Foreign News
Bloody siege ends Myanmar army control of western border

The end, when it came for the BGP5 barracks, was loud and brutal. First, a crackly speaker calling out for their surrender; then, a thunderous barrage of artillery, rockets and rifle fire that tore chunks out of the buildings in which hundreds of soldiers were hiding.
BGP5 – the letters stand for Border Guard Police – was the Myanmar military junta’s last stand in northern Rakhine State, which lies along the border with Bangladesh.
Video by the insurgent Arakan Army (AA) which was besieging the base shows their rag-tag fighters, many barefoot, firing an assortment of weapons into the base, while air force jets roar over their heads.
It was a ferocious battle – perhaps the bloodiest of the civil war which has consumed Myanmar since the military seized power in a coup in 2021.
“They had dug deep ditches filled with spikes around the base,” an AA source told the BBC. “There were bunkers and reinforced buildings. They laid more than a thousand mines. Many of our fighters lost limbs, or their lives, trying to get through.”
For the coup leader, General Min Aung Hlaing, this has been yet another humiliating defeat after a year of military setbacks.
For the first time his regime has lost control of an entire border: the 270km (170 miles) dividing Myanmar from Bangladesh now wholly under AA control.
And with only the Rakhine State capital Sittwe still firmly in military hands, though cut off from the rest of the country, the AA is likely to be the first insurgent group to take complete control of a state.
The army has been in headlong retreat from the Arakan Army since the beginning of the year, losing town after town.
The last army units withdrew in September to BGP5, a compound covering around 20 hectares just outside the border town of Maungdaw, where the AA laid siege.
BGP5 was built on the site of a Muslim Rohingya village, Myo Thu Gyi, which was burned down during the violent expulsion of much of the Rohingya population by the armed forces in 2017.
It was the first of many burned villages I saw on a visit to Maungdaw right after the military operation in September of that year, a mass of charred debris in among the lush tropical vegetation, its inhabitants killed or forced to flee to Bangladesh.
When I returned two years later, the new police complex had already been built, with all the trees removed, giving defenders a clear view of any attacking force.
The AA source told us their advance towards it was painfully slow, requiring the insurgents to dig their own ditches for cover.
It does not publish its own casualties. But judging from the intensity of fighting in Maungdaw, which began in June, it is likely to have lost hundreds of its own troops.
Throughout the siege, the Myanmar air force kept up a constant bombardment of Maungdaw, driving the last civilians out of the town.
Its planes dropped supplies to the besieged soldiers at night, but it was never enough. They had plenty of rice stored in the bunkers, a local source told us, but they could not get any treatment for their injuries, and the soldiers became demoralised.
They started to surrender last weekend.
AA video shows them coming out in a pitiful state, waving white cloths. Some are hobbling on makeshift crutches, or hopping, their injured legs wrapped in rags. Few are wearing shoes.
Inside the wrecked buildings the victorious insurgents filmed piles of bodies.
The AA says more than 450 soldiers died in the siege. It has published images of the captured commander, Brigadier-General Thurein Tun, and his officers kneeling beneath the flagpole, now flying the insurgents’ banner.

Pro-military commentators in Myanmar have been venting their frustration on social media.
“Min Aung Hlaing, you have not asked any of your children to serve in the military,” wrote one. “Is this how you use us? Are you happy seeing all those deaths in Rakhine?”
“At this rate, all that will be left of the Tatmadaw [military] will be Min Aung Hlaing and a flagpole,” wrote another.
The capture of BGP5 also shows the Arakan Army to be one of the most effective fighting forces in Myanmar.
Formed only in 2009 – much later than most of Myanmar’s other insurgent groups – by young ethnic Rakhine men who had migrated to the Chinese border on the other side of the country in search of work, the AA is part of the Three Brotherhood Alliance which has inflicted most of the defeats suffered by the junta since last year.
The other two members of the alliance have stayed on the border, in Shan State.
But the AA moved back to Rakhine eight years ago to start its armed campaign for self-government, tapping into historic resentment among the Rakhine population of the poverty, isolation and central government neglect of their state.
The AA leaders have proven to be smart, disciplined and able to motivate their fighters.
They are already administering the large areas of Rakhine State they control as though they were running their own state.
And they also have good weapons, thanks to their links with the older insurgent groups on the Chinese border, and appear to be well-funded.
There is a bigger question, though, over how much the various ethnic insurgent groups are willing to prioritise the goal of overthrowing the military junta.
Publicly they say they do, alongside the shadow government which was deposed by the coup, and the hundreds of volunteer peoples’ defence forces which have sprung up to support it.
In return for the support it is getting from the ethnic insurgents, the shadow government is promising a new federal political system which will give Myanmar’s regions self-rule.
But already the other two members of the Three Brotherhood Alliance have accepted China’s request for a ceasefire.
China is seeking a negotiated end to the civil war which would almost certainly leave the military with much of its power intact.

The Rohingya village of Myo Thu Gyi, burned by the military in 2017. There are fears for the remaining Rohingya population under an Arakan Army administration [BBC].
The opposition insists the military must be reformed and removed from politics. But having already made so many territorial gains at the expense of the junta, the ethnic insurgents may be tempted to strike a deal with China’s blessing rather than keep fighting to oust the generals.
The AA’s victory poses more worrying questions.
The group’s leadership is tight-lipped about its plans. But it takes over a state that was always poor and which has suffered greatly from the intense fighting of the past year.
“Eighty per cent of the housing in Maungdaw and the surrounding villages has been destroyed,” one Rohingya man who left Maungdaw recently for Bangladesh told the BBC. “The town is deserted. Almost all the shops and houses have been looted.”
Last month the United Nations, whose agencies are being given very little access to Rakhine, warned of looming famine, because of the huge numbers of displaced people and the difficulty of getting any supplies in, past a military blockade.
The AA is trying to set up its own administration, but the BBC has been told by some of those displaced by the fighting that the group cannot feed or shelter them.
It is also unclear how the AA will treat the Rohingya population, still thought to number around 600,000 in Rakhine, even after the expulsionof 700,000 in 2017.
The largest number live in northern Rakhine State and Maungdaw has long been a predominantly Rohingya town. Relations with the ethnic Rakhine majority, the support base for the AA, have long been fraught.
They are now a great deal worse after Rohingya militant groups, which have their power base in the vast refugee camps in Bangladesh, chose to take sides with the military, against the AA, despite the army’s track record of persecuting Rohingyas.
Many Rohingyas do not like these groups, and some say they are happy to live in an AA-run Rakhine State. But tens of thousands have been expelled by the AA from towns it has conquered, and not been allowed back.
The AA has promised to include all communities in its vision for a future independent of the central government, but it has also denounced the Rohingyas it found itself fighting alongside the army. In August dozens of Rohingyas, many of them women and children trying to cross over to Bangladesh, were killed by bombs, almost certainly dropped from AA drones.
“We cannot deny the fact that Rohingyas have been persecuted by Myanmar governments for many years, and the Rakhine people supported that,” said the Rohingya man we spoke to in Bangladesh.
“The government wants to keep Rohingyas from becoming citizens, but the Rakhine people believe there should be no Rohingyas at all in Rakhine State. Our situation today is even more difficult than it was under the rule of the military junta.”
[BBC]
Foreign News
Meta blocks 550,000 accounts under Australia’s social media ban

About 550,000 accounts were blocked by Meta during the first days of Australia’s landmark social media ban for kids.
In December, a new law began requiring that the world’s most popular social media sites – including Instagram and Facebook – stop Australians aged under 16 from having accounts on their platforms.
The ban, which is being watched closely around the world, was justified by campaigners and the government as necessary to protect children from harmful content and algorithms.
Companies including Meta have said they agree more is needed to keep young people safe online. However they continue to argue for other measures, with some experts raising similar concerns.
“We call on the Australian government to engage with industry constructively to find a better way forward, such as incentivising all of industry to raise the standard in providing safe, privacy-preserving, age appropriate experiences online, instead of blanket bans,” Meta said in a blog update.
The company said it blocked 330,639 accounts on Instagram, 173,497 on Facebook, and 39,916 on Threads during it’s first week of compliance with the new law.
They again put the argument that age verification should happen at an app store level – something they suggested lowers the burden of compliance on both regulators and the apps themselves – and that exemptions for parental approval should be created.
“This is the only way to guarantee consistent, industry-wide protections for young people, no matter which apps they use, and to avoid the whack-a-mole effect of catching up with new apps that teens will migrate to in order to circumvent the social media ban law.”
Various governments, from the US state of Florida to the European Union, have been experimenting with limiting children’s use of social media. But, along with a higher age limit of 16, Australia is the first jurisdiction to deny an exemption for parental approval in a policy like this – making its laws the world’s strictest.
The policy is wildly popular with parents and envied by world leader, with the Tories this week pledging to follow suit if they win power at the next election, due before 2029.
However some experts have raised concerns that Australian kids can circumvent the ban with relative ease – either by tricking the technology that’s performing the age checks, or by finding other, potentially less safe, places on the net to gather.
And backed by some mental health advocates, many children have argued it robs young people of connection – particularly those from LGBTQ+, neurodivergent or rural communities – and will leave them less equipped to tackle the realities of life on the web.
(BBC)
Foreign News
Bride and groom killed by gas explosion day after Pakistan wedding
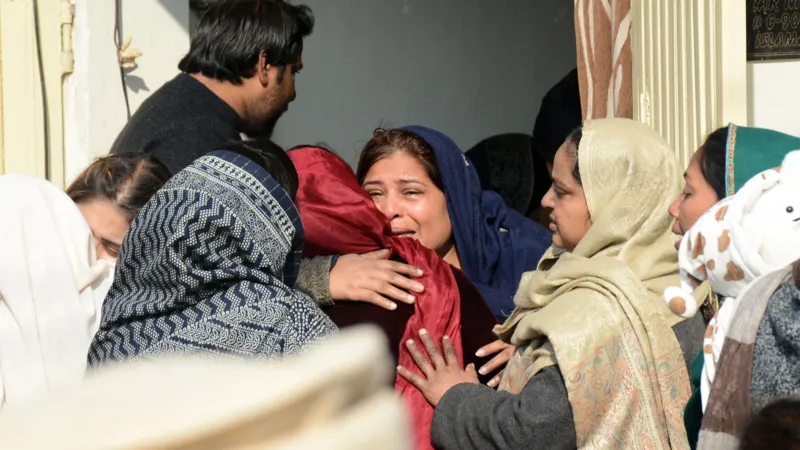

A newly married couple were killed when a gas cylinder exploded at a house in Islamabad where they were sleeping after their wedding party, police have said.
A further six people – including wedding guests and family members – who were staying there also died in the blast. More than a dozen people were injured.
The explosion took place at 07:00 local time (02:00 GMT) on Sunday, causing the roof to collapse.
Parts of the walls were blown away, leaving piles of bricks, large concrete slabs and furniture strewn across the floor. Injured people were trapped under the rubble and had to be carried out on stretchers by rescue workers.
(BBC)
Foreign News
Rescuers race to find dozens missing in deadly Philippines landfill collapse

Rescue workers are racing to find dozens of people still missing following a landslide at a landfill site in the central Philippines that occurred earlier this week, an official has said.
Mayor Nestor Archival said on Saturday that signs of life had been detected at the site in Cebu City, two days after the incident.
Four people have been confirmed dead so far, Archival said, while 12 others have been taken to hospital.
Conditions for emergency services working at the site were challenging, the mayor added, with unstable debris posing a hazard and crew waiting for better equipment to arrive.
The privately-owned Binaliw landfill collapsed on Thursday while 110 workers were on site, officials said.
Archival said in a Facebook post on Saturday morning: “Authorities confirmed the presence of detected signs of life in specific areas, requiring continued careful excavation and the deployment of a more advanced 50-ton crane.”
Relatives of those missing have been waiting anxiously for any news of their whereabouts. More than 30 people, all workers at the landfill, are thought to be missing.
“We are just hoping that we can get someone alive… We are racing against time, that’s why our deployment is 24/7,” Cebu City councillor Dave Tumulak, chairman of the city’s disaster council, told news agency AFP.

Jerahmey Espinoza, whose husband is missing, told news agency Reuters at the site on Saturday: “They haven’t seen him or located him ever since the disaster happened. We’re still hopeful that he’s alive.”
The cause of the collapse remains unclear, but Cebu City councillor Joel Garganera previously said it was likely the result of poor waste management practices.
Operators had been cutting into the mountain, digging the soil out and then piling garbage to form another mountain of waste, Garganera told local newspaper The Freeman on Friday.
The Binaliw landfill covers an area of about 15 hectares (37 acres).
Landfills are common in major Philippine cities like Cebu, which is the trading centre and transportation gateway of the Visayas, the archipelago nation’s central islands.
[BBC]
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoDialog and UnionPay International Join Forces to Elevate Sri Lanka’s Digital Payment Landscape
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoSajith: Ashoka Chakra replaces Dharmachakra in Buddhism textbook
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoThe Paradox of Trump Power: Contested Authoritarian at Home, Uncontested Bully Abroad
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoSubject:Whatever happened to (my) three million dollars?
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoLevel I landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Badulla, Kandy, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya extended
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days ago65 withdrawn cases re-filed by Govt, PM tells Parliament
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoNational Communication Programme for Child Health Promotion (SBCC) has been launched. – PM
-

 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoThe minstrel monk and Rafiki, the old mandrill in The Lion King – II













