Geneva-based Human Rights Council (HRC) in Oct 2015. In fact, the UNP worked closely with the JVP from 2009/2010 to 2019 when the latter decided to quit the alliance to contest the 2019 presidential election.
Lessons from Nugegoda
Among those who had been on the front row of the Nugegoda rally were SLPP General Secretary Sagara Kariyawasam, Prof. G. L. Peiris, Nimal Siripala de Silva, Vajira Abeywardena, Udaya Gammanpila, Tiran Alles, Mahinda Amaraweera, Duminda Dissanayake and Lasantha Alagiyawanna.
Prof. Peiris as the government’s chief negotiator during peace talks with the LTTE between 2002 and 2003 period is one of the few politicians fully aware of the developments that led to breakdown of talks in April 2003 and resumption of war in August 2006. Prof. Peiris also served as foreign minister in the post-war period and was closely associated with efforts to counter war crimes accusations. Harin Fernando’s declaration, about the way Sri Lanka brought the war to a successful conclusion may help the country to counter Geneva war crimes allegations. Unfortunately, the UNP worked overtime against President Rajapaksa thereby betraying the country by co-sponsoring an accountability resolution in Oct 2015.
The JVP though not represented in the cabinet fully backed the Sirisena-Wickremesinghe led yahapalana administration that co-sponsored the Geneva resolution
The Nugegoda rally was silent on the Geneva betrayal. Speakers on the Nugegoda platform couldn’t have referred to that outright treachery in Geneva as the UNP had joined ‘Maha Jana Handa.’ Nugegoda platform was also conveniently silent on ongoing investigations into accountability issues. In fact, ‘Maha Jana Handa’ conveniently avoided contentious issues ranging from Memorandums of Understandings (MoUs) with India in April this year to formalisation of collaboration between the Montana National Guard, U.S. Coast Guard District 13, and the Sri Lanka Armed Forces under the U.S. Department of Defence’s State Partnership Programme (SPP) earlier this month.
Against the backdrop of the UPFA first entering into Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement (ACSA) in 2007 and then UNP-SLFP yahapalanaya extending the same in 2017, Nugegoda platform couldn’t have accused the NPP of undermining sovereignty. Similarly, they couldn’t have attacked the NPP over the IMF agenda as all of them accepted that formula by the passage of the Economic Transformation Bill in July 2024 without a vote.
The failure on their part at least to mention India taking over 51% stake of the Colombo Dockyard Limited (CDL) for USD 52 mn within weeks after the signing of seven MoUs proved that Nugegoda rally simply didn’t take key developments into consideration. The success of a rally cannot be under any circumstances gauged by the presence of a sizable crowd as people do not on their own attend political rallies. The meeting addressed by President Anura Kumara Dissanayake at Tangalle on the day before the Nugegoda rally is a case in point. At least one third of the Tangalle gathering happened to be serving military and police in civies and government officials and the rest brought in by the party. The only difference at Tangalle and Nugegoda had been loud speakers outside the venue at Tangalle whereas ‘Maha Jana Handa’ was denied the same citing the on-going Advance Level examination. NDF lawmaker Chamara Sampath Dassanayake quite rightly pointed out this at the Nugegoda meeting.
The SJB and UNP need to address their internal issues as soon as possible. Sajith Premadasa and Ranil Wickremesinghe cannot further delay in reaching a consensus on the leadership issue. If they do not set aside their petty squabbling for the greater good of the country the people themselves might consign them to the dust bin of history. The setback suffered at Nugegoda must compel them to unify the two parties to face the NPP as the SLPP with just three MPs in current parliament cannot be expected to give leadership to the combined Opposition. It would be a grave mistake on the Opposition’s part to think that it can achieve the transformation of the JVP’s three MPs to 159. Such a massive change would never have been possible without Aragalaya that caused political upheaval and turned the party system upside down.
The SLPP now down to just three from near 2/3 majority in 2020 shouldn’t forget that the indictments were forwarded to the Colombo High Court by the Attorney General in late January this year, alleging that Namal Rajapaksa misappropriated funds to the tune of Rs 70 mn received from the Indian real estate company Krrish for the development of rugby in Sri Lanka.
Disastrous UNP strategy
The UNP still seems unable to come to terms with the situation. In spite of the party being reduced to a nonentity with no parliamentary representation at the moment and no hope of coming back at the next national elections, that party is still trying to reach a consensus with the SJB at the latter’s expense. Their effort is geared to safeguard Ranil Wickremesinghe’s leadership at any cost. They haven’t realised Wickremesinghe’s folly in contesting the last presidential election as an independent candidate thereby causing a split in the vote that ensured Anura Kumara Dissanayake’s victory at the presidential election. Dissanayake polled 5.6 mn votes whereas Sajith Premadasa and Ranil Wickremesinghe polled 4.3 mn and 2.2 mn votes respectively.
The bottom line is that Wickremesinghe and the former UNP deputy leader Premadasa polled 6.5 mn votes, 900,000 votes more than Dissanayake who also failed to secure 50% of the vote. Regardless of that, the UNP pursued a strategy that only helped the NPP to consolidate its position with a resounding victory at the parliamentary election last November, three months after the presidential poll.
Instead of reaching a consensus with the SJB, Wickremesinghe caused political mayhem by contesting under the NDF symbol gas cylinder. That move divided the SLPP, undermined the SJB and delivered a knockout blow to the UNP. The NDF that had never been represented in parliament secured five seats, including two NL slots while the SLPP ended up with just three seats including one NL slot. The UNP that secured one NL slot at the 2020 parliamentary election was reduced to zero at the 2024 general election.
Harin Fernando’s declaration at the Nugegoda rally that Wickremesinghe restored the collapsed national economy is debatable. The Treasury bond scams perpetrated in 2015 February and 2016 March under Wickremesinghe’s watch by Singaporean Arjuna Mahendran who served as the Governor of the Central Bank at that time remains a thorny issue. Having compelled President Maithripala Sirisena to appoint close associate Mahendran as the Governor regardless of him being a foreign passport holder Wickremesinghe cannot absolve himself of the responsibility for Treasury bond scams.
Mahendran was allowed to leave the country. The Singaporean remains at large. Those who now represent the SJB protected Mahendran and engaged in cover up of Treasury bond scams throughout yahapalanaya (2015 to 2019). The then UNPer and current SJB lawmaker Sujeewa Senasinghe went to the extent of authoring a booklet denying Treasury bond scams while others undermined the COPE (Committee of Public Enterprises) process intended to identify the culprits.
The JVP, too, cooperated in that cover-up. It would be pertinent to mention that the JVP transformed the party in 2009/2010 to align with the UNP. That partnership completely changed the JVP. That transformation took place during the late Somawansa’s leadership. Anura Kumara Dissanayake who succeeded Somawansa in 2014 has taken the party to the next level. Securing both presidency and unprecedented 2/3 majority in parliament is certainly not a simple task and he has achieved the impossible as the leader of both JVP and NPP.
However, the President’s continuing success depends largely on the failure on the part of the sharply divided Opposition to reach a consensus on a workable plan of action. The resolution of the SJB-UNP dispute is the key to adoption of a successful Opposition strategy.
-
News7 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
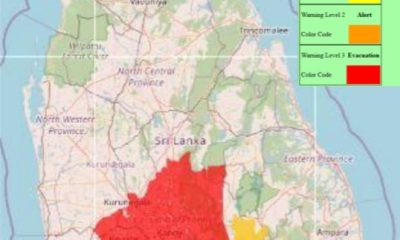
 News5 days ago
News5 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Midweek Review7 days ago
Midweek Review7 days agoHouse erupts over Met Chief’s 12 Nov unheeded warning about cyclone Ditwah













