Features
The changing faces of Galle Face

by Ismeth Raheem and Angeline Ondaatjie
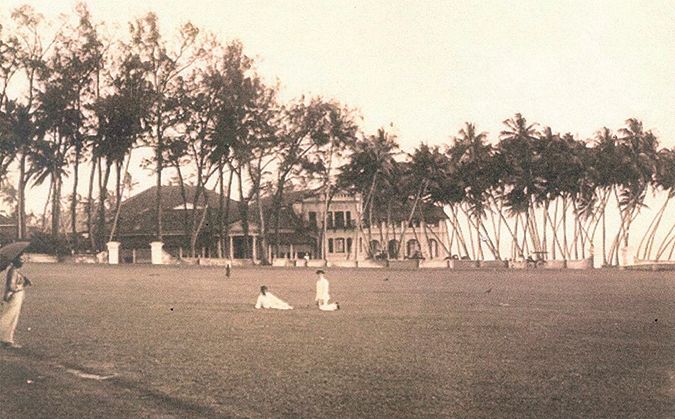
Galle Face is Colombo’s most-prized open-aired public space, extending over a mile along the Fort oceanfront in Colombo. Over the course of Sri Lanka’s history, it has been the de facto stage for landmark public gatherings. Most recently over the months of April to July 2022, the Galle Face Green was the centerstage of the People’s Aragalaya, a protest movement that arose from economic hardship in Sri Lanka. During those weeks the protestors renamed it Gotagogama (GGG) and even had a Google marker to prove it. On July 9, 2022, unprecedented crowds from all parts of Sri Lanka gathered in the Galle Face Area breaking attendance records of Prime Minister D.S. Senanayake’s funeral in 1952, the 1953 hartal, and Pope Francis’s holy mass in 2015.
While it seems like it has been iconized by the Aragalaya over just the last few months, Galle Face’s rich history dates back centuries. Prior to the first fortifications that adorn it today (built by the Portuguese in the 16th century) it was referred to as Mapanne, meaning “large open plain”. Long before it became the open stretch of grassy plain sans trees/plants that we know it as, it was a large marsh land and part of the Colombo Lake (later known as the Beira Lake).
In this vast marshland, there were numerous small streams, ponds, and boulders. This extensive delta was created by numerous branches of the Kelani Ganga, the main river that flows to the sea by the ancient Kelani Temple, and is the third longest in the island. The Portuguese used the flooded areas as a defensive measure against possible attacks from the Kandyan Kingdom. Later the Dutch put their efforts into controlling and channeling the lake by creating a network of connected canals.
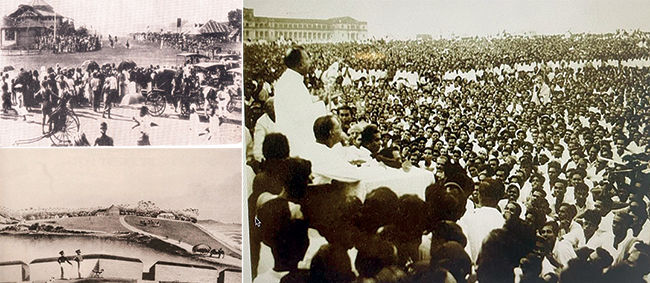
On the other hand, the British, who succeeded the Dutch in 1789, spent their efforts in reclaiming much of the lake area, believing that this would alleviate the flooding of Colombo’s low-lying areas. The original open stretch on the Southern side of the Fort (now known as Galle Face Esplanade) somehow gained more land around its periphery. Many of the new buildings that adorn the skyline of Slave Island (which owes its name to the slave tenements confined to a moat-surrounded land mass during the Dutch period) are in this reclaimed area of the Beira Lake.The open “Green” stretch was only seldom used for recreation under the Portuguese and Dutch occupations. This changed during the first decades of the 19th century, when it came into its own as the amusement, exercise, and sports venue that it is used as today.
The Galle Face Burial Grounds
Galle Face hosted the site of the first British burial grounds for over half a century from 1803, until the tombstones were translocated to the General Cemetery at Kanatte in 1877. This land may have been a part of the site that was reclaimed by the Dutch Administration of the East India Company around 1700-1750. [See Map of Colombo, 1750]. The timber palisade enclosing the cemetery and the tombstones are clearly indicated in the views of the Galle Face in the coloured engravings by John Deschamps [1848]. The burials were necessitated by the British army’s heavy military casualties from the wars with the King of Kandy during the administration of Governor North between 1801-1805.
For years, the Galle Face Cemetery was known as the “Padre Bailey’s Godown”, after the Archdeacon Bailey who officiated at the burials. J. P. Lewis’s “Tombstones and Monuments of Ceylon”, records the inscriptions on the headstones.
The open stretch of land outside the South Gate of the Colombo Fort was the site of military executions. In close proximity, at the northern end of the current esplanade, featured a guardhouse and a large block of wood: a “whipping post” where punishments were administered by public flogging.
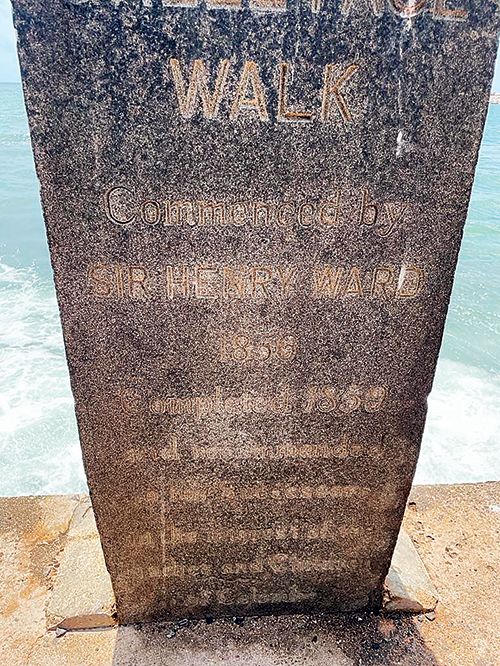
The Esplanade and the Recreation Galle Face Green
In 1853, the sea-front walk of the Galle Face was constructed by Governor Henry Ward. An inscription on the pillar midway through the walk still stands; it reads “Galle Face Walk completed in 1856 and recommended to his successors in the interest of the Ladies and Children of Colombo”.
Henry Charles, the author of “Ceylon and the Cingalese” compared Galle Face Green to Hyde Park in London. “At half past five the “Galle Face, or the Hyde Park of Colombo, begins to wear an animated appearance, there being many vehicles and horses in motion. Every description of conveyance to be seen driving around the Galle Face, from the Long Acre Built carriages of the Governor, the dashing phaeton of the wealthy merchant, the unassuming gig, the country- built palanquin and the humble bandy.”
The Galle Face Esplanade by John Deschamps shows the view from the ramparts of the Fort of Colombo facing the Galle Face Green. In the foreground are two Royal Military officers enjoying the scene. The Beira Lake, which was used for aquatic sports, the Round Pavilion, and Grand Stand of the Race Course are also in the background. The large bungalow towards the right of their view is the building that was later replaced by the Galle Face Hotel. The country house in the distant far right is the home of Governor Maitland, which later became the Mount Lavinia Hotel. The Race Bungalow, as the Grand Stand was later called, became The Colombo Club and still exists within the premises of the Taj Hotel.
In 1829, Sir Edward Barnes introduced horse racing at Galle Face after leveling a mile and a quarter of the grounds. While the upper floor of the conical-roofed race stand had the best views of the horse racing, it was also the venue for grand balls. The verandahs of the ball room were used for card playing, darts, and other favorite past times. By the 1830s, cricket and a whole host of Victorian sports and leisure activities were introduced and enjoyed by both the British and middle class locals, making it the most popular space in Colombo.
The Galle Face Railway Line Controversy (1873-75)
The railway line from Fort to the coast was originally planned to cut through the Galle Face Green. The Railway authorities set out an intended rail track from Maradana (the first railway station in Ceylon), Colombo Fort to Moratuwa cutting across Galle Face created a major controversy which involved the public, the legislative council, and the Governor of Ceylon.
The Times of Ceylon of Dec 4, 1873 stated – It is intended “to carry a line from a station to be constructed in the vacant plot near the Lotus Pond road, where passengers and goods from the Fort may be loaded, and where trains may run in connection with the railway station at Maradana; from the Fort Station, the line will diverge at the Police Station on the Galle Face, and skirt the sea-beach as far as Mount Lavinia”.
Public discontent at the impending desecration of the Galle Face walk soon became articulate – but the official trace by the railway planners did not appear to admit any change. On October 14, 1874, the Governor gave another version where he stated, “Inconvenience has been apprehended from trains running so near the road of the Galle Face, but care shall be taken that the train shall not run during evening”.
Some of the members of the Council were still discontent and by January 6, 1875 the tender notices for the construction of the Southern Line were published in the public press. The debate continued. The Government was prominently reminded of Sir Henry Ward’s recommendation of Galle Face to the Women and Children of Colombo by the Council and the public refused to be reconciled of this infringement. Yet the notices calling for tenders did not weaken the effort to save the Galle Face Walk.
The Council reminded the Governor of Galle Face’s dedication to the public and refused that it be desecrated and rendered unsafe by the “snorting and rattling and smoking vapours of the railway train”. The Governor responded by accepting the protest, since they represented the ladies of Colombo who were afraid that they will be deprived of their drive, and stated “I feel there is a good deal in this objection”.
On March 13, 1875, the Government took serious notice of the protests and assured the public that an alternate route will be used, which prompted the Observer in proclaiming in its issue of March 15, 1975: “GALLE FACE SAVED.”
Subsequently, the railway line from Fort as we see it today is connected to Compani Vidiya via an underground tunnel to the coast at Kollupitiya, honouring the decision to leave Galle Face Green untouched.The public recreation space and sacredness of Galle Face was saved, and allowed Sri Lankans to witness the historic mass independence rally on February 4, 1948. Radio Ceylon broadcasts were heard as far as Mount Everest, legendary school cricket matches, and most recently, the peaceful protests of the Aragalaya were also on Galle Face. The current legislators should learn their history and maintain the freedom and sanctity of this earth lung that is the only true free space in Colombo.
Features
End of ‘Western Civilisation’?

“All animals are equal, but some animals are more equal than others” ––George Orwell, Animal Farm
 When I wrote in this column an essay on 4th February 2026 titled, the ‘Beginning of Another ‘White Supremacist’ World Order?’, my focus was on the hypocrisy of Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney’s Davos address on 20 January 2026 to the World Economic Forum. It was embraced like the gospel by liberal types and the naïve international relations ‘experts’ in our country and elsewhere. My suspicion of Carney’s words stemmed from the consistent role played by countries like Canada and others which he called ‘middle powers’ or ‘intermediate powers’ in the world order he critiqued in Davos. He wanted such countries, particularly Canada, “to live the truth?” which meant “naming reality” as it exists; “acting consistently” towards all in the world; “applying the same standards to allies and rivals” and “building what we claim to believe in, rather than waiting for the old order to be restored.” These are some memorable pieces of Carney’s mantra.
When I wrote in this column an essay on 4th February 2026 titled, the ‘Beginning of Another ‘White Supremacist’ World Order?’, my focus was on the hypocrisy of Canadian Prime Minister Mark Carney’s Davos address on 20 January 2026 to the World Economic Forum. It was embraced like the gospel by liberal types and the naïve international relations ‘experts’ in our country and elsewhere. My suspicion of Carney’s words stemmed from the consistent role played by countries like Canada and others which he called ‘middle powers’ or ‘intermediate powers’ in the world order he critiqued in Davos. He wanted such countries, particularly Canada, “to live the truth?” which meant “naming reality” as it exists; “acting consistently” towards all in the world; “applying the same standards to allies and rivals” and “building what we claim to believe in, rather than waiting for the old order to be restored.” These are some memorable pieces of Carney’s mantra.
Yet unsurprisingly, it only took the Trump-Netanyahu illegal war against Iran to prove the hollowness in Carney’s words. If he placed any premium on his own words, he should have at least voiced his concern against the continuing atrocities in the Middle East unilaterally initiated by the US and Israel. But his concern is only about Iran’s seemingly indiscriminate attacks across the region targeting US and Israeli installations and even civilian locations in countries allied with the Us-Israel coalition.
Issuing a statement on 3 March 2026 from Sydney he noted, “Canada has long seen Iran as the principal source of instability and terror in the Middle East” and “despite more than two decades of negotiations and diplomatic efforts, Iran has not dismantled its nuclear programme, nor halted its enrichment activities.” A sensible observer would note how the same statement would also apply to Israel. In fact, Israel has been the bigger force of instability in the Middle East surpassing Iran. After all, it has exiled an entire population of people — the Palestinians — from their country to absolute statelessness has not halted its genocide of the same people unfortunate enough to find themselves in Gaza after their homeland was taken over to create Israel in 1948 and their properties to build illegal Jewish settlements in more recent times. And then there is the matter of nuclear weapons. Israel has never been hounded to stop its nuclear programme unlike Iran. There is, in the world order Carney criticixed and the one in his fantasy, a fundamental difference between a ‘Jewish bomb’ and a ‘Muslim bomb’ in the ‘clash of civilisations’ as imagined by Samuel P. Huntington and put into practice by the likes of Messers Trump, Netanyahu, and Carney. That is, the Jewish bomb is legitimate, and the Muslim one is not, which to me evokes the commandments in the dystopian novella Animal Farm.
But Carney, in his new rhetoric closely echoing those of the leaders of Germany, UK and France, did not completely forget his Davos words too. He noted, in the same statement, “we take this position with regret, because the current conflict is another example of the failure of the international order.” But in reality, it is not the failure of the current international order, but its reinforcement by the likes of Mr Carney, reiterating why it will not change.
Coming back to the US-Israel attack on Iran, anyone even remotely versatile in the craft of warfare should have known, sooner or later, the rapidly expanding theatre of devastation in the Middle East was likely to happen for two obvious reasons. One, Iran had warned of this outcome if attacked as it considered those countries hosting US and Israeli bases or facilities as enemies. This is military common sense. Two, this was also likely because it is the only option available for a country under attack when faced with superior technology, firepower and the silence of much of the world. I cannot but feel deep shame about the lukewarm and generic statements urging restraint issued by our political leaders notwithstanding the support of Iran to our country in many times of difficulty at the hands of this very same world order.
When I say this, I am not naïvely embracing Iran as a shining example of democracy. I am cognizant of the Iranian regime’s maltreatment of some of its own citizens, stifling of dissent within the country and its proxy support for armed groups in the region. But in real terms, this is no different from similar actions of Israel and the US. The difference is, the actions of these countries, particularly of the US, have been far more devastating for the world than anything Iran has done or could do. US’s misadventures in Vietnam, Iraq, Syria, and Afghanistan come to mind — to take only a handful of examples.
But it is no longer about Carney and the hollowness of his liberal verbal diarrhoea in Davos. What is of concern now is twofold. One is the unravelling fiction of what he called the ‘new world order’ in which he located countries like Canada at the helm. And the second is the reality of continuing to live in the same old world order where countries like Canada and other middle and intermediate powers will continue to do the bidding of powerful aggressors like the US and Israel as they have done since the 20th century.
Yet, one must certainly thank Trump and Mr Natenyahu for one thing. That is, they have effectively exposed the myth of what used to be euphemistically called the ‘western civilisation.’ Despite its euphemism, the notion and its reality were omnipresent and omnipotent, because of the devastating long term and lingering consequences of its tools of operation, which were initially colonialism and later postcolonial and neocolonial forms of control to which all of us continue to be subjected.
One thing that was clearly lacking in the long and devastating history of the ‘western civilisation’ in so far as it affected the lives of people like us is its lack of ‘civilisation’ and civility at all times. Therefore, Trump and Mr Netanyahu must be credited for exposing this reality in no uncertain terms.
But what does illegal and unprovoked military action and the absence so far of accountability mean in real terms? It simply means that rules no longer matter. If Israel and the US can bomb and murder heads of state of a sovereign country, its citizens including children, cause massive destruction claiming a non-existent imminent threat violating both domestic and international law, it opens a wide playing field for the powerful and the greedy. Hypothetically, in this free-for-all, China can invade India through Arunachal Pradesh and occupy that Indian state which it calls Zangnan simply because it has been claiming the territory of itself for a very long time and also simply because it can. India can invade and occupy Sri Lanka, if it so wishes because this can so easily be done and also because it is part of the extended neighbourhood of the Ramayana and India’s ‘Akhand Bharat’ political logic. Sri Lanka can perhaps invade and occupy the Maldives if it wants a free and perennial supply of Maldive Fish. Incidentally, the Sri Lankan Tamil guerrilla group, People’s Liberation Organization of Tamil Eelam nearly succeeded in doing so 1988.
Sarcasm aside, even more dangerous is the very real possibility of this situation opening the doors for small, violent and mobile militant groups to target citizens of these aggressor countries and their allies as we saw in the late 1960s and 1970s. This will occur because in this kind of situation, many people would likely believe this form of asymmetric warfare is the only avenue of resistance open to them. It is precisely under similar conditions that the many Palestinian armed factions and Lebanese militia groups emerged in the first place. If this happens, the victims will not be the fathers and the vociferous supporters of the present aggression but all of us including those who had nothing to do with the atrocities or even opposed it in their weak and inaudible voices.
If I may go back to Carney’s Davos words, what would “to live the truth?”, “naming reality”, “acting consistently” and “applying the same standards to allies and rivals” mean in the emerging situation in the Middle East? Would this kind of hypocrisy, hyperbole, choreographed silence and selective accusations only end if a US invasion of Greenland, an integral part of the ‘White Supremacist’ World Order’ takes place? By then, however, all of us would have been well-trained in the art of feeling numb. By that time, we too would have forgotten yet another important line in Animal Farm: “No animal shall kill any other animal without cause.”
Features
Silence is not protection: Rethinking sexual education in Sri Lanka

Sexual education is a vital component of holistic education, contributing to physical health, emotional well-being, gender equality, and social responsibility. Despite its importance, sexual education remains a sensitive and often controversial subject in many societies, particularly in culturally conservative contexts. In Sri Lanka, discussions around sexuality are frequently avoided in formal and informal settings, leaving young people to rely on peers, social media, or misinformation. This silence creates serious social, health, and psychological consequences. By examining the Sri Lankan context alongside international examples, the importance of comprehensive and age-appropriate sexual education becomes clear.
Understanding Sexual Education
Sexual education goes beyond biological explanations of reproduction. Comprehensive sexual education includes knowledge about human anatomy, puberty, consent, relationships, emotional health, gender identity, sexual orientation, reproductive rights, contraception, prevention of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), and personal safety. Importantly, it also promotes values such as respect, responsibility, dignity, and mutual understanding. When delivered appropriately, sexual education empowers individuals to make informed decisions rather than encouraging early or risky sexual behavior.
The Sri Lankan Context: Silence and Its Consequences
In Sri Lanka, sexual education is included in school curricula mainly through subjects such as Health Science and Life Competencies, however the content is often limited and taught with hesitation. Many teachers feel uncomfortable discussing sexual topics openly due to cultural norms, religious sensitivities, and fear of parental backlash. As a result, lessons are rushed, skipped, or delivered in a purely biological manner without addressing emotional, social, or ethical dimensions.
This lack of open education has led to several social challenges. Teenage pregnancies, although less visible, remain a significant issue, particularly in rural and estate sectors. Young girls who become pregnant often face school dropouts, social stigma, and limited future opportunities. Many of these pregnancies occur due to lack of knowledge about contraception, consent, and bodily autonomy.
Another serious concern in Sri Lanka is child sexual abuse. Numerous reports indicate that many children do not recognize abusive behaviour or lack the confidence and language to report it. Proper sexual education, especially lessons on body boundaries and consent, can help children identify inappropriate behavior and seek help early. In the Sri Lankan context, where respect for elders often discourages questioning authority, this knowledge is especially crucial.
Furthermore, misinformation about menstruation, nocturnal emissions, and bodily changes during puberty causes anxiety and shame among adolescents. Many Sri Lankan girls experience menarche without prior knowledge, leading to fear and confusion. Similarly, boys often receive no guidance about emotional or physical changes, reinforcing unhealthy notions of masculinity and silence around mental health.
Cultural Resistance and Misconceptions
Opposition to sexual education in Sri Lanka often stems from the belief that it promotes immoral behaviour or encourages premarital sex. However, international research consistently shows the opposite: young people who receive comprehensive sexual education tend to delay sexual initiation and engage in safer behaviours. The resistance is therefore rooted more in cultural fear than empirical evidence.
Religious and cultural values are important, but they need not conflict with sexual education. In fact, sexual education can be framed within moral discussions about responsibility, respect, family values, and care for others principles shared across Sri Lanka’s major religious traditions. Ignoring sexuality does not protect cultural values; rather, it leaves young people vulnerable.
International Evidence: Lessons from Other Countries
Several countries demonstrate how effective sexual education contributes to positive social outcomes.
In the Netherlands, sexual education begins at an early age and is age-appropriate, focusing on respect, relationships, and communication rather than explicit sexual activity. As a result, the Netherlands has one of the lowest rates of teenage pregnancy and STIs in the world. Young people are encouraged to discuss feelings, boundaries, and consent openly, both in schools and at home.
Similarly, Sweden introduced compulsory sexual education as early as the 1950s. Swedish programs emphasise gender equality, reproductive rights, and sexual health. This long-term commitment has contributed to high levels of sexual health awareness, low maternal mortality among young mothers, and strong societal acceptance of gender diversity. Sexual education in Sweden is also closely linked to public health services, ensuring access to counseling and contraception.
In many developing contexts, international organisations have supported sexual education as a tool for social development. UNESCO promotes Comprehensive Sexuality Education (CSE) globally, emphasising that it equips young people with knowledge, skills, attitudes, and values that enable them to protect their health and dignity. Studies supported by UNESCO show that CSE reduces risky behaviours, improves academic outcomes, and supports gender equality.
In countries such as Rwanda and South Africa, sexual education has been integrated with HIV/AIDS prevention programs. These initiatives demonstrate that sexual education is not a luxury of developed nations but a necessity for public health and social stability.
Comparing Sri Lanka with International Models
When compared with international examples, Sri Lanka’s challenges are not due to lack of capacity but lack of open dialogue and political will. Sri Lanka has a strong education system, high literacy rates, and an extensive public health network. These strengths provide an excellent foundation for implementing comprehensive sexual education that is culturally sensitive yet scientifically accurate.
Unlike the Netherlands or Sweden, Sri Lanka may not adopt early-age sexuality discussions in the same manner, but age-appropriate education during late primary and secondary school is both feasible and necessary. Topics such as puberty, menstruation, consent, online safety, and respectful relationships can be introduced gradually without violating cultural norms.
Sexual Education in the Digital Era
The urgency of sexual education has increased in the digital age. Sri Lankan adolescents are exposed to sexual content through social media, films, and online platforms, often without guidance. Pornography frequently becomes a primary source of sexual knowledge, leading to unrealistic expectations, objectification, and distorted ideas about consent and relationships.
Sexual education can counter these influences by developing critical thinking, media literacy, and ethical understanding. Teaching young people how to navigate digital relationships, cyber harassment, and online exploitation is now an essential component of sexual education.
Gender Equality and Social Change
Sexual education also plays a crucial role in promoting gender equality. In Sri Lanka, traditional gender roles often limit open discussion about female sexuality while excusing male dominance. Comprehensive sexual education challenges these norms by emphasizing mutual respect, shared responsibility, and equality in relationships.
Educating boys about consent and emotional expression helps reduce gender-based violence, while educating girls about bodily autonomy strengthens empowerment. In the long term, this contributes to healthier families and more equitable social structures.
The Way Forward for Sri Lanka
For sexual education to be effective in Sri Lanka, several steps are necessary. Teachers must receive proper training to handle the subject confidently and sensitively. Parents should be engaged through awareness programs to reduce fear and misconceptions. Curriculum developers must ensure that content is age-appropriate, culturally grounded, and scientifically accurate.
Importantly, sexual education should not be treated as a one-time lesson but as a continuous process integrated into broader life skills education. Collaboration between schools, healthcare providers, religious leaders, and community organisations can help normalise discussions around sexual health while respecting cultural values.
Finally , sexual education is not merely about sex; it is about health, dignity, safety, and responsible citizenship. The Sri Lankan experience demonstrates how silence and taboo can lead to misinformation, vulnerability, and social harm. International examples from the Netherlands, Sweden, and global initiatives supported by UNESCO clearly show that comprehensive sexual education leads to positive individual and societal outcomes.
For Sri Lanka, embracing sexual education does not mean abandoning cultural values. Rather, it means equipping young people with knowledge and ethical understanding to navigate modern social realities responsibly. In an era of rapid social and technological change, sexual education is not optional it is essential for building a healthy, informed, and compassionate society.
by Milinda Mayadunna ✍️
Features
A long-running identity conflict flares into full-blown war

 It was Iran’s first spiritual head of state, the late Ayatollah Khomeini, who singled out and castigated the US as the ‘Great Satan’ in the revolutionary turmoil of the late seventies of the last century that ushered in the Islamic Republic of Iran. The core issue driving the long-running confrontation between Islamic Iran and the West has been religious identity and the seasoned observer cannot be faulted for seeing the explosive emergence of the current war in the Middle East as having the elements of a religious conflict.
It was Iran’s first spiritual head of state, the late Ayatollah Khomeini, who singled out and castigated the US as the ‘Great Satan’ in the revolutionary turmoil of the late seventies of the last century that ushered in the Islamic Republic of Iran. The core issue driving the long-running confrontation between Islamic Iran and the West has been religious identity and the seasoned observer cannot be faulted for seeing the explosive emergence of the current war in the Middle East as having the elements of a religious conflict.
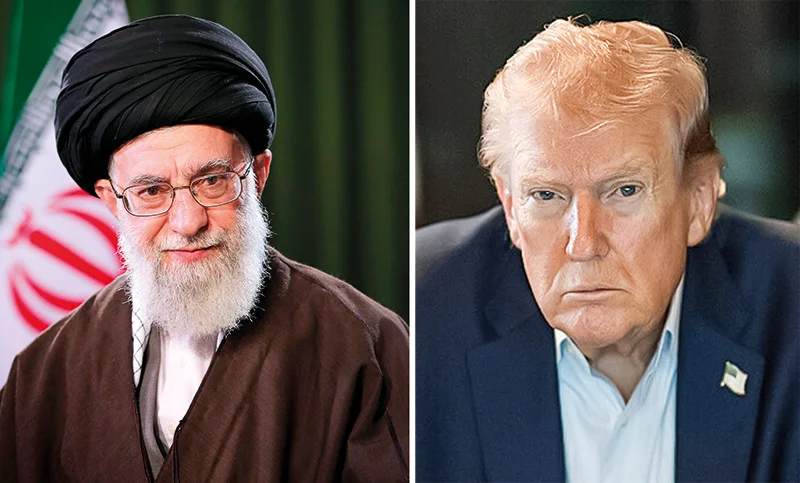
The current crisis in the Middle East which was triggered off by the recent killing of Iranian spiritual head of state Ayatollah Ali Khamenei in a combined US-Israel military strike is multi-dimensional and highly complex in nature but when the history of relations between Islamic Iran and the West, read the US, is focused on the religious substratum in the conflict cannot be glossed over.
In fact it is not by accident that US President Donald Trump resorts to Biblical language when describing Iran in his denunciations of the latter. Iran, from Trump’s viewpoint, is a primordial source of ‘evil’ and if the Middle East has collapsed into a full-blown regional war today it is because of the ‘evil’ influence and doings of Iran; so runs Trump’s narrative. It is a language that stands on par with that used by the architects of the Iranian revolution in the crucial seventies decade.
In other words, it is a conflict between ‘good’ and ‘evil’ and who is ‘good’ and who is ‘evil’ in the confrontation is determined mainly by the observer’s partialities and loyalties which may not be entirely political in kind. It should not be forgotten that one of President Trump’s support bases is the Christian Right in the US and in the rest of the West and the Trump administration’s policy outlook and actions should not be divorced from the needs of this segment of supporters to be fully made sense of.
The reasons for the strong policy tie-up between Rightist administrations in the US in particular and Israel could be better comprehended when the above religious backdrop is taken into consideration. Israel is the principal actor in the ‘Old Testament’ of the Bible and is seen as ‘the Chosen People of God’ and this characterization of Israel ought to explain the partialities of the Republican Right in particular towards Israel. Among other things, this partiality accounts for the strong defence of Israel by the US.
For the purposes of clarity it needs to be mentioned here that the Bible consists of two parts, an ‘Old’ and ‘New Testament’ , and that the ‘New Testament’ or ‘Message’ embodies the teachings of Jesus Christ and the latter teachings are seen as completing and in a sense giving greater substance to the ‘Old Testament’. However, Judaism is based mainly on ‘Old Testament’ teachings and Judaism is distinct from Christianity.
To be sure, the above theological explanation does not exhaust all the reasons for the war in the Middle East but the observer will be allowing an important dimension to the war to slip past if its importance is underestimated.
It is not sufficiently realized that the Iranian Islamic Revolution of 1979 utterly changed international politics and re-wrote as it were the basic parameters that must be brought to bear in understanding it. So important is the Islamic factor in contemporary world politics that it helped define to a considerable degree the new international political order that came into existence with the collapsing of the Cold War and the disintegration of the USSR .
Since the latter developments ‘political Islam’ could be seen as a chief shaping influence of international politics. For example, it accounts considerably for the 9/11 calamity that led to the emergence of fresh polarities in world politics and ushered in political terrorism of a most destructive kind that is today disquietingly visible the world over.
It does not follow from the foregoing that Islam, correctly understood, inspires terrorism of any kind. Islam proclaims peace but some of its adherents with political aims interpret the religion in misleading, divisive ways that run contrary to the peaceful intents of the faith. This is a matter of the first importance that sincere adherents of the faith need to address.
However, there is no denying that the Islamic Revolution in Iran of 1979 has been over the past decades a great shaper of international politics and needs to be seen as such by those sections that are desirous of changing the course of the world for the better. The revolution’s importance is such that it led to US political scientist Dr. Samuel P. Huntingdon to formulate his historic thesis that a ‘Clash of Civilizations’ is upon the world currently.
If the above thesis is to be adopted in comprehending the principal trends in contemporary world politics it could be said that Islam, misleadingly interpreted by some, is pitting a good part of the Southern hemisphere against the West, which is also misleadingly seen by some, as homogeneously Christian in orientation. Whereas, the truth is otherwise. The West is not necessarily entirely synonymous with Christianity, correctly understood.
Right now, what is immediately needed in the Middle East is a ceasefire, followed up by a negotiated peace based on humanistic principles. Turning ‘Spears into Ploughshares’ is a long gestation project but the warring sides should pay considerable attention to former Iranian President Mohammad Khatami’s memorable thesis that the world needs to transition from a ‘Clash of Civilizations’ to a ‘Dialogue of Civilizations’. Hopefully, there would emerge from the main divides leaders who could courageously take up the latter challenge.
It ought to be plain to see that the current regional war in the Middle East is jeopardising the best interests of the totality of publics. Those Americans who are for peace need to not only stand up and be counted but bring pressure on the Trump administration to make peace and not continue on the present destructive course that will render the world a far more dangerous place than it is now.
In the Middle East region a durable peace could be ushered if only the just needs of all sides to the conflict are constructively considered. The Palestinians and Arabs have their needs, so does Israel. It cannot be stressed enough that unless and until the security needs of the latter are met there could be no enduring peace in the Middle East.
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoBrilliant Navy officer no more
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoSri Lanka – world’s worst facilities for cricket fans
-

 Business1 day ago
Business1 day agoCabinet nod for the removal of Cess tax imposed on imported good
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoA life in colour and song: Rajika Gamage’s new bird guide captures Sri Lanka’s avian soul
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoOverseas visits to drum up foreign assistance for Sri Lanka
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoSri Lanka to Host First-Ever World Congress on Snakes in Landmark Scientific Milestone
-

 Latest News1 day ago
Latest News1 day agoAround 140 people missing after Iranian navy ship sinks off coast of Sri Lanka
-

 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoCan resourceful New Zealand lock in semi-final spot against already-qualified England?























