Features
“… And death will have its day” Shakespeare

Hearing of the death of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, on Saturday April 10 was like losing a family member. I acknowledged to myself that was strange for who are we to the Royal Family – the House of Windsor – not even their Commonwealth subjects now. But there was that transitory sorrow and the desire to listen to the details of his life as presented on BBC, and read about him. I found later that a young Lankan man, now domiciled in the US, felt the same. “I felt sad on hearing he had died, though he lived long enough.”
This direct descendant of Queen Victoria, a Greek Prince, gave up his citizenship and his name and became British. Much of it, as also the proposed marriage to Princess Elizabeth, was maneuvered by his ambitious uncle, Lord Louis Mountbatten. Princess Elizabeth conveniently fell in love with the dashingly handsome Naval Officer, Philip, when on a visit to the British fleet with her father King George VI, the Queen Mother and Princess Margaret. She was 13 when first attracted, and he a mature 19, already in the Royal Navy.
The Netflix film series of the House of Windsor/Mountbatten
I also ascribe his death being like the goodbye of a person known, as I had watched the Netflix film series The Crown which traces the life of the Queen from childhood up with Clair Foy playing the Princess and young Queen and Olivia Coleman playing the aging sovereign, brilliantly. Incidentally Tobias Menzies who played the role of the Duke in series three and four resembled the Prince more than the younger Matt Smith. The Crown is claimed to be true to life and therefore warts being shown, plus of course the incidents that prove the Queen’s regality, constancy, dedication and dealing tactfully with her stubbornly rash sister, five Prime Ministers including Churchill and Margaret Thatcher, when personalities clashed just a wee bit.
 And then the annus horribilis – year of disaster and misfortune of family divorces and fire at Windsor Castle. In all these personal and national travails, Prince Philip stood steadily by her side; in public one step behind, and she leaned on him though steely strong herself. She acknowledged this fact and her gratitude to him on many occasions. It is accepted that Philip steered the Royal Family through troublous times. I include here Tobias Menzies’ tribute to the Duke on hearing of his death:
And then the annus horribilis – year of disaster and misfortune of family divorces and fire at Windsor Castle. In all these personal and national travails, Prince Philip stood steadily by her side; in public one step behind, and she leaned on him though steely strong herself. She acknowledged this fact and her gratitude to him on many occasions. It is accepted that Philip steered the Royal Family through troublous times. I include here Tobias Menzies’ tribute to the Duke on hearing of his death:
“If I know anything about the Duke of Edinburgh I’m fairly sure he wouldn’t want an actor who portrayed him on TV giving his opinion on his life, so I’ll leave it to Shakespeare. ‘O good old man! How well on thee appears the constant service of the antique world. When service sweat for duty, not for need. Thou art not for the fashion of these times where none will sweat but for promotion, and having that do choke their service up even with the having. It is not so with thee;’” (As You Like It – Orlando in Act 2, Sc 3)
When the Navy Officer Philip was questioned by King George VI, who with his wife did not quite approve of this seeker of their daughter’s hand in marriage due to his penury and family connections to Germany, he promised he would always stand by Elizabeth, care for her and protect her. Which he did. It was no easy task for a strong man to be consort and play second fiddle to the Queen of Great Britain, and far flung Commonwealth countries which accepted her sovereignty. She told her parents she would marry Philip and no other and the love story unsentimentally yet sincerely continued for 70 years.
Poignant and revealing
I remember well the narrative in the series of The Crown of one of his rumoured major discretions. His physio invited him for a weekend party convincing him he was under mental stress and needed relaxation and diversion. Thus while the Queen had to travel alone to Sandringham, he went off with a couple of men for a weekend of golf and drinking. It was on this occasion that Christine Keeler who rocked the political stability of Britain with her ‘charms’, was present. Photographs had been surreptitiously taken and in one, the Prince’s rear view was seen.
Princess Margaret stormed into Queen Elizabeth’s solitary breakfast with the newspaper published picture and said there was no mistaking her husband having been partying. What followed was so revealing. The Queen was devastated emotionally but was completely stoic. She was seated on a window sill in Buckingham Palace when Philip came in. She was aloof. He knelt by her and apologized. Then he sat on the window sill himself. Slowly she moved her hand to his extended arm. And he said: “I promised your father I would care for you? Haven’t I done that all these years?”
Early Life
He was born in Corfu in 1921. The following year, his father, Prince Andrew of Greece, was banished from the country. The family was taken to Italy on board a British naval destroyer. The baby Philip slept in a cradle made from a box that had been used to store oranges. For the next ten years or so, he lived a peripatetic existence, with no fixed home. His mother, Princess Alice, was diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia and consigned to a sanatorium. (Later, she sheltered Jews in Athens during the German occupation and was honored, in 1994, as Righteous Among the Nations).
Prince Andrew, the father, exited to Monte Carlo to live with a mistress. He left nothing to his children. Netflix’s BBC-approved The Crown showed that his mother, now a nun, was invited to stay with their family in Buckingham Palace, the move being more Queen Elizabeth’s. He somewhat ignored his mother, who was befriended by Princess Anne. Later, the film shows Philip walking with her to the garden beside her quarters. She died December 5, 1964 aged 84 in Buckingham Palace and was buried in St George’s Chapel, Windsor Castle, and in 1988 in the Church of Mary Magdalene, Gethsemane, Jerusalem.
All four of Philip’s sisters married Germans. One of the sisters died in 1937 with her entire family in a plane crash. He attended her funeral amid throngs of Germans giving the Nazi salute. None of them was invited for his wedding, though his mother was present, later at the coronation of the Queen, dressed in a sort of nun’s habit designed by her.
When the Duke was asked whether he had been traumatized by his fractured upbringing, with so much turmoil, he replied: “My family broke up. My mother was ill. My sisters were married, my father was in the South of France, I just had to get on with it. You do, One does.” However,the Mountbattens in Britain took him over and then his uncle Dickie, Lord Louise Mountbatten, his wife and two female cousins, welcomed him. Lord Mountbatten continued the role of mentor and advisor and later shifted to Prince Charles who was completely devastated when Lord Louis died at the hands of the IRA while sailing.
Gaffes and quotes and doing good
Of course Prince Philip had his quirks, mostly through being frank verbally. Many are the undiplomatic comments of his. “I would very much like to go to Russia,” he said at the height of the Cold War, “although the bastards murdered half my family.” I distinctly heard on TV Prince Philip give vent to annoyance at one of his final public appearances of meeting a special group of soldiers. He and others were seated while all else stood behind. The cameraman was fussing.
Then came Prince Philip loud and clear: “Take that f….. picture!” (The f-word pronounced full).
“That fierce and funny view of the world was at once a boon and a curse. It both stood Philip in good stead and, notoriously landed him in trouble which made headlines and drew accusations of racism. …. There is no denying the pressure was there from the start, long before he was forced to become a liege.” Archbishop of Canterbury, Justin Welby, said: “He consistently put the interest of others ahead of his own.”
In the New Yorker of April 9, Anthony Lane titled his article – ‘Prince Philip‘s death is the last embers of British Stoicism.” Lane wrote: “That is indisputably true and was demonstrated for decades by the sight of Philip patrolling in the slipstream of the Queen, like a frigate in the wake of an aircraft carrier – a step or two behind her, to one side with his hands diplomatically clasped behind his back. To maintain that secondary position without tiring requires a formidable level of self control, especially in a man who had once as a naval officer enjoyed command of a ship. Renouncing his own career in 1951, he was required to kneel before Her Majesty, at her coronation, two years later, and swear to be ‘liege man of life and limb.’”
He was also, considering Prince Charles’ life, too strict in his upbringing of the heir to the throne. By any measure sending him to the Spartan boarding life at Gordonstone, which he had enjoyed but was near traumatic to the sensitive Charles, was a mistake. However, to compensate, as seen in The Crown, he tried to sort things out between Charles and Diana when cracks appeared in their marriage. He spoke to her as a father saying they were both strangers and aliens in the royal family that was so different to other families, but tradition and duty called for restraint, sacrifice and dignity. He had overcome strains and restraints by taking an interest in matters global (wild life), service (his help to young people) and for recreation to polo, after being a good cricketer.
Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, was much more than that. He was an outstanding global figure with peculiarities tempering a stoic, strong personality.
Features
Wishes, Resolutions and Climate Change

Exchanging greetings and resolving to do something positive in the coming year certainly create an uplifting atmosphere. Unfortunately, their effects wear off within the first couple of weeks, and most of the resolutions are forgotten for good. However, this time around, we must be different, because the nation is coming out of the most devastating natural disaster ever faced, the results of which will impact everyone for many years to come. Let us wish that we as a nation will have the courage and wisdom to resolve to do the right things that will make a difference in our lives now and prepare for the future. The truth is that future is going to be challenging for tropical islands like ours.
We must not have any doubts about global warming phenomenon and its impact on local weather patterns. Over its 4.5-billion-year history, the earth has experienced drastic climate changes, but it has settled into a somewhat moderate condition characterised by periods of glaciation and retreat over the last million years. Note that anatomically modern Homo sapiens have been around only for two to three hundred thousand years, and it is reasoned that this stable climate may have helped their civilisation. There have been five glaciation periods over the last five hundred thousand years, and these roughly hundred-thousand-year cycles are explained by the astronomical phenomenon known as the Milankovitch Cycle (the lows marked with stars in Figure 1). At present, the earth is in an inter glacial period and the next glaciation period will be in about eighty thousand years.
 (See Figure 1. Glaciation Cycles)
(See Figure 1. Glaciation Cycles)
During these cycles, the global mean temperature has changed by about 7-8 degrees Centigrade. In contrast to this natural variation, earth has been experiencing a rapid temperature increase over the past hundred years. There is ample scientific evidence from multiple sources that this is caused by the increase in carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere, which has seen a 50% increase over the historical levels in just hundred years (Figure 2). Carbon dioxide is one of the greenhouse gases which traps heat from the sun and slows the natural cooling process of the earth. This increase of carbon dioxide is due to human activities: fossil fuel burning, industrial processes, deforestation, and agricultural practices. Ironically, those who suffer from the consequences did not contribute to these changes; those who did contribute are trying their best to convince the world that the temperature changes we see are natural, and nothing should be done. We must have no illusions that global warming is a human-caused phenomenon, and it has serious repercussions.
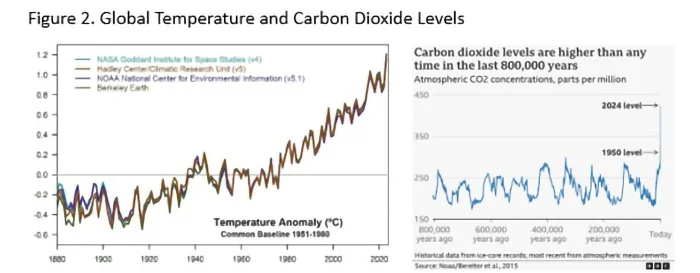
(See Figure 2. Global Temperature and Carbon Dioxide Levels)
Why should we care about global warming? Well, there are many reasons, but let us focus on earth’s water cycle. Middle schoolers know that water evaporates from the oceans, rises into the atmosphere where it cools, condenses, and falls back onto earth as rain or snow. When the oceans warm, the evaporation increases, and the warmer atmosphere can hold more water vapour. Water laden atmosphere results in severe and erratic weather. Ironically, water vapour is also a greenhouse gas, and this has a snowballing effect. The increased ocean temperature also disrupts ocean currents that influence the weather on land. The combined result is extreme and severe weather: violent storms and droughts depending on the geographic location. What is happening on the West coast of the USA is an example. The net result will be major departures from what is considered normal weather over millennia.
International organisations have been talking for 30 years about limiting global temperature increase to 1.5oC above pre-industrial levels by curtailing greenhouse gas emissions. But not much has been done and the temperature has risen by 1.2oC already. The challenge is that even if we can stop greenhouse gas emissions completely, right now, we have the problem of removing already existing 2,500 billion tons of carbon from the atmosphere, for which there are no practical solutions yet. Scientists worry about the consequences of runaway temperature increase and its effect on human life, which are many. It is not a doomsday prediction of life disappearing from earth, but a warning that life will be quite different from what humans are used to. All small tropical nations like ours are burdened with mitigating the consequences; in other words, get ready for more Ditwahs, do not wait for the twelve-day forecast.
Some opined that not enough warning was given regarding Ditwah; the truth is that the tools available for long-term prediction of the path or severity of a weather event (cyclone, typhoon, hurricane, tornado) are not perfect. There are multitude of rapidly changing factors contributing to the behavior of weather events. Meteorologists feed most up to date data to different computer models and try to identify the prediction with the highest probability. The multiple predictions for the same weather event are represented by what is known as spaghetti plots. Figure 3 shows the forecasted paths of a 2019 Atlantic hurricane five days ahead on the right and the actual path it followed on the left. While the long-term prediction of the path of a cyclone remains less accurate, its strength can vary within hours. There are several Indian ocean cyclones tracking sites online accessible to the public.

Figure 3. Forecasting vs Reality
There is no argument that short-term forecasts of this nature are valuable in saving lives and movable assets, but having long term plans in place to mitigate the effects of natural disasters is much more important than that. If a sizable section of the population must start over their lives from ground zero after every storm, how can a country economically develop?
The degree of our unpreparedness came to light during Ditwah disaster. It is not for lack of awareness; judging by the deluge of newspaper articles, blogs, vlogs, and speeches made, there is no shortage of knowledge and technical expertise to meet the challenge. The government has assured the necessary resources, and there is good reason to trust that the funds will be spent properly and not to line the pockets as happened during previous disasters. However, history tells us that despite the right conditions and good intentions, we could miss the opportunity again. Reasons for such skepticisms emerged during the few meetings the President held with the bureaucrats while visiting effected areas. Also, the COPE committee meetings plainly display the inherent inefficiencies and irregularities of our system and the absence of work ethics among all levels of the bureaucracy.
What it tells us is that we as a nation have an attitude problem. There are ample scholarly analyses by local as well as international researchers on this aspect of Sri Lankan psyche, and they label it as either island or colonial mentality. The first refers to the notion of isolated communities perceiving themselves as exceptional or superior to the rest of the world, and that the world is hell-bent on destroying or acquiring what they have. This attitude is exacerbated by the colonial mentality that promoted the divide and conquer rules and applied it to every societal characteristic imaginable; and plundered natural resources. As a result, now we are divided along ethnic, linguistic, religious, political, class, caste, geography, wealth, and many more real and imagined lines. Sadly, politicians, some religious leaders, and other opportunists keep inflaming these sentiments for their benefit when most of the population is willing to move on.
The first wish, therefore, is to get the strength, courage, and wisdom to think rationally, and discard outdated and outmoded belief systems that hinder our progress as a nation. May we get the courage to stop venerating elite who got there by exploiting the masses and the country’s wealth. More importantly, may we get the wisdom to educate the next generation to be free thinkers, give them the power and freedom to reject fabrications, myths, and beliefs that are not based on objective facts.
This necessitates altering our attitude towards many aspects of life. There is no doubt that free thinking does not come easily, it involves the proverbial ‘exterminating the consecrated bull.’ We are rightfully proud about our resplendent past. It is true that hydraulic engineering, art, and architecture flourished during the Anuradhapura period.
However, for one reason or another, we have lost those skills. Nowadays, all irrigation projects are done with foreign aid and assistance. The numerous replicas of the Avukana statue made with the help of modern technology, for example, cannot hold a candle to the real one. The fabled flying machine of Ravana is a figment of marvelous imagination of a skilled poet. Reality is that today we are a nation struggling with both natural and human-caused disasters, and dependent on the generosity of other nations, especially our gracious neighbor. Past glory is of little help in solving today’s problems.
Next comes national unity. Our society is so fragmented that no matter how beneficial a policy or an idea for the nation could be, some factions will oppose it, not based on facts, but by giving into propaganda created for selfish purposes. The island mentality is so pervasive, we fail to trust and respect fellow citizens, not to mention the government. The result is absence of long-term planning and stability. May we get the insight to separate policy from politics; to put nation first instead of our own little clan, or personal gains.
With increasing population and decreasing livable and arable land area, a national land management system becomes crucial. We must have an intelligent zoning system to prevent uncontrolled development. Should we allow building along waterways, on wetlands, and road easements? Should we not put the burden of risk on the risk takers using an insurance system instead of perpetual public aid programs? We have lost over 95% of the forest cover we had before European occupation. Forests function as water reservoirs that release rainwater gradually while reducing soil erosion and stabilizing land, unlike monocultures covering the hill country, the catchments of many rivers. Should we continue to allow uncontrolled encroachment of forests for tourism, religious, or industrial purposes, not to mention personal enjoyment of the elite? Is our use of land for agricultural purposes in keeping with changing global markets and local labor demands? Is haphazard subsistence farming viable? What would be the impact of sea level rising on waterways in low lying areas?
These are only a few aspects that future generations will have to grapple with in mitigating the consequences of worsening climate conditions. We cannot ignore the fact that weather patterns will be erratic and severe, and that will be the new normal. Survival under such conditions involves rational thinking, objective fact based planning, and systematic execution with long term nation interests in mind. That cannot be achieved with hanging onto outdated and outmoded beliefs, rituals, and traditions. Weather changes are not caused by divine interventions or planetary alignments as claimed by astrologers. Let us resolve to lay the foundation for bringing up the next generation that is capable of rational thinking and be different from their predecessors, in a better way.
by Geewananda Gunawardana
Features
From Diyabariya to Duberria: Lanka’s Forgotten Footprint in Global Science

For centuries, Sri Lanka’s biological knowledge travelled the world — anonymously. Embedded deep within the pages of European natural history books, Sinhala words were copied, distorted and repurposed, eventually fossilising into Latinised scientific names of snakes, bats and crops found thousands of kilometres away.
Africa’s reptiles, Europe’s taxonomic catalogues and global field guides still carry those echoes, largely unnoticed and uncredited.
Now, a Sri Lankan herpetologist is tracing those forgotten linguistic footprints back to their source.
Through painstaking archival research into 17th- and 18th-century zoological texts, herpetologist and taxonomic researcher Sanjaya Bandara has uncovered compelling evidence that several globally recognised scientific names — long assumed to be derived from Greek or Latin — are in fact rooted in Sinhala vernacular terms used by villagers, farmers and hunters in pre-colonial Sri Lanka.
“Scientific names are not just labels. They are stories,” Bandara told The Island. “And in many cases, those stories begin right here in Sri Lanka.”

Sanjaya Bandara
At the heart of Bandara’s work is etymology — the study of word origins — a field that plays a crucial role in zoology and taxonomy.
While classical languages dominate scientific nomenclature, his findings reveal that Sinhala words were quietly embedded in the foundations of modern biological classification as early as the 1700s.
One of the most striking examples is Ahaetulla, the genus name for Asian vine snakes. “The word Ahaetulla is not Greek or Latin at all,” Bandara explained. “It comes directly from the Sinhala vernacular used by locals for the Green Vine Snake.” Remarkably, the term was adopted by Carl Linnaeus himself, the father of modern taxonomy.
Another example lies in the vespertilionid bat genus Kerivoula, described by British zoologist John Edward Gray. Bandara notes that the name is a combination of the Sinhala words kiri (milky) and voula (bat). Even the scientific name of finger millet, Eleusine coracana, carries linguistic traces of the Sinhala word kurakkan, a cereal cultivated in Sri Lanka for centuries.
Yet Bandara’s most intriguing discoveries extend far beyond the island — all the way to Africa and the Mediterranean.
In a research paper recently published in the journal Bionomina, Bandara presented evidence that two well-known snake genera, Duberria and Malpolon, both described in 1826 by Austrian zoologist Leopold Fitzinger, likely originated from Sinhala words.
The name Duberria first appeared in Robert Knox’s 1681 account of Ceylon, where Knox refers to harmless water snakes called “Duberria” by locals. According to Bandara, this was a mispronunciation of Diyabariya, the Sinhala term for water snakes.
“Mispronunciations are common in Knox’s writings,” Bandara said. “English authors of the time struggled with Sinhala phonetics, and distorted versions of local names entered European literature.”
Over time, these distortions became formalised. Today, Duberria refers to African slug-eating snakes — a genus geographically distant, yet linguistically tethered to Sri Lanka.
Bandara’s study also proposes the long-overdue designation of a type species for the genus, reviving a 222-year-old scientific name in the process.
Equally compelling is the case of Malpolon, the genus of Montpellier snakes found across North Africa, the Middle East and southern Europe. Bandara traced the word back to a 1693 work by English zoologist John Ray, which catalogued snakes from Dutch India — including Sri Lanka.
“The term Malpolon appears alongside Sinhala vernacular names,” Bandara noted. “It is highly likely derived from Mal Polonga, meaning ‘flowery viper’.” Even today, some Sri Lankan communities use Mal Polonga to describe patterned snakes such as the Russell’s Wolf Snake.
Bandara’s research further reveals Sinhala roots in the African Red-lipped Herald Snake (Crotaphopeltis hotamboeia), whose species name likely stems from Hothambaya, a regional Sinhala term for mongooses and palm civets.
“These findings collectively show that Sri Lanka was not just a source of specimens, but a source of knowledge,” Bandara said. “Early European naturalists relied heavily on local names, local guides and local ecological understanding.”
 Perhaps the most frequently asked question Bandara encounters concerns the mighty Anaconda. While not a scientific name, the word itself is widely believed to be a corruption of the Sinhala Henakandaya, another snake name recorded in Ray’s listings of Sri Lankan reptiles.
Perhaps the most frequently asked question Bandara encounters concerns the mighty Anaconda. While not a scientific name, the word itself is widely believed to be a corruption of the Sinhala Henakandaya, another snake name recorded in Ray’s listings of Sri Lankan reptiles.
“What is remarkable,” Bandara reflected, “is that these words travelled across continents, entered global usage, and remained there — often stripped of their original meanings.”
For Bandara, restoring those meanings is about more than taxonomy. It is about reclaiming Sri Lanka’s rightful place in the history of science.
“With this study, three more Sinhala words formally join scientific nomenclature,” he said.
“Who would have imagined that a Sinhala word would be used to name a snake in Africa?”
Long before biodiversity hotspots became buzzwords and conservation turned global, Sri Lanka’s language was already speaking through science — quietly, persistently, and across continents.
By Ifham Nizam
Features
Children first – even after a disaster

However, the children and their needs may be forgotten after a disaster.
Do not forget that children will also experience fear and distress although they may not have the capacity to express their emotions verbally. It is essential to create child-friendly spaces that allow them to cope through play, draw, and engage in supportive activities that help them process their experiences in a healthy manner.
The Institute for Research & Development in Health & Social Care (IRD), Sri Lanka launched the campaign, titled “Children first,” after the 2004 Tsunami, based on the fundamental principle of not to medicalise the distress but help to normalise it.

The Island picture page
The IRD distributed drawing material and play material to children in makeshift shelters. Some children grabbed drawing material, but some took away play material. Those who choose drawing material, drew in different camps, remarkably similar pictures; “how the tidal wave came”.
“The Island” supported the campaign generously, realising the potential impact of it.
The campaign became a popular and effective public health intervention.
“A public health intervention (PHI) is any action, policy, or programme designed to improve health outcomes at the population level. These interventions focus on preventing disease, promoting health, and protecting communities from health threats. Unlike individual healthcare interventions (treating individuals), which target personal health issues, public health interventions address collective health challenges and aim to create healthier environments for all.”
The campaign attracted highest attention of state and politicians.
The IRD continued this intervention throughout the protracted war, and during COVID-19.
The IRD quick to relaunch the “children first” campaign which once again have received proper attention by the public.
While promoting a public health approach to handling the situation, we would also like to note that there will be a significant smaller percentage of children and adolescents will develop mental health disorders or a psychiatric diagnosis.
We would like to share the scientific evidence for that, revealed through; the islandwide school survey carried out by the IRD in 2007.
 During the survey, it was found that the prevalence of emotional disorder was 2.7%, conduct disorder 5.8%, hyperactivity disorder was 0.6%, and 8.5% were identified as having other psychiatric disorders. Absenteeism was present in 26.8%. Overall, previous exposure to was significantly associated with absenteeism whereas exposure to conflict was not, although some specific conflict-related exposures were significant risk factors. Mental disorder was strongly associated with absenteeism but did not account for its association with tsunami or conflict exposure.
During the survey, it was found that the prevalence of emotional disorder was 2.7%, conduct disorder 5.8%, hyperactivity disorder was 0.6%, and 8.5% were identified as having other psychiatric disorders. Absenteeism was present in 26.8%. Overall, previous exposure to was significantly associated with absenteeism whereas exposure to conflict was not, although some specific conflict-related exposures were significant risk factors. Mental disorder was strongly associated with absenteeism but did not account for its association with tsunami or conflict exposure.
The authors concluded that exposure to traumatic events may have a detrimental effect on subsequent school attendance. This may give rise to perpetuating socioeconomic inequality and needs further research to inform policy and intervention.
Even though, this small but significant percentage of children with psychiatric disorders will need specialist interventions, psychological treatment more than medication. Some of these children may complain of abdominal pain and headaches or other physical symptoms for which doctors will not be able to find a diagnosable medical cause. They are called “medically unexplained symptoms” or “somatization” or “bodily distress disorder”.
Sri Lanka has only a handful of specialists in child and adolescent psychiatric disorders but have adult psychiatrists who have enough experience in supervising care for such needy children. Compared to tsunami, the numbers have gone higher from around 20 to over 100 psychiatrists.
Most importantly, children absent from schools will need more close attention by the education authorities.
In conclusion, going by the principles of research dissemination sciences, it is extremely important that the public, including teachers and others providing social care, should be aware that the impact of Cyclone Ditwah, which was followed by major floods and landslides, which is a complex emergency impact, will range from normal human emotional behavioural responses to psychiatric illnesses. We should be careful not to medicalise this normal distress.
It’s crucial to recall an important statement made by the World Health Organisation following the Tsunam
Prof. Sumapthipala MBBS, DFM, MD Family Medicine, FSLCFP (SL), FRCPsych, CCST (UK), PhD (Lon)]
Director, Institute for Research and Development in Health and Social Care, Sri Lanka
Emeritus Professor of Psychiatry, School of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences, Keele University, UK
Emeritus Professor of Global Mental Health, Kings College London
Secretary General, International society for Twin Studies
Visiting Professor in Psychiatry and Biomedical Research at the Faculty of Medicine, Kotelawala Defence University, Sri Lanka
Associate Editor, British Journal Psychiatry
Co-editor Ceylon Medical Journal.
Prof. Athula Sumathipala
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoMembers of Lankan Community in Washington D.C. donates to ‘Rebuilding Sri Lanka’ Flood Relief Fund
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoBritish MP calls on Foreign Secretary to expand sanction package against ‘Sri Lankan war criminals’
-

 Features7 days ago
Features7 days agoGeneral education reforms: What about language and ethnicity?
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoSuspension of Indian drug part of cover-up by NMRA: Academy of Health Professionals
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoChief selector’s remarks disappointing says Mickey Arthur
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoStreet vendors banned from Kandy City
-

 Editorial7 days ago
Editorial7 days agoA very sad day for the rule of law
-

 News7 days ago
News7 days agoUS Ambassador to Sri Lanka among 29 career diplomats recalled













