Features
Day three of April 1971 insurrection, on duty at Hambantota/Kataragama

by Capt F.R.A.B.Musafer 4th Regt SLA (Retd)
Very early in the morning the OIC Inspector Arthanayake informed us that the Katargama Police station had been attacked but was successfully repulsed. We immediately proceeded towards Kataragama. When near the Tissa rest house I heard a shot that happened to be a rifle being discharged. This was an unfortunate incident, a mentally retarded person happened to break the curfew and when challenged had run away and was fired upon killing him.It was harrowing sight to see a family member wailing over the dead body. I felt bad that this incident happened in broad daylight and unnecessarily. The police arrived at the scene soon after and asked us to proceed to Kataragama.
Months later unknown to me this death had been investigated by the Field Security Division. This was a division that was created in 1970 to provide for the security of the Prime Minister and it also screened applicants hoping to join the armed services and among other things the anonymous petitions against serving service personnel of other political affiliations.
The FSD was headed by Major Denzil Kobekadduwa who was a political victim of the previous regime but as all and sundry knew was a perfect officer and gentleman. In 1970 on his return to the Army he captained the Army rugger team having already captained the Kandy Sports Club and represented Sri Lanka.
During his period of interdiction he was not allowed to enter any Army establishment or premises and as a result the Army vs. Kandy Sports Club Clifford Cup matches had to be played on neutral grounds and many a serving officer dared not be even seen with him. This was not the case when he was reinstated and exerted plenty of influence with the government in power. During the insurgency he was in England following a staff officers course.
The inquiry may have been instigated by an anonymous petition or on the strength of what happened in Kataragama later under Lt Alfred Wijesuriya (a volunteer army officer) where the local beauty queen, Miss Premawathie Manamperi, alleged to be a JVP sympathiser was allegedly raped, shot and left to die in a shallow grave. It transpired later that the bullet that killed her was fired by a soldier to put her out of her misery.
Lt Wijesuriya was found guilty of attempted murder and sentenced to life imprisonment. He suffered a fatal heart attack and died in prison a few years later. It was reported that the co-accused was murdered on his release from prison at Matara.
I was totally unaware that an investigation to the death at Tissamaharama was conducted until conveyed to me by one in the FSD unit who happened to be a rugby player a year later when I captained the Army rugby team in 1972. There were no formal charges laid which I presume cleared me of any blame for this death. Nevertheless it was an unfortunate and needless death under my watch that remains as a scar in my mind and conscience.
On our way to Kataragama which was not under my area of operations, we encountered a bus load of students from Trinity College who happened to have stayed overnight at Kataragama I can’t recall if they had witnessed or seen anything. Although a curfew was in operation we allowed them to proceed and make their way to Hambantota. They were put up by the GA till it was safe to return to Kandy.
At Kataragama we found the Police station had been attacked. The power and telephone lines had been cut. The police had been prepared and had successfully repulsed the attack. We were told that an injured insurgent had taken refuge in a nearby temple and proceeded towards the temple. Sitting at the entrance was this young man staring in a daze, bare bodied in a sarong with his hands across his blood soaked and swollen face. He had a bullet lodged in his face that had not exited and was in great pain.
I assumed this would have been from a semi automatic weapon or a shotgun pellet. There were some locals around but they were quite calm and showed no signs of any anger but pity. The police who accompanied me on the other hand suggested that I bump him off. They had an impression that the Army had the license to kill. I very politely told them that I could not do so and that I had to account for every round of ammunition. Much to their disappointment we took him and dropped him off at the Tissa Hospital.
Later in the day we headed for Hambantota and heard through our regimental wireless link that the Polonnaruwa police station had been attacked and the army had killed many insurgents. They had been dressed in blue uniforms and had come in buses. Speaking to Lt Lionel Balagalla months later, he told me he had heard of the attack at Wellawaya on the regimental net and on April 5 evening was tipped off that the Polonnaruwa police station was to be attacked and as a result was prepared for it.
The insurgents walked into a trap set up by the police and the army and as a result suffered very heavy losses. The siege went on till the early hours of April 6. Lionel told me that the resolve of the insurgents was strong, demonstrated by an insurgent who was seriously wounded and dying but still trying to grasp a homemade bomb and throw it .
He also told me that there was a magisterial inquiry held that day as this was the first time in the history of Sri Lanka that so many were killed by the army and police in an internal security operation. The use of weapons in any IS operation had a cardinal rule that the “minimum of force” was to be exercised at all times. The strategy of the insurgents was to overrun the police station with a human wave, they certainly had the superior numbers though not the weapons and were mowed down by rifle and machine gun fire.
Lionel was glad of the inquiry as he was fearful of the repercussions if this was an isolated incident. He treasured the piece of paper that cleared him of any wrong doing although the numbers did not tally to an article written later by a police officer who put the number at over 130. There were no mass graves, the bodies were cremated in the cemetery with probably no record of their identities. Lt Lionel Balagalla ended his military career as the Army Commander and retired as a Lieutenant General .
Weerawila abandoned on April 7
We totally abandoned Weerawila and moved into the Hambantota police station from which we would operate as a mobile force and patrol the area at night. There were reports that there were many police stations that had fallen to insurgent hands and more attacks expected. It was not an encouraging picture. That night we continued to patrol the roads aided by dusk to dawn curfews that was a common occurrence.
News was coming through that the Warakapola police station together with several other police stations had fallen. It was a very worrying situation. We were tuning in to BBC, ABC and the Voice of America for news on a world transistor owned by a gunner. Local radio were guarded in the news conveyed.
Communications were difficult as our battery operated radio equipment could not be charged as there was no electricity, this was previously done at the CTB depot at Kataragama. We were worried that if the police stations were overrun we would be isolated and even contemplated an exit strategy by sea. There was not much a single platoon could do.
Hambantota April 8
In a wireless conversation the adjutant Capt Samarakoon in very flattering and in unbelievable terms said that I was the ‘ Supreme Commander of Hambantota” and was no longer to take orders from the Government Agent. He had a tendency to exaggerate but I was flabbergasted as I was only a lieutenant with only a platoon under my command and a big responsibility shoved on my shoulders to oversee an entire district.
He mentioned that coordinating officers were to be appointed and till such time I was to take charge and take any action I thought fit. I conveyed this communication to the GA who was taken by surprise as he had not received anything official to this effect and asked me if he had done something wrong. I told him that the situation island wide had deteriorated to such an extent that total military intervention was necessary and assured him it was not a coup. He assured me of all the support he could extend.
There were many curfews enforced from time to time. Some for a period of 24 hours which caused a lot of hardship and inconvenience more so for the townsfolk rather than those in the villages. As water was a commodity in short supply in Hambantota, parents opted to send their children to collect water having instructed them to raise their hands at the sight of an army patrol. We had to turn a blind eye to enforcing the curfew. Rumours were afloat that the curfew was imposed to facilitate the receipt of weapons from foreign sources and to consolidate the positions in the ground with some foreign troops..
Some of the police stations were ordered to withdraw to Hambantota and Tangalle.
Reinforcements from Colombo on April 9
On the morning of April 9 I was informed that there were two volunteer platoons being sent to assist me to take back Tissamaharama supposedly in insurgent hands. and then move to Tangalle by nightfall. Meanwhile we received the news that Capt Noel Weerakoon had been killed in an ambush on April 8 at Rambewa/Welioya together with bombadier Munasinghe and the civilian driver of the jeep.
He and his troops were being airlifted to Anuradhpura but as the airfield was in the hands of the insurgents the plane was diverted to Vavuniya. Alternative arrangements were made to travel to Anuradhapura by road. Determined to reach his objective he made the fatal decision to travel at night. His dedication and commitment to follow orders cost him his life. His body was retrieved from the riverbed at the site of the ambush by sergeant Ameer who had returned the enemy fire and caused the insurgents to retreat.
It was Capt Weerakoon’s men I was commanding and that was a devastating blow to them, a much loved officer. It affected their morale and also brought to our realization that the situation was becoming a serious problem with the army and police on the back foot.
Lt Mohan Mootatamby was recalled from his deployment at Hingurakgoda and sent to take over command of the platoon which was at Vavuniya. He was the sole passenger of an Air Ceylon plane, something he was very proud of stating that no one else ever had that privilege as a lieutenant let alone a general or even a head of state.
There was talk that the army cantonment at Panagoda had been attacked and it was later confirmed that Gunner Beckmeyer had been killed by friendly fire at the panic and confusion that prevailed in the vicinity of the artillery officers mess. If there really was an insurgent attack on the cantonment is unknown to me. There were many unconfirmed reports of police stations being withdrawn or taken over by the JVP.
That afternoon the two volunteer platoons arrived in Hambantota under the command of Lt Alfred Wijesuriya and Lt Gallapatti. The meeting was not a cordial one as Lt Wijesuriya refused to take orders from me. I was taken aback at his decision and was also not impressed by the beret he wore, one worn by the French Resistance fighters. He insisted that he was to report to the GA to which I responded by taking him to the wireless set and contacted Capt Samarakoon who once again confirmed that I was in charge; and the Supreme Commander, protocol was, though senior in age and equal in rank I was his senior by virtue of being a regular officer.
A few hours later we made plans to proceed to Tissamaharama. Before I left the Divisional Revenue Officer came up to me with a glass of gin and tonic saying that he might never see me alive again. Tired as I was I had to refuse his kind offer. He was wrong, there was no opposition whatsoever. It was ghost town with hardly a person in sight. The town had not been taken over but simply abandoned and untouched since the police had withdrawn. Having reached the main town square I drove past the town to see if the areas ahead were safe and secure whilst the volunteer troops had alighted from their vehicles.
On my return I was shocked to see some volunteer troops and a few policeman looting the shops. They had in their hands bales of cloth and whatever was worthwhile. I told Lt Wijesuriya that his men were looting to which he replied that ‘Let them take what they want’. This was something I could not tolerate and I reacted by cocking my sterling sub machine gun and shouting out that “I would shoot anybody who did not return the goods they had taken;” they all responded by walking back to the shops that had been broken into and replaced the goods.
Among them was a police driver whom I knew as a youngster. He o had worked with my father was sheepishly returning the cash box still intact with the money inside. Soon after the chairman of the Town council appeared on the scene whose cooperation I sought to seal the doors of the shops broken into. An incident like this did not augur well, as proved subsequently with the murder of the local beauty queen.
Having done that we drove to the Tissa police station where the two volunteer unit platoons were to take up positions that night They appeared to be inexperienced and lacking in basic military skills. I suppose it was the first time that they were deployed in this role as the volunteers would have in the past been used in noncombatant roles of static guards providing security to key installations. This was a different scenario as it was an attacking unconventional force we were encountering.
firozm@optusnet.com.au
Features
Crucial test for religious and ethnic harmony in Bangladesh

 Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
Will the Bangladesh parliamentary election bring into being a government that will ensure ethnic and religious harmony in the country? This is the poser on the lips of peace-loving sections in Bangladesh and a principal concern of those outside who mean the country well.
The apprehensions are mainly on the part of religious and ethnic minorities. The parliamentary poll of February 12th is expected to bring into existence a government headed by the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) and the Islamist oriented Jamaat-e-Islami party and this is where the rub is. If these parties win, will it be a case of Bangladesh sliding in the direction of a theocracy or a state where majoritarian chauvinism thrives?
Chief of the Jamaat, Shafiqur Rahman, who was interviewed by sections of the international media recently said that there is no need for minority groups in Bangladesh to have the above fears. He assured, essentially, that the state that will come into being will be equable and inclusive. May it be so, is likely to be the wish of those who cherish a tension-free Bangladesh.
The party that could have posed a challenge to the above parties, the Awami League Party of former Prime Minister Hasina Wased, is out of the running on account of a suspension that was imposed on it by the authorities and the mentioned majoritarian-oriented parties are expected to have it easy at the polls.
A positive that has emerged against the backdrop of the poll is that most ordinary people in Bangladesh, be they Muslim or Hindu, are for communal and religious harmony and it is hoped that this sentiment will strongly prevail, going ahead. Interestingly, most of them were of the view, when interviewed, that it was the politicians who sowed the seeds of discord in the country and this viewpoint is widely shared by publics all over the region in respect of the politicians of their countries.
Some sections of the Jamaat party were of the view that matters with regard to the orientation of governance are best left to the incoming parliament to decide on but such opinions will be cold comfort for minority groups. If the parliamentary majority comes to consist of hard line Islamists, for instance, there is nothing to prevent the country from going in for theocratic governance. Consequently, minority group fears over their safety and protection cannot be prevented from spreading.
Therefore, we come back to the question of just and fair governance and whether Bangladesh’s future rulers could ensure these essential conditions of democratic rule. The latter, it is hoped, will be sufficiently perceptive to ascertain that a Bangladesh rife with religious and ethnic tensions, and therefore unstable, would not be in the interests of Bangladesh and those of the region’s countries.
Unfortunately, politicians region-wide fall for the lure of ethnic, religious and linguistic chauvinism. This happens even in the case of politicians who claim to be democratic in orientation. This fate even befell Bangladesh’s Awami League Party, which claims to be democratic and socialist in general outlook.
We have it on the authority of Taslima Nasrin in her ground-breaking novel, ‘Lajja’, that the Awami Party was not of any substantial help to Bangladesh’s Hindus, for example, when violence was unleashed on them by sections of the majority community. In fact some elements in the Awami Party were found to be siding with the Hindus’ murderous persecutors. Such are the temptations of hard line majoritarianism.
In Sri Lanka’s past numerous have been the occasions when even self-professed Leftists and their parties have conveniently fallen in line with Southern nationalist groups with self-interest in mind. The present NPP government in Sri Lanka has been waxing lyrical about fostering national reconciliation and harmony but it is yet to prove its worthiness on this score in practice. The NPP government remains untested material.
As a first step towards national reconciliation it is hoped that Sri Lanka’s present rulers would learn the Tamil language and address the people of the North and East of the country in Tamil and not Sinhala, which most Tamil-speaking people do not understand. We earnestly await official language reforms which afford to Tamil the dignity it deserves.
An acid test awaits Bangladesh as well on the nation-building front. Not only must all forms of chauvinism be shunned by the incoming rulers but a secular, truly democratic Bangladesh awaits being licked into shape. All identity barriers among people need to be abolished and it is this process that is referred to as nation-building.
On the foreign policy frontier, a task of foremost importance for Bangladesh is the need to build bridges of amity with India. If pragmatism is to rule the roost in foreign policy formulation, Bangladesh would place priority to the overcoming of this challenge. The repatriation to Bangladesh of ex-Prime Minister Hasina could emerge as a steep hurdle to bilateral accord but sagacious diplomacy must be used by Bangladesh to get over the problem.
A reply to N.A. de S. Amaratunga
A response has been penned by N.A. de S. Amaratunga (please see p5 of ‘The Island’ of February 6th) to a previous column by me on ‘ India shaping-up as a Swing State’, published in this newspaper on January 29th , but I remain firmly convinced that India remains a foremost democracy and a Swing State in the making.
If the countries of South Asia are to effectively manage ‘murderous terrorism’, particularly of the separatist kind, then they would do well to adopt to the best of their ability a system of government that provides for power decentralization from the centre to the provinces or periphery, as the case may be. This system has stood India in good stead and ought to prove effective in all other states that have fears of disintegration.
Moreover, power decentralization ensures that all communities within a country enjoy some self-governing rights within an overall unitary governance framework. Such power-sharing is a hallmark of democratic governance.
Features
Celebrating Valentine’s Day …

 Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
Valentine’s Day is all about celebrating love, romance, and affection, and this is how some of our well-known personalities plan to celebrate Valentine’s Day – 14th February:
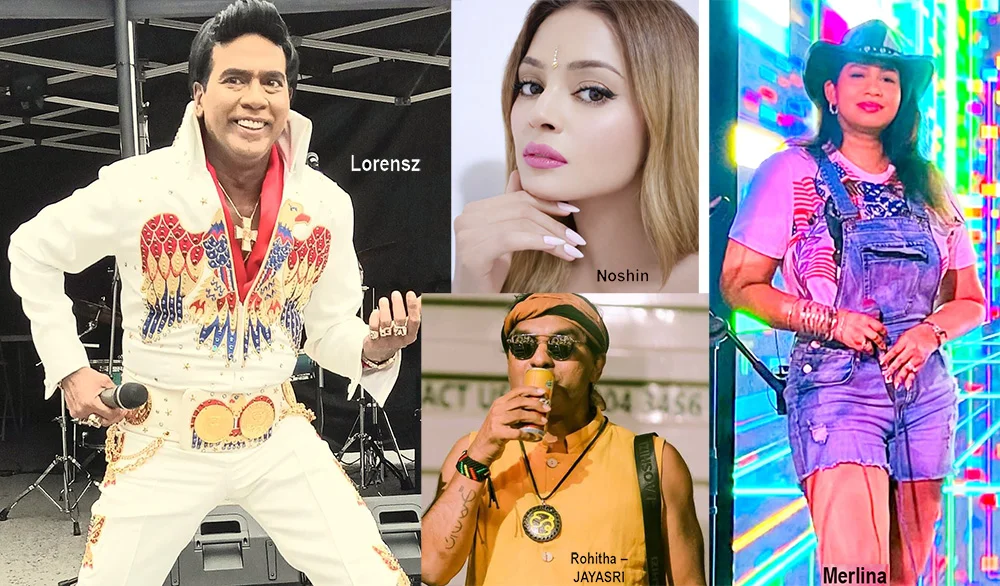
Merlina Fernando (Singer)
Yes, it’s a special day for lovers all over the world and it’s even more special to me because 14th February is the birthday of my husband Suresh, who’s the lead guitarist of my band Mission.
We have planned to celebrate Valentine’s Day and his Birthday together and it will be a wonderful night as always.
We will be having our fans and close friends, on that night, with their loved ones at Highso – City Max hotel Dubai, from 9.00 pm onwards.
Lorensz Francke (Elvis Tribute Artiste)
On Valentine’s Day I will be performing a live concert at a Wealthy Senior Home for Men and Women, and their families will be attending, as well.
I will be performing live with romantic, iconic love songs and my song list would include ‘Can’t Help falling in Love’, ‘Love Me Tender’, ‘Burning Love’, ‘Are You Lonesome Tonight’, ‘The Wonder of You’ and ‘’It’s Now or Never’ to name a few.
To make Valentine’s Day extra special I will give the Home folks red satin scarfs.
Emma Shanaya (Singer)
I plan on spending the day of love with my girls, especially my best friend. I don’t have a romantic Valentine this year but I am thrilled to spend it with the girl that loves me through and through. I’ll be in Colombo and look forward to go to a cute cafe and spend some quality time with my childhood best friend Zulha.
JAYASRI
Emma-and-Maneeka
This Valentine’s Day the band JAYASRI we will be really busy; in the morning we will be landing in Sri Lanka, after our Oman Tour; then in the afternoon we are invited as Chief Guests at our Maris Stella College Sports Meet, Negombo, and late night we will be with LineOne band live in Karandeniya Open Air Down South. Everywhere we will be sharing LOVE with the mass crowds.
Kay Jay (Singer)
I will stay at home and cook a lovely meal for lunch, watch some movies, together with Sanjaya, and, maybe we go out for dinner and have a lovely time. Come to think of it, every day is Valentine’s Day for me with Sanjaya Alles.
Maneka Liyanage (Beauty Tips)
On this special day, I celebrate love by spending meaningful time with the people I cherish. I prepare food with love and share meals together, because food made with love brings hearts closer. I enjoy my leisure time with them — talking, laughing, sharing stories, understanding each other, and creating beautiful memories. My wish for this Valentine’s Day is a world without fighting — a world where we love one another like our own beloved, where we do not hurt others, even through a single word or action. Let us choose kindness, patience, and understanding in everything we do.
Janaka Palapathwala (Singer)

Janaka
Valentine’s Day should not be the only day we speak about love.
From the moment we are born into this world, we seek love, first through the very drop of our mother’s milk, then through the boundless care of our Mother and Father, and the embrace of family.
Love is everywhere. All living beings, even plants, respond in affection when they are loved.
As we grow, we learn to love, and to be loved. One day, that love inspires us to build a new family of our own.
Love has no beginning and no end. It flows through every stage of life, timeless, endless, and eternal.
Natasha Rathnayake (Singer)
We don’t have any special plans for Valentine’s Day. When you’ve been in love with the same person for over 25 years, you realise that love isn’t a performance reserved for one calendar date. My husband and I have never been big on public displays, or grand gestures, on 14th February. Our love is expressed quietly and consistently, in ordinary, uncelebrated moments.
With time, you learn that love isn’t about proving anything to the world or buying into a commercialised idea of romance—flowers that wilt, sweets that spike blood sugar, and gifts that impress briefly but add little real value. In today’s society, marketing often pushes the idea that love is proven by how much money you spend, and that buying things is treated as a sign of commitment.
Real love doesn’t need reminders or price tags. It lives in showing up every day, choosing each other on unromantic days, and nurturing the relationship intentionally and without an audience.
This isn’t a judgment on those who enjoy celebrating Valentine’s Day. It’s simply a personal choice.
Melloney Dassanayake (Miss Universe Sri Lanka 2024)
 I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I truly believe it’s beautiful to have a day specially dedicated to love. But, for me, Valentine’s Day goes far beyond romantic love alone. It celebrates every form of love we hold close to our hearts: the love for family, friends, and that one special person who makes life brighter. While 14th February gives us a moment to pause and celebrate, I always remind myself that love should never be limited to just one day. Every single day should feel like Valentine’s Day – constant reminder to the people we love that they are never alone, that they are valued, and that they matter.
I’m incredibly blessed because, for me, every day feels like Valentine’s Day. My special person makes sure of that through the smallest gestures, the quiet moments, and the simple reminders that love lives in the details. He shows me that it’s the little things that count, and that love doesn’t need grand stages to feel extraordinary. This Valentine’s Day, perfection would be something intimate and meaningful: a cozy picnic in our home garden, surrounded by nature, laughter, and warmth, followed by an abstract drawing session where we let our creativity flow freely. To me, that’s what love is – simple, soulful, expressive, and deeply personal. When love is real, every ordinary moment becomes magical.
Noshin De Silva (Actress)
Valentine’s Day is one of my favourite holidays! I love the décor, the hearts everywhere, the pinks and reds, heart-shaped chocolates, and roses all around. But honestly, I believe every day can be Valentine’s Day.
It doesn’t have to be just about romantic love. It’s a chance to celebrate love in all its forms with friends, family, or even by taking a little time for yourself.
Whether you’re spending the day with someone special or enjoying your own company, it’s a reminder to appreciate meaningful connections, show kindness, and lead with love every day.
And yes, I’m fully on theme this year with heart nail art and heart mehendi design!
Wishing everyone a very happy Valentine’s Day, but, remember, love yourself first, and don’t forget to treat yourself.
Sending my love to all of you.
Features
Banana and Aloe Vera
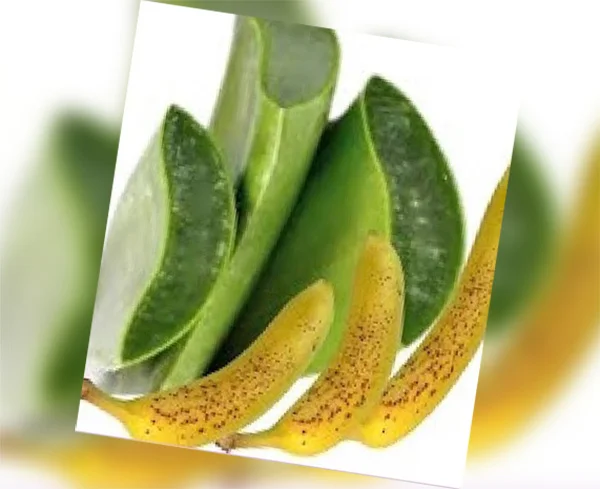

 To create a powerful, natural, and hydrating beauty mask that soothes inflammation, fights acne, and boosts skin radiance, mix a mashed banana with fresh aloe vera gel.
To create a powerful, natural, and hydrating beauty mask that soothes inflammation, fights acne, and boosts skin radiance, mix a mashed banana with fresh aloe vera gel.
This nutrient-rich blend acts as an antioxidant-packed anti-ageing treatment that also doubles as a nourishing, shiny hair mask.
* Face Masks for Glowing Skin:
Mix 01 ripe banana with 01 tablespoon of fresh aloe vera gel and apply this mixture to the face. Massage for a few minutes, leave for 15-20 minutes, and then rinse off for a glowing complexion.
* Acne and Soothing Mask:
Mix 01 tablespoon of fresh aloe vera gel with 1/2 a mashed banana and 01 teaspoon of honey. Apply this mixture to clean skin to calm inflammation, reduce redness, and hydrate dry, sensitive skin. Leave for 15-20 minutes, and rinse with warm water.
* Hair Treatment for Shine:
Mix 01 fresh ripe banana with 03 tablespoons of fresh aloe vera gel and 01 teaspoon of honey. Apply from scalp to ends, massage for 10-15 minutes and then let it dry for maximum absorption. Rinse thoroughly with cool water for soft, shiny, and frizz-free hair.
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoMy experience in turning around the Merchant Bank of Sri Lanka (MBSL) – Episode 3
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoZone24x7 enters 2026 with strong momentum, reinforcing its role as an enterprise AI and automation partner
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoRemotely conducted Business Forum in Paris attracts reputed French companies
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoFour runs, a thousand dreams: How a small-town school bowled its way into the record books
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoComBank and Hayleys Mobility redefine sustainable mobility with flexible leasing solutions
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoHNB recognized among Top 10 Best Employers of 2025 at the EFC National Best Employer Awards
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoGREAT 2025–2030: Sri Lanka’s Green ambition meets a grid reality check
















