Features
Constitutions and amendments
By Neville Ladduwahetty
The 20th Amendment (20A) to the Constitution has become a topic of spirited debate and discussion. Much of it is generated by misunderstanding the true intent of 20A. It should not be a durable amendment to the Constitution. Instead, it should be temporary, until a comprehensive new Constitution is developed and presented to the nation.
Until then, 20A should serve as a stop gap for the Executive President to address the unprecedented challenges the country has to face following the COVID-19 pandemic. With this in mind, the intent of 20A should be to either repeal those provisions that had been introduced by the 19th Amendment to seriously dilute executive powers as admitted by the framers of 19A or to repeal 19A altogether and restore the executive powers the President had under the 1978 Constitution. It is only by removing the constraints that exist under 19A that the President would be in a position to address the daunting challenges that lie ahead. Without strengthening the hand of the Executive, the formidable task of social and economic recovery that the country is compelled to face because of the global pandemic would be a near impossibility.
THE NEED for 20A
The two most formidable issues that should engage the full attention of the government and the nation are:
(1) The need to continue with the very effective measures adopted to contain COVID-19 in order to prevent the possibility of a resurgance.
(2) The absolute urgency to revive the seriously depressed economy, brought about nationally and globally by the pandemic.
As far as the first issue is concerned, the government has demonstrated very effectively that it has the capabilities and organizing abilities to implement procedures and practices to maintain the health of the nation to such a degree that the President and the Sri Lankan nation have received international acclaim. An equally encouraging aspect is the support extended by the public to the call of the government to practice the health safeguards recommended by the government. What the government and the nation have collectively achieved is a shining example to the world for which we as a nation could be proud of.
The elephant in the room is how to revive the depressed economy. While the measures that need to be adopted are bound to test the skills and ingenuities of the entire nation, an equally important factor that would have a direct bearing is the freedom for the government, in particular the President and the executive branch, to act without being constrained by the fetters introduced by 19A.
There is no denying the fact that 19A was introduced with the deliberate intent of diluting executive powers of the President. In fact, Dr. Jayampathy Wickramaratne P.C., (Dr. JW) referring to 19A, has admitted that the initial attempt was “to completely abolish the Presidential system of government”. This attempt failed because the Supreme Court ruled that the intended attempt would require a referendum. The end result was the compromised version of 19A. According to Dr. JW, “The experience under 19A clearly showed the need to completely abolish the Presidential form of government and move towards a Parliamentary form…” (The Island, September 8, 2020).
The approach should not be to analyze which Article should be amended and to what degree, since such an exercise would not only be time consuming but also would add to the confusion that already exists in 19A. Instead, the approach should be to undo the entirety of 19A, and for the executive power of the President that had existed under the 1978 Constitution to be restored, for the simple reason that tough measures are needed to overcome the economic black hole Sri Lanka is in, the likes of which the nation as a whole has never seen.
The argument that such an approach would restore what is often described as draconian executive power amounting to a Presidential dictatorship that had existed under the 1978 Constitution, is unfounded if one realizes the full impact of the economic catastrophe the nation is currently facing. The situation is so dire that the bulk of the nation is more concerned with the basics of existence and survival rather than about niceties of Democracy and Good Governance that only the fortunate few could afford to be concerned about.
THE NEED for a NEW CONSTITUTION
Having addressed the short term issues, the next is the long term issue of a new Constitution. The genesis for 19A and 20A is the 1978 Constitution. Therefore, any anomalies and contradictions that exist in amendments invariably are a result of anomalies and contradictions in the 1978 Constitution. Describing the system of government under the 1978 Constitution, Dr. JW quotes Dr. Colvin R. De Silva as having described the 1978 Constitution “as a constitutional presidential dictatorship dressed in the raiment of a parliamentary democracy’ (Ibid). The comment is justified because the 1978 Constitution has features of Presidential and Parliamentary systems, notwithstanding that each represents one of the two ideologically completely different systems of government by which practically all democracies are governed. If such contrasting systems are incorporated in a single constitution confusion is inevitable, as evident from the 1978 Constitution and its related amendments. Therefore, the framers of a new constitution should endeavour to base it on either one or the other, a Presidential or a Parliamentary system, but certainly not a mix of both.
PARLIAMENTARY and PRESIDENTIAL
FORMS of GOVERNMENT
Under a Parliamentary system, Parliament is supreme and as described in the 1972 Constitution is the “supreme instrument of State Power”. This means that Parliament is responsible for Legislative and Executive functions. A few members of Parliament are selected by the Prime Minister to form the Cabinet of Ministers to exercise the executive functions of the government. Consequently, the Cabinet of Ministers is responsible and answerable to Parliament.
On the other hand, under a Presidential system, the cardinal principle is the separation of Legislative and Executive power. This separation is underscored by the fact that each branch is separately elected by the people and responsible for the exercise of separate powers, namely Legislative and Executive. This separation is clearly outlined in Articles 4 (a) and 4 (b) respectively, of the 1978 Constitution.
Article 4 (a) states: “the legislative power of the People shall be exercised by parliament…”.
Article 4 (b) states: “the executive power of the People, including the defence of Sri Lanka, shall be exercised by the President…”.
Commenting on the executive power of the people, the Supreme Court in S.D. No. 04/2015 stated: “It is in this background that the Court in the Nineteenth Amendment Determination came to a conclusion that the transfer, relinquishment or removal of the power attributed to one organ of government to another organ or body would be inconsistent with Article 3 read with Article 4 of the Constitution. Though Article 4 provides the form and manner of the sovereignty of the people, the ultimate act or decision of the executive functions must be retained by the President. So long as the President remains the Head of the Executive, the exercise of his powers remain supreme or sovereign in the executive field and to others to whom such power is given must derive the authority from the President or exercise the Executive power vested in the President as a delegate of the President”.
On the other hand, Article 43 (1) states: “There shall be a Cabinet of Ministers charged with the direction and control of the Government of the Republic which shall be collectively responsible and answerable to Parliament”.
Commenting on Article 43 (1) the Supreme Court in the same case, S.D. No. 04/2015 stated: “This important Article underscores that the Cabinet collectively is charged with the exercise of Executive power, which is expressed as the direction and control of the Government of the Republic and the collective responsibility of Cabinet of which the President is the Head. It establishes conclusively that the President is not the sole repository of Executive power under the Constitution. It is the Cabinet of Ministers collectively, and not the President alone, which is charged with the direction and control of the Government.
This Cabinet is answerable to Parliament. Therefore, the Constitution itself recognizes that Executive power is exercised by the President and by the Cabinet of Ministers, and that the President shall be responsible to Parliament and the Cabinet of Ministers, collectively responsible and answerable to Parliament with regard to the exercise of such powers…”.
It is evident from the opinions cited above that the powers of the President depend on whether he acts under provisions of Article 4 (b) or Article 43 (1). For instance, under provisions of 4 (b) the “President as the Head of the Executive is sovereign in the executive field”. However, if the President acts under provisions of Article 43 (1) the Court stated that “the Constitution itself recognizes that Executive power is exercised by the President and by the Cabinet of Ministers”. The potential for such contrasting interpretations that exist in the 1978 Constitution have been blindly repeated in 19A without regard for their relevance or irrelevance.
Another serious contradiction often overlooked is that a President elected by the People should be recognized as being co-equal with Parliament under provisions of separation of power. Therefore, the President cannot be responsible to another organ of government– the Parliament. Furthermore, if the Cabinet of Ministers derive their authority from the President as interpreted by the Supreme Court, the Cabinet cannot be responsible and answerable to Parliament either. Under the circumstances, Article 33A that calls for the President to be responsible to Parliament “for the due exercise performance and discharge of his powers, duties and functions” is a violation of the principle of separation of power.
The few examples cited above amply demonstrate that while the framework of the 1978 Constitution is essentially Presidential, it has sufficient elements of a Parliamentary Democracy to warrant the Judiciary from giving contrasting opinions depending on which Article it interprets. This ambiguity requires Sri Lanka to adopt either a Presidential or a Parliamentary system, but not a mix of both systems. Despite the fact that such contradictions have been brought to the attention of the public, confusion has reigned uninterrupted. Therefore, the need is for Parliament to vote on which system of government is best suited to govern Sri Lanka. Furthermore, when formulating a new constitution, it is also recommended that a fresh approach be incorporated to devolve power to the smallest practical workable unit in order to strengthen operations in the periphery.
CONCLUSION
According to media reports the intention of the government is to introduce the 20th Amendment. Indications are that each Article would be reviewed and amended where necessary. Such an exercise is bound to repeat the contradictions in 19A because the framers mechanically copied provisions from the 1978 Constitution without understanding what separation of power is all about in a Presidential system. Therefore, it is best to repeal 19A completely, and go back to the powers exercised by the President under the 1978 Constitution as a stop gap measure until a new constitution is formulated. Such an interim measure is vital in order to prevent a resurgence of COVID-19 and to equip the executive with necessary powers to revive the depressed economy.
Critics to such an approach may consider it to be the death knell to Parliamentary democracy. What such critics forget is that the country is in such dire straits economically, that drastic measures need to be introduced if the country is to get back to some degree of normalcy. Proof of the merits of such an approach is evident from the uncompromising measures successfully adopted by the government to contain COVID-19; a fact acknowledged internationally. The reversal to the past is intended to be only until such time that a new constitution is tabled and adopted by Parliament and the People at a referendum.
In summary, the essence of the recommendation is for the 20A to define a clear two-step approach. Step One is to repeal all of 19A and strengthen the hand of the President and the executive with necessary powers to address all issues relating to COVID-19, and to also adopt all necessary measures to revive the economy. Step Two is for Parliament to vote and give clear direction as to whether the new constitution should be based on a Presidential or Parliamentary system to address all issues relating to good governance in all respects. Adopting such a clear cut approach without ambiguities would enable Sri Lanka to be free of the current fog of confusion, and embark on a fresh Chapter in her history.
Features
The invisible crisis: How tour guide failures bleed value from every tourist

 (Article 04 of the 04-part series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation)
(Article 04 of the 04-part series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation)
If you want to understand why Sri Lanka keeps leaking value even when arrivals hit “record” numbers, stop staring at SLTDA dashboards and start talking to the people who face tourists every day: the tour guides.
They are the “unofficial ambassadors” of Sri Lankan tourism, and they are the weakest, most neglected, most dysfunctional link in a value chain we pretend is functional. Nearly 60% of tourists use guides. Of those guides, 57% are unlicensed, untrained, and invisible to the very institutions claiming to regulate quality. This is not a marginal problem. It is a systemic failure to bleed value from every visitor.
The Invisible Workforce
The May 2024 “Comprehensive Study of the Sri Lankan Tour Guides” is the first serious attempt, in decades, to map this profession. Its findings should be front-page news. They are not, because acknowledging them would require admitting how fundamentally broken the system is. The official count (April 2024): SLTDA had 4,887 licensed guides in its books:
* 1,892 National Guides (39%)
* 1,552 Chauffeur Guides (32%)
* 1,339 Area Guides (27%)
* 104 Site Guides (2%)
The actual workforce: Survey data reveals these licensed categories represent only about 75% of people actually guiding tourists. About 23% identify as “other”; a polite euphemism for unlicensed operators: three-wheeler drivers, “surf boys,” informal city guides, and touts. Adjusted for informal operators, the true guide population is approximately 6,347; 32% National, 25% Chauffeur, 16% Area, 4% Site, and 23% unlicensed.
But even this understates reality. Industry practitioners interviewed in the study believe the informal universe is larger still, with unlicensed guides dominating certain tourist hotspots and price-sensitive segments. Using both top-down (tourist arrivals × share using guides) and bottom-up (guides × trips × party size) estimates, the study calculates that approximately 700,000 tourists used guides in 2023-24, roughly one-third of arrivals. Of those 700,000 tourists, 57% were handled by unlicensed guides.
Read that again. Most tourists interacting with guides are served by people with no formal training, no regulatory oversight, no quality standards, and no accountability. These are the “ambassadors” shaping visitor perceptions, driving purchasing decisions, and determining whether tourists extend stays, return, or recommend Sri Lanka. And they are invisible to SLTDA.
The Anatomy of Workforce Failure
The guide crisis is not accidental. It is the predictable outcome of decades of policy neglect, regulatory abdication, and institutional indifference.
1. Training Collapse and Barrier to Entry Failure
Becoming a licensed National Guide theoretically requires:
* Completion of formal training programmes
* Demonstrated language proficiency
* Knowledge of history, culture, geography
* Passing competency exams
In practice, these barriers have eroded. The study reveals:
* Training infrastructure is inadequate and geographically concentrated
* Language requirements are inconsistently enforced
* Knowledge assessments are outdated and poorly calibrated
* Continuous professional development is non-existent
The result: even licensed guides often lack the depth of knowledge, language skills, or service standards that high-yield tourists expect. Unlicensed guides have no standards at all. Compare this to competitors. In Mauritius, tour guides undergo rigorous government-certified training with mandatory refresher courses. The Maldives’ resort model embeds guide functions within integrated hospitality operations with strict quality controls. Thailand has well-developed private-sector training ecosystems feeding into licensed guide pools.
2. Economic Precarity and Income Volatility
Tour guiding in Sri Lanka is economically unstable:
* Seasonal income volatility: High earnings in peak months (December-March), near-zero in low season (April-June, September)
* No fixed salaries: Most guides work freelance or commission-based
* Age and experience don’t guarantee income: 60% of guides are over 40, but earnings decline with age due to physical demands and market preference for younger, language-proficient guides
* Commission dependency: Guides often earn more from commissions on shopping, gem purchases, and restaurant referrals than from guiding fees
The commission-driven model pushes guides to prioritise high-commission shops over meaningful experiences, leaving tourists feeling manipulated. With low earnings and poor incentives, skilled guides exist in the profession while few new entrants join. The result is a shrinking pool of struggling licensed guides and rising numbers of opportunistic unlicensed operators.
3. Regulatory Abdication and Unlicensed Proliferation
Unlicensed guides thrive because enforcement is absent, economic incentives favour avoiding fees and taxes, and tourists cannot distinguish licensed professionals from informal operators. With SLTDA’s limited capacity reducing oversight, unregistered activity expands. Guiding becomes the frontline where regulatory failure most visibly harms tourist experience and sector revenues in Sri Lanka.
4. Male-Dominated, Ageing, Geographically Uneven Workforce
The guide workforce is:
* Heavily male-dominated: Fewer than 10% are women
* Ageing: 60% are over 40; many in their 50s and 60s
* Geographically concentrated: Clustered in Colombo, Galle, Kandy, Cultural Triangle—minimal presence in emerging destinations
This creates multiple problems:
* Gender imbalance: Limits appeal to female solo travellers and certain market segments (wellness tourism, family travel with mothers)
* Physical limitations: Older guides struggle with demanding itineraries (hiking, adventure tourism)
* Knowledge ossification: Ageing workforce with no continuous learning rehashes outdated narratives, lacks digital literacy, cannot engage younger tourist demographics
* Regional gaps: Emerging destinations (Eastern Province, Northern heritage sites) lack trained guide capacity
1. Experience Degradation Lower Spending
Unlicensed guides lack knowledge, language skills, and service training. Tourist experience degrades. When tourists feel they are being shuttled to commission shops rather than authentic experiences, they:
* Cut trips short
* Skip additional paid activities
* Leave negative reviews
* Do not return or recommend
The yield impact is direct: degraded experiences reduce spending, return rates, and word-of-mouth premium.

2. Commission Steering → Value Leakage
Guides earning more from commissions than guiding fees optimise for merchant revenue, not tourist satisfaction.
This creates leakage: tourism spending flows to merchants paying highest commissions (often with foreign ownership or imported inventory), not to highest-quality experiences.
The economic distortion is visible: gems, souvenirs, and low-quality restaurants generate guide commissions while high-quality cultural sites, local artisan cooperatives, and authentic restaurants do not. Spending flows to low-value, high-leakage channels.
3. Safety and Security Risks → Reputation Damage
Unlicensed guides have no insurance, no accountability, no emergency training. When tourists encounter problems, accidents, harassment, scams, there is no recourse. Incidents generate negative publicity, travel advisories, reputation damage. The 2024-2025 reports of tourists being attacked by wildlife at major sites (Sigiriya) with inadequate safety protocols are symptomatic. Trained, licensed guides would have emergency protocols. Unlicensed operators improvise.
4. Market Segmentation Failure → Yield Optimisation Impossible
High-yield tourists (luxury, cultural immersion, adventure) require specialised guide-deep knowledge, language proficiency, cultural sensitivity. Sri Lanka cannot reliably deliver these guides at scale because:
* Training does not produce specialists (wildlife experts, heritage scholars, wellness practitioners)
* Economic precarity drives talent out
* Unlicensed operators dominate price-sensitive segments, leaving limited licensed capacity for premium segments
We cannot move upmarket because we lack the workforce to serve premium segments. We are locked into volume-chasing low-yield markets because that is what our guide workforce can provide.
The way forward
Fixing Sri Lanka’s guide crisis demands structural reform, not symbolic gestures. A full workforce census and licensing audit must map the real guide population, identify gaps, and set an enforcement baseline. Licensing must be mandatory, timebound, and backed by inspections and penalties. Economic incentives should reward professionalism through fair wages, transparent fees, and verified registries. Training must expand nationwide with specialisations, language standards, and continuous development. Gender and age imbalances require targeted recruitment, mentorship, and diversified roles. Finally, guides must be integrated into the tourism value chain through mandatory verification, accountability measures, and performancelinked feedback.
The Uncomfortable Truth
Can Sri Lanka achieve high-value tourism with a low-quality, largely unlicensed guide workforce? The answer is NO. Unambiguously, definitively, NO. Sri Lanka’s guides shape tourist perceptions, spending, and satisfaction, yet the system treats them as expendable; poorly trained, economically insecure, and largely unregulated. With 57% of tourists relying on unlicensed guides, experience quality becomes unpredictable and revenue leaks into commission-driven channels.
High-yield markets avoid destinations with weak service standards, leaving Sri Lanka stuck in low-value, volume tourism. This is not a training problem but a structural failure requiring regulatory enforcement, viable career pathways, and a complete overhaul of incentives. Without professionalising guides, high-value tourism is unattainable. Fixing the guide crisis is the foundation for genuine sector transformation.
The choice is ours. The workforce is waiting.
This concludes the 04-part series on Sri Lanka’s tourism stagnation. The diagnosis is complete. The question now is whether policymakers have the courage to act.
For any concerns/comments contact the author at saliya.ca@gmail.com
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT, Malabe. The views and opinions expressed in this article are personal.)
Features
Recruiting academics to state universities – beset by archaic selection processes?

Time has, by and large, stood still in the business of academic staff recruitment to state universities. Qualifications have proliferated and evolved to be more interdisciplinary, but our selection processes and evaluation criteria are unchanged since at least the late 1990s. But before I delve into the problems, I will describe the existing processes and schemes of recruitment. The discussion is limited to UGC-governed state universities (and does not include recruitment to medical and engineering sectors) though the problems may be relevant to other higher education institutions (HEIs).
How recruitment happens currently in SL state universities
Academic ranks in Sri Lankan state universities can be divided into three tiers (subdivisions are not discussed).
* Lecturer (Probationary)
– recruited with a four-year undergraduate degree. A tiny step higher is the Lecturer (Unconfirmed), recruited with a postgraduate degree but no teaching experience.
* A Senior Lecturer can be recruited with certain postgraduate qualifications and some number of years of teaching and research.
* Above this is the professor (of four types), which can be left out of this discussion since only one of those (Chair Professor) is by application.
State universities cannot hire permanent academic staff as and when they wish. Prior to advertising a vacancy, approval to recruit is obtained through a mind-numbing and time-consuming process (months!) ending at the Department of Management Services. The call for applications must list all ranks up to Senior Lecturer. All eligible candidates for Probationary to Senior Lecturer are interviewed, e.g., if a Department wants someone with a doctoral degree, they must still advertise for and interview candidates for all ranks, not only candidates with a doctoral degree. In the evaluation criteria, the first degree is more important than the doctoral degree (more on this strange phenomenon later). All of this is only possible when universities are not under a ‘hiring freeze’, which governments declare regularly and generally lasts several years.
Problem type 1
– Archaic processes and evaluation criteria
Twenty-five years ago, as a probationary lecturer with a first degree, I was a typical hire. We would be recruited, work some years and obtain postgraduate degrees (ideally using the privilege of paid study leave to attend a reputed university in the first world). State universities are primarily undergraduate teaching spaces, and when doctoral degrees were scarce, hiring probationary lecturers may have been a practical solution. The path to a higher degree was through the academic job. Now, due to availability of candidates with postgraduate qualifications and the problems of retaining academics who find foreign postgraduate opportunities, preference for candidates applying with a postgraduate qualification is growing. The evaluation scheme, however, prioritises the first degree over the candidate’s postgraduate education. Were I to apply to a Faculty of Education, despite a PhD on language teaching and research in education, I may not even be interviewed since my undergraduate degree is not in education. The ‘first degree first’ phenomenon shows that universities essentially ignore the intellectual development of a person beyond their early twenties. It also ignores the breadth of disciplines and their overlap with other fields.
This can be helped (not solved) by a simple fix, which can also reduce brain drain: give precedence to the doctoral degree in the required field, regardless of the candidate’s first degree, effected by a UGC circular. The suggestion is not fool-proof. It is a first step, and offered with the understanding that any selection process, however well the evaluation criteria are articulated, will be beset by multiple issues, including that of bias. Like other Sri Lankan institutions, universities, too, have tribal tendencies, surfacing in the form of a preference for one’s own alumni. Nevertheless, there are other problems that are, arguably, more pressing as I discuss next. In relation to the evaluation criteria, a problem is the narrow interpretation of any regulation, e.g., deciding the degree’s suitability based on the title rather than considering courses in the transcript. Despite rhetoric promoting internationalising and inter-disciplinarity, decision-making administrative and academic bodies have very literal expectations of candidates’ qualifications, e.g., a candidate with knowledge of digital literacy should show this through the title of the degree!
Problem type 2 – The mess of badly regulated higher education
A direct consequence of the contemporary expansion of higher education is a large number of applicants with myriad qualifications. The diversity of degree programmes cited makes the responsibility of selecting a suitable candidate for the job a challenging but very important one. After all, the job is for life – it is very difficult to fire a permanent employer in the state sector.
Widely varying undergraduate degree programmes.
At present, Sri Lankan undergraduates bring qualifications (at times more than one) from multiple types of higher education institutions: a degree from a UGC-affiliated state university, a state university external to the UGC, a state institution that is not a university, a foreign university, or a private HEI aka ‘private university’. It could be a degree received by attending on-site, in Sri Lanka or abroad. It could be from a private HEI’s affiliated foreign university or an external degree from a state university or an online only degree from a private HEI that is ‘UGC-approved’ or ‘Ministry of Education approved’, i.e., never studied in a university setting. Needless to say, the diversity (and their differences in quality) are dizzying. Unfortunately, under the evaluation scheme all degrees ‘recognised’ by the UGC are assigned the same marks. The same goes for the candidates’ merits or distinctions, first classes, etc., regardless of how difficult or easy the degree programme may be and even when capabilities, exposure, input, etc are obviously different.
Similar issues are faced when we consider postgraduate qualifications, though to a lesser degree. In my discipline(s), at least, a postgraduate degree obtained on-site from a first-world university is preferable to one from a local university (which usually have weekend or evening classes similar to part-time study) or online from a foreign university. Elitist this may be, but even the best local postgraduate degrees cannot provide the experience and intellectual growth gained by being in a university that gives you access to six million books and teaching and supervision by internationally-recognised scholars. Unfortunately, in the evaluation schemes for recruitment, the worst postgraduate qualification you know of will receive the same marks as one from NUS, Harvard or Leiden.
The problem is clear but what about a solution?
Recruitment to state universities needs to change to meet contemporary needs. We need evaluation criteria that allows us to get rid of the dross as well as a more sophisticated institutional understanding of using them. Recruitment is key if we want our institutions (and our country) to progress. I reiterate here the recommendations proposed in ‘Considerations for Higher Education Reform’ circulated previously by Kuppi Collective:
* Change bond regulations to be more just, in order to retain better qualified academics.
* Update the schemes of recruitment to reflect present-day realities of inter-disciplinary and multi-disciplinary training in order to recruit suitably qualified candidates.
* Ensure recruitment processes are made transparent by university administrations.
Kaushalya Perera is a senior lecturer at the University of Colombo.
(Kuppi is a politics and pedagogy happening on the margins of the lecture hall that parodies, subverts, and simultaneously reaffirms social hierarchies.)
Features
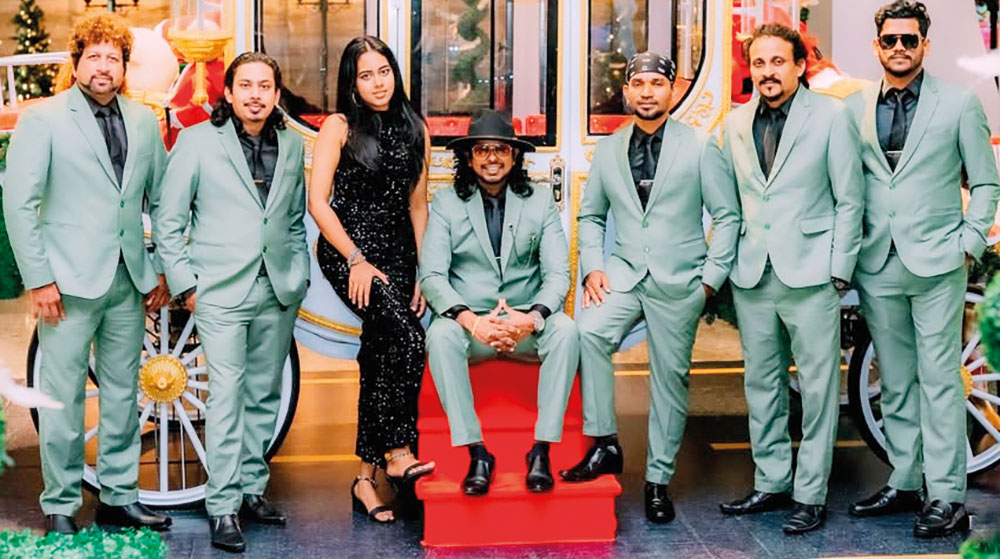
Talento … oozing with talent

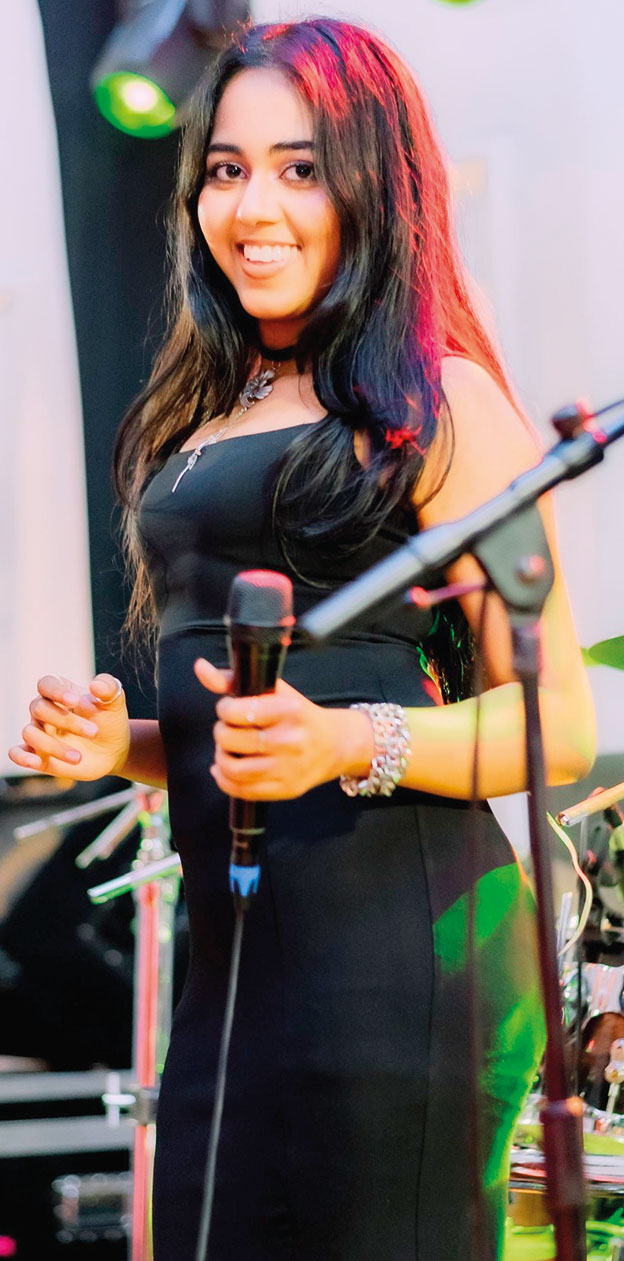
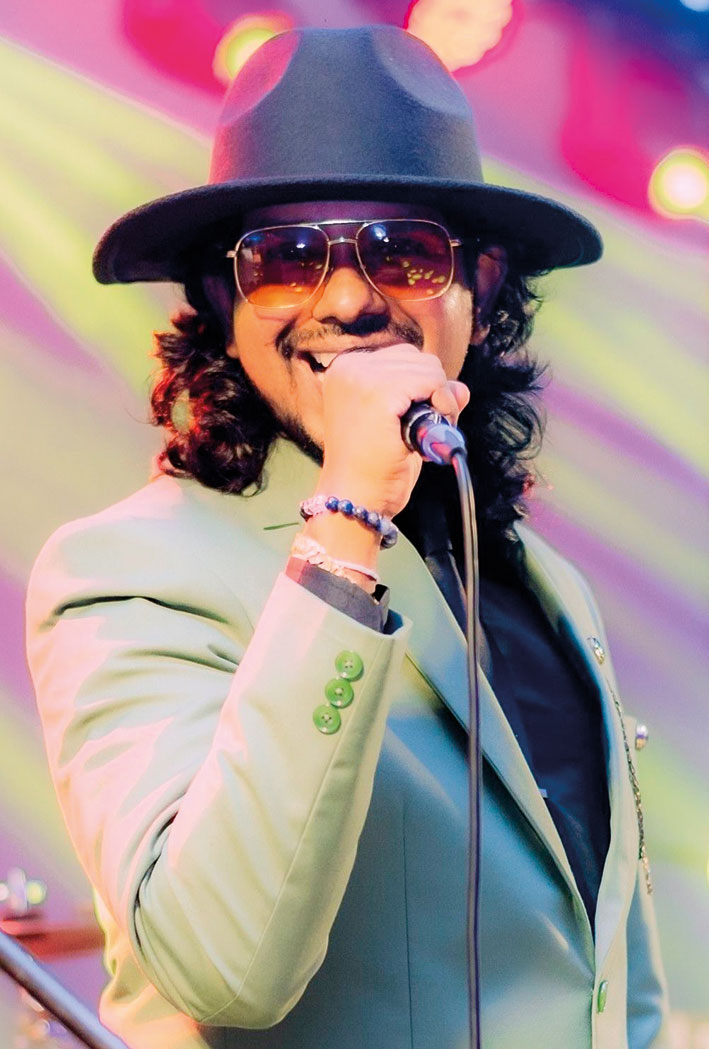
 This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
This week, too, the spotlight is on an outfit that has gained popularity, mainly through social media.
Last week we had MISTER Band in our scene, and on 10th February, Yellow Beatz – both social media favourites.
Talento is a seven-piece band that plays all types of music, from the ‘60s to the modern tracks of today.
The band has reached many heights, since its inception in 2012, and has gained recognition as a leading wedding and dance band in the scene here.
The members that makeup the outfit have a solid musical background, which comes through years of hard work and dedication
Their portfolio of music contains a mix of both western and eastern songs and are carefully selected, they say, to match the requirements of the intended audience, occasion, or event.
Although the baila is a specialty, which is inherent to this group, that originates from Moratuwa, their repertoire is made up of a vast collection of love, classic, oldies and modern-day hits.
The musicians, who make up Talento, are:
Prabuddha Geetharuchi:
(Vocalist/ Frontman). He is an avid music enthusiast and was mentored by a lot of famous musicians, and trainers, since he was a child. Growing up with them influenced him to take on western songs, as well as other music styles. A Peterite, he is the main man behind the band Talento and is a versatile singer/entertainer who never fails to get the crowd going.
Geilee Fonseka (Vocals):
A dynamic and charismatic vocalist whose vibrant stage presence, and powerful voice, bring a fresh spark to every performance. Young, energetic, and musically refined, she is an artiste who effortlessly blends passion with precision – captivating audiences from the very first note. Blessed with an immense vocal range, Geilee is a truly versatile singer, confidently delivering Western and Eastern music across multiple languages and genres.
Chandana Perera (Drummer):
His expertise and exceptional skills have earned him recognition as one of the finest acoustic drummers in Sri Lanka. With over 40 tours under his belt, Chandana has demonstrated his dedication and passion for music, embodying the essential role of a drummer as the heartbeat of any band.
Harsha Soysa:
(Bassist/Vocalist). He a chorister of the western choir of St. Sebastian’s College, Moratuwa, who began his musical education under famous voice trainers, as well as bass guitar trainers in Sri Lanka. He has also performed at events overseas. He acts as the second singer of the band
Udara Jayakody:
(Keyboardist). He is also a qualified pianist, adding technical flavour to Talento’s music. His singing and harmonising skills are an extra asset to the band. From his childhood he has been a part of a number of orchestras as a pianist. He has also previously performed with several famous western bands.
Aruna Madushanka:
(Saxophonist). His proficiciency in playing various instruments, including the saxophone, soprano saxophone, and western flute, showcases his versatility as a musician, and his musical repertoire is further enhanced by his remarkable singing ability.
Prashan Pramuditha:
(Lead guitar). He has the ability to play different styles, both oriental and western music, and he also creates unique tones and patterns with the guitar..
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoJamming and re-setting the world: What is the role of Donald Trump?
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoAn innocent bystander or a passive onlooker?
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoRatmalana Airport: The Truth, The Whole Truth, And Nothing But The Truth
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoIRCSL transforms Sri Lanka’s insurance industry with first-ever Centralized Insurance Data Repository
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoAn efficacious strategy to boost exports of Sri Lanka in medium term
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoOverseas visits to drum up foreign assistance for Sri Lanka
















