Features
SECRETARY MINISTRY OF EDUCATION, RETIREMENT AND BEYOND

by Eric. J. de Silva
The Ministry of Education was a totally new experience. When I called over at the Ministry to meet Mr. Ranil Wickremasinghe, the new minister, at the old colonial building at Malay Street in Colombo-2, he was candid enough to accept that things had not got better despite the political change at the Education Ministry, and that meant under the UNP administration which took over from its predecessor in 1977. He went on to say that I could make whatever changes that were necessary to rectify this situation and help the government to achieve the ultimate objective.
I was thus able to proceed to my room and take my seat without having any qualms about it. The discussions I had with Ministry officials and, wherever possible, with district officials showed in no uncertain terms that both at the center and the regions the Ministry was functioning at a pretty low level of efficiency and a thorough shake-up and appropriate remedial action seemed overdue.
This is what I set out to do with the fullest backing of the Minister. At my very first meeting with him, he made it clear that his priorities were to (i) re-organize the Ministry and make it a working outfit and (ii) prepare a White Paper on education reforms for the purpose of reaching some basic agreement with the general public. As far as re-organizing the Ministry was concerned he gave me a ‘carte blanche’ to pick the best possible team to man the key posts in the administration.
After a few days of deliberation and consultation with relevant persons both inside and outside the Ministry, I presented the Minister with a blueprint for a totally new structure for the Ministry with four divisions each under an Additional Secretary reporting to me. I suggested to bring into the Ministry several distinguished individuals – E.L. Wijemanne, M.B.C. Silva, and Neil Fernando – to head three of these divisions, towards which the Minister had no hesitation in giving his approval. Since Edward (E.L. Wijemanne) had already retired from service, he was offered the post of ‘Chief Adviser’ while others took up posts of Additional Secretary.
Thereafter, the Minister set up a number of Working Committees, involving the Ministries of Education, Higher Education and Youth Affairs, to prepare the contents of the White Paper on education reforms to be placed before Parliament and the people. An interesting feature in this exercise was the involvement of key officials associated with the formulation of the 1972 educational reforms in the drafting of the new proposals.
The 1972 reforms, despite being revolutionary and well-intentioned, had unfortunately fallen short in practice owing to their hasty implementation and the lack of prior public discussion, eventually becoming the subject of political controversy in the period leading to the 1977 General Elections.
Thus, the White Paper containing proposals for reforming general education, university education and tertiary (vocational, technical and professional) education was published in 1981 for public perusal and discussion, as White Papers are meant to do.
It contained a number of proposals relating to the formation of school clusters for better management, the diversification of university and tertiary-level courses, curriculum development, teachers’ service, administration of the education system and so on, making the White Paper a very comprehensive document that provided an excellent opportunity for agreement to be reached across the political divide. Unfortunately, this did not happen.
The UNP, while being in the opposition, had exploited public disaffection with the 1972 reforms to gain political advantage – and now it was the turn of their opponents, the constituent parties of the previous United Front government. The White Paper got caught up in what Dr. P. Udagama so aptly described as “Education in Sri Lanka is very much a political act and sometimes it is a party political act.” Much of the debate sparked off by the White Paper was based not on its contents but on hearsay and partisan political propaganda, including claims that it was an insidious attempt to make inroads into free education and introduce privatization through the backdoor as part of the open economy that the ruling party was wedded to.
There was very little informed discussion but an abundance of slogan shouting, highly charged political protests and street demonstrations, often fuelled by the JVP that had come out of its shell since the debacle it suffered in the early seventies.
With a General Election not too far away, Government MPs got cold feet and pressurized President J.R. Jayewardene not to proceed with the White Paper other than for a few non-controversial proposals. What this experience showed us was that even White Papers can get caught up in political hailstorms, instead of paving the way for rational discussion.
RETIREMENT FROM
GOVERNMENT SERVICE
AND BEYOND
Following my stint at the Ministry of Education, I went on a five-year period of leave from government service to serve as the Chief Technical Advisor for the ‘Quality Improvement of General Education’ project implemented by UNDP and UNESCO in the 1980s. The objective of this project was to introduce a new subject known as ‘Life Skills’ into the secondary school curriculum, which was to help students acquire a number of skills needed in day to day life as the name suggests; such as changing a light bulb, fixing a tyre puncture and so on.
Many distinguished individuals from the field of education, including Prof J. E. Jayasuriya, served as advisors to this project alongside foreign consultants. I was fortunate to have the services of a team of very committed professionals such as J.H.S. Tissera and D. S. Mettananda to assist me. Together, we developed the curriculum for the new subject, conducted a number of pilot programmes and implemented it in a phased-out manner. Although regrettably this subject is not taught in schools today, I believe it would have undoubtedly been useful to those students who had the opportunity to study it in school.
Thereafter, I returned to the public service to take up the position of Director at Sri Lanka Institute of Development Administration (SLIDA), the country’s premier training institute for the public service. It needs mention that this was a position I had held many years before, when the institution was called the Academy of Administrative Studies. I remained as the Director of SLIDA until my retirement from the service in 1990, upon which I engaged in an independent capacity in several projects both locally and overseas.
The first such project I took up post-retirement was to serve as the Senior Technical Adviser to a UN-ESCAP initiative, the Jakarta Plan of Action for Human Resource Development in Asia and the Pacific Region.
This appointment required me to reside in Bangkok for over two years, and marked the first time that I had lived overseas for such a long period. I was fortunate enough to secure accommodation at an apartment block where one of my close friends, Mr. Selvaratnam and his wife, also lived.
Immediately following this assignment, I undertook a short stint as the team leader of a UNDP Mission to evaluate the National Institute of Education in 1993, back in Sri Lanka.
The year 1993 bore witness to a dramatic upheaval in Sri Lankan political history with the assassination of President R. Premadasa. When Mr. Ranil Wickramasinghe – with whom I had worked closely during my time at the Ministry of Education – succeeded to the position of Prime Minister, he invited me in November 1993 to serve as an Advisor to him in my capacity as a retired government official.
At the time, Mr K.M. Abeysingha was serving as the Secretary to the Prime Minister. One of my responsibilities in this role was to coordinate the Development Secretaries’ meeting that was presided over by the PM, which facilitated the expediting of many development projects during this time. I held this position until September, 1994.
My involvement in educational policy did not end with the change of government as I was invited in May 1997 to take on the position of Director-General of the Education Reforms Implementation Unit, a separate unit set up by President Chandrika Kumaratunge for the purpose of fast-tracking the reforms proposed by the Presidential Task Force set up in 1996 with regard to improvements in general education. I held this position for a period slightly exceeding one year. More information on these reforms can be found in my book, Politics of Education Reform.
Sometime thereafter, together with Dr. G. Usvatte-Aratchi, Dr. W.M.K. Wijetunga, D.S. Mettananda and Dr. K.S.E. Jayatilleke, I convened an independent group of individuals interested in educational policy, which was named the Education Research and Study Group (ERSG). In 1999, the ERSG organized a policy dialogue on the subject of the Ministry’s proposal on the restructuring of schools, the proceedings of which were published and made available to Parliamentarians and the general public.
This discussion (which too can be found as an addendum in Politics of Education Reform) provided valuable insights on the education policy-making process in Sri Lanka, as well as arguments for and against the proposed restructuring. Suffice it to say that the restructuring proposal was abandoned by the Ministry soon thereafter.
Nearly five years later and having declined multiple opportunities offered to me from time to time, I finally accepted the position of Adviser to the Ministry of Policy Development and Implementation in April 2003, which was to be my last formal engagement in policy matters. During the next one year up to April 2004, I served as the Convener of the Steering Committee on Human Resources Development under the Regaining Sri Lanka initiative spearheaded by Mr Ranil Wickramasinghe in his second period as Prime Minister.
The committee consisted of a number of individuals from diverse backgrounds of expertise, such as well-known academics and representatives of the private sector. Thus ended my 45-year spell in public service and administration.
Features
US foreign policy-making enters critical phase as fascist threat heightens globally

 It could be quite premature to claim that the US has closed ranks completely with the world’s foremost fascist states: Russia, China and North Korea. But there is no denying that the US is breaking with tradition and perceiving commonality of policy orientation with the mentioned authoritarian states of the East rather than with Europe and its major democracies at present.
It could be quite premature to claim that the US has closed ranks completely with the world’s foremost fascist states: Russia, China and North Korea. But there is no denying that the US is breaking with tradition and perceiving commonality of policy orientation with the mentioned authoritarian states of the East rather than with Europe and its major democracies at present.
Increasingly, it is seemingly becoming evident that the common characterization of the US as the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’, could be a gross misnomer. Moreover, the simple fact that the US is refraining from naming Russia as the aggressor in the Russia-Ukraine conflict and its refusal to perceive Ukraine’s sovereignty as having been violated by Russia, proves that US foreign policy is undergoing a substantive overhaul, as it were. In fact, one could not be faulted, given this backdrop, for seeing the US under President Donald Trump as compromising its democratic credentials very substantially.
Yet, it could be far too early to state that in the traditional East-West polarity in world politics, that the US is now squarely and conclusively with the Eastern camp that comprises in the main, China and Russia. At present, the US is adopting an arguably more nuanced approach to foreign policy formulation and the most recent UN Security Council resolution on Ukraine bears this out to a degree. For instance, the UN resolution in question reportedly ‘calls for a rapid end to the war without naming Russia as the aggressor.’
That is, the onus is being placed on only Ukraine to facilitate an end to the war, whereas Russia too has an obligation to do likewise. But it is plain that the US is reflecting an eagerness in such pronouncements to see an end to the Ukraine conflict. It is clearly not for a prolongation of the wasting war. It could be argued that a negotiated settlement is being given a try, despite current international polarizations.
However, the US could act constructively in the crisis by urging Russia as well to ensure an end to the conflict, now that there is some seemingly friendly rapport between Trump and Putin.
However, more fundamentally, if the US does not see Ukraine’s sovereignty as having been violated by Russia as a result of the latter’s invasion, we are having a situation wherein the fundamental tenets of International Law are going unrecognized by the US. That is, international disorder and lawlessness are being winked at by the US.
It follows that, right now, the US is in cahoots with those powers that are acting autocratically and arbitrarily in international politics rather than with the most democratically vibrant states of the West, although a facile lumping together of the US, Russia and China, is yet not possible.
It is primarily up to the US voting public to take clear cognizance of these developments, draw the necessary inferences and to act on them. Right now, nothing substantive could be done by the US voter to put things right, so to speak, since mid-term US elections are due only next year. But there is ample time for the voting public to put the correct perspective on these fast-breaking developments, internationally and domestically, and to put their vote to good use in upcoming polls and such like democratic exercises. They would be acting in the interest of democracy worldwide by doing so.
More specifically it is up to Donald Trump’s Republican voter base to see the damage that is being done by the present administration to the US’ standing as the ‘world’s mightiest democracy’. They need to bring pressure on Trump and his ‘inner cabinet’ to change course and restore the reputation of their country as the foremost democracy. In the absence of such action it is the US citizenry that would face the consequences of Trump’s policy indiscretions.
Meanwhile, the political Opposition in the US too needs to get its act together, so to speak, and pressure the Trump administration into doing what is needed to get the US back to the relevant policy track. Needless to say, the Democratic Party would need to lead from the front in these efforts.
While, in the foreign policy field the US under President Trump could be said to be acting with a degree of ambivalence and ambiguity currently, in the area of domestic policy it is making it all to plain that it intends to traverse a fascistic course. As has been proved over the past two months, white supremacy is being made the cardinal principle of domestic governance.
Trump has made it clear, for example, that his administration would be close to ethnic chauvinists, such as the controversial Ku Klux Klan, and religious extremists. By unceremoniously rolling back the ‘diversity programs’ that have hitherto helped define the political culture of the US, the Trump administration is making no bones of the fact that ethnic reconciliation would not be among the government’s priorities. The steady undermining of USAID and its main programs worldwide is sufficient proof of this. Thus the basis has been adequately established for the flourishing of fascism and authoritarianism.
Yet, the US currently reflects a complex awareness of foreign policy questions despite having the international community wondering whether it is sealing a permanent alliance with the main powers of the East. For instance, President Trump is currently in conversation on matters in the external relations sphere that are proving vital with the West’s principal leaders. For example, he has spoken to President Emmanuel Macron of France and is due to meet Prime Minister Keir Starmer of the UK.
Obviously, the US is aware that it cannot ‘go it alone’ in resolving currently outstanding issues in external relations, such as the Ukraine question. There is a clear recognition that the latter and many more issues require a collaborative approach.
Besides, the Trump administration realizes that it cannot pose as a ‘first among equals’, given the complexities at ground level. It sees that given the collective strength of the rest of the West that a joint approach to problem solving cannot be avoided. This is particularly so in the case of Ukraine.
The most major powers of the West are no ‘pushovers’ and Germany, under a possibly Christian Democratic Union-led alliance in the future, has indicated as much. It has already implied that it would not be playing second fiddle to the US. Accordingly, the US is likely to steer clear of simplistic thinking in the formulation of foreign policy, going forward.
Features
Clean Sri Lanka – hiccups and remedies

by Upali Gamakumara,
Upali.gamakumara@gmail.com
The Clean Sri Lanka (CSL) is a project for the true renaissance the NPP government launched, the success of which would gain world recognition. It is about more than just cleaning up places. Its broader objectives are to make places attractive and happy for people who visit or use services in the country, focusing more on the services in public institutions and organisations like the SLTB. Unfortunately, these broader objectives are not apparent in its theme, “Clean Sri Lanka,” and therefore there is a misconception that keeping the environment clean is the main focus.
People who realise the said broader objectives are excited about a cleaner Sri Lanka, hoping the President and the government will tackle this, the way they are planning to solve other big problems like the economy and poverty. However, they do not see themselves as part of the solution.
From the management perspective, the CSL has a strategic plan that is not declared in that manner. When looking at the government policies, one can perceive its presence, the vision being “A Prosperous Nation and a Beautiful Life,” the mission “Clean Sri Lanka” and the broader objectives “a disciplined society, effective services, and a cleaner environment.” If the government published these as the strategy, there would have been a better understanding.
Retaining the spirit and expectations and continuing the ‘Clean Sri Lanka’ project is equally important as much as understanding its deep idea. For this, it needs to motivate people, which differs from those motivators that people push to achieve selfish targets. The motivation we need here is to evolve something involuntarily, known as Drivers. Drivers push for the survival of the evolution or development of any entity. We see the absence of apparent Drivers in the CSL project as a weakness that leads to sporadic hiccups and free flow.
Drivers of Evolution
Drivers vary according to the nature of envisaged evolution for progress. However, we suggest that ‘the force that pushes anything to evolve’ would fit all evolutions. Some examples are: ‘Fitting to survival’ was the driver of the evolution of life. Magnetism is a driver for the unprecedented development of physics – young Einstein was driven to enquire about the ‘attraction’ of magnets, eventually making him the greatest scientist of the 20th century.
Leadership is a Driver. It is essential but do not push an evolution continually as they are not sprung within a system involuntarily. This is one of the reasons why CSL has lost the vigour it had at its inception.
CSL is a teamwork. It needs ‘Drives’ for cohesion and to push forward continually, like the Quality Improvement Project of the National Health Service (NHS) in England. Their drivers are outlined differently keeping Aims as their top driver and saying: Aims should be specific and measurable, not merely to “improve” or “reduce,” engage stakeholders to define the aim of the improvement project and a clear aim to identify outcome measures.
So, we think that CSL needs Aims as defined by NHS, built by stakeholder participation to help refine the project for continuous evolution. This approach is similar to Deming’s Cycle for continual improvement. Further, two more important drivers are needed for the CSL project. That is Attitudinal Change and Punishment. We shall discuss these in detail under Psychoactive Environment (pSE) below.
Aside from the above, Competition is another driver in the business world. This helps achieve CSL objectives in the private sector. We can see how this Driver pushes, with the spread of the Supermarket chains, the evolution of small and medium retail shops to supermarket level, and in the private banks and hospitals, achieving broader objectives of CSL; a cleaner environment, disciplined behaviuor, efficient service, and the instillation of ethics.
The readers can now understand the importance of Drivers pushing any project.
Three Types of Entities and Their Drives
We understand, that to do the transformation that CSL expects, we need to identify or adopt the drivers separately to suit the three types of entities we have in the country.
Type I entities are the independent entities that struggle for their existence and force them to adopt drivers involuntarily. They are private sector entities, and their drivers are the commitment of leadership and competition. These drivers spring up involuntarily within the entity.
Type II are the dependent entities. To spring up drivers of these entities commitment of an appointed trustee is a must. Mostly in state-owned entities, categorized as Boards, Authorities, Cooperations, and the like. Their drivers do not spring up within or involuntarily unless the leader initiates. The Government of a country also falls into this type and the emergence of drivers depends on the leader.
Type III entities have neither independent nor dependent immediate leader or trustee. They are mostly the so-called ‘Public’ places like public-toilets, public-playgrounds, and public-beaches. No team can be formed as these places are open to any, like no-man-land. Achieving CSL objectives at these entities depends on the discipline of the public or the users.
Clean Sri Lanka suffers the absence of drivers in the second and third types of entities, as the appointed persons are not trustees but temporary custodians.
The writer proposes a remedy to the last two types of entities based on the theory of pSE explained below.
Psychoactive Environment (pSE) –
The Power of Customer Attraction
Research by the writer introduced the Psychoactive Environment (pSE) concept to explain why some businesses attract more customers than others who provide the same service. Presented at the 5th Global Conference on Business and Economics at Cambridge University in 2006, the study revealed that a “vibe” influences customer attraction. This vibe, termed pSE, depends on Three Distinct Elements, which can either attract or repel customers. A positive pSE makes a business more attractive and welcoming. This concept can help develop Drivers for Type II and III entities.
pSE is not an all-inclusive solution for CSL, but it lays the foundation for building Drivers and motivating entities to keep entrants attractive and contented.
The structure of the pSE
The three distinct Elements are the Occupants, Systems, and Environment responsible for making a pSE attractive to any entity, be it a person, institution, organization, or county. Each of these elements bears three qualities named Captivators. These captivators are, in simple terms, Intelligent, Nice, and Active in their adjective forms.
pSE theorizes that if any element fails to captivate the entrant’s mood by not being Intelligent, Nice, or Active, the pSE becomes negative, repelling the entrant (customer). Conversely, the positive pSE attracts the entrants if the elements are Intelligent, Nice, and Active.
For example, think person who comes to a Government Office for some service. He sees that the employees, service, and environment are intelligent, nice, and active, and he will be delighted and contented. He will not get frustrated or have any deterioration in national productivity.
The Significance of pSE in CSL
The Elements and the Captivators are universal for any entity. Any entity can easily find its path to Evolution or Progress determined by these elements and captivators. The intangible broader objectives can be downsised to manageable targets by pSE. Achievements of these targets make the entrants happy and enhance productivity – the expectation of Clean Sri Lanka (CSL).
From the perspective of pSE, now we can redefine the Clean Sri Lanka project thus:
To make the Elements of every entity in Sri Lanka: intelligent, Nice, and Active.
How Would the pSE be A Remedy for The Sporadic Hiccups?
We have seen two possible reasons for sporadic setbacks and the discontinuity of some projects launched by the CSL. They are:
The absence of involuntary Drivers for evolvement or progress
Poor attitudes and behaviors of people and leaders
Remedy for the Absence of Drivers
Setting up a system to measure customer or beneficiary satisfaction, and setting aims can build Drivers. The East London NHS principles help build the Aims that drive type II & II entities. The system must be designed to ensure continual improvement following the Deming Cycle. This strategy will create Drivers for Type I & II entities.
This process is too long to explain here therefore we refrain from detailing.
Attitudinal Change
The most difficult task is the attitudinal and behavioural change. Yet it cannot be postponed.
Punishment as a strategy
In developed countries, we see that people are much more disciplined than in the developing countries. We in developing countries, give credit to their superior culture, mitigating ours as rudimental. The long experience and looking at this affair from a vantage point, one will understand it is not the absolute truth. Their ruthless wars in the past, rules, and severe punishment are the reasons behind this discipline. For example, anyone who fails to wear a car seatbelt properly will be fined 400 AUD, nearly 80,000 LKR!
The lesson we can learn is, that in Sri Lanka, we need strong laws and strict punishment together with a type of strategic education as follows.
Psychological Approach as a Strategy
The psychological theory of attitude formation can be used successfully if some good programmes can be designed.
All attitude formations start with life experience. Formed wrong or negative attitudes can be reversed or instilled with correct attitudes by exposure to designed life experiences. The programmes have been developed using the concepts of Hoshin Kanri, Brainstorming, Cause-and-Effect analysis, and Teamwork, in addition to London NTS Quality Improvement strategies.
The experience and good responses we received for our pSE programs conducted at several institutions prove and have built confidence in our approach. However, it was a time, when governments or organisations did not pay much attention to cultural change as CSL expects in the country.
Therefore, we believe this is a golden opportunity to take the CSL supported by the pSE concept.
Features
Visually impaired but ready to do it their way
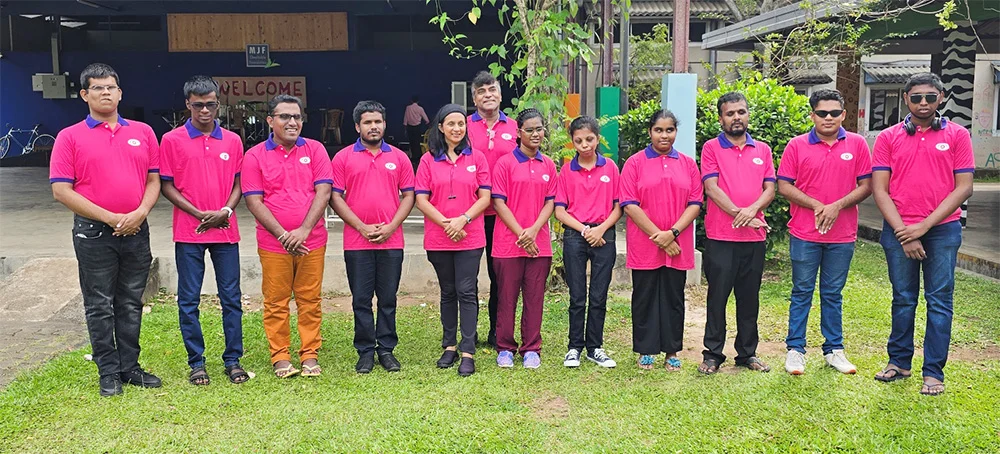

 Although they are visually impaired youngsters, under the guidance of renowned musician Melantha Perera, these talented individuals do shine bright … hence the name Bright Light.
Although they are visually impaired youngsters, under the guidance of renowned musician Melantha Perera, these talented individuals do shine bright … hence the name Bright Light.
Says Melantha: “My primary mission is to nurture their talent and ensure their sustainable growth in music, and I’m thrilled to announce that Bright Light’s first public performance is scheduled for 7th June, 2025. The venue will be the MJF Centre Auditorium in Katubadda, Moratuwa.”
Melantha went on to say that two years of teaching, online, visually impaired youngsters, from various parts of the island, wasn’t an easy ride.
There were many ups and downs but Melantha’s determination has paid off with the forming of Bright Light, and now they are gearing up to go on stage.
According to Melantha, they have come a long way in music.
“For the past few months, we have been meeting, physically, where I guide them to play as a band and now they show a very keen interest as they are getting to the depth of it. They were not exposed to English songs, but I’ve added a few English songs to widen their repertoire.

Melantha Perera: Invented a notation
system for the guitar
“On 7th June, we are opening up for the public to come and witness their talents, and I want to take this product island-wide, giving the message that we can do it, and I’m hoping to create a database so there will be a following. Initially, we would like your support by attending the show.”
Melantha says he didn’t know what he was getting into but he had confidence teaching anyone music since he has been in the scene for the past 45 years. He began teaching in 2015,
“When I opened my music school, Riversheen School of Music, the most challenging part of teaching was correcting tone deaf which is the theoretical term for those who can’t pitch a note, and also teaching students to keep timing while they sang and played.”
Melantha has even invented a notation system for the guitar which he has named ‘MelaNota’. He has received copyrights from the USA and ISO from Australia, but is yet to be recognised in Sri Lanka.
During Covid-19, Melantha showcased MelaNota online and then it was officially launched with the late Desmond De Silva playing one of his tunes, using MelaNota.
Melantha says that anyone, including the visually impaired, can play a simple melody on a guitar, within five minutes, using his notation system.
“I’ve completed the system and I’m now finalising the syllabus for the notation system.”
Melantha has written not only for the guitar, but also for drums, keyboards, and wind instruments.
For any queries, or additional information, you could contact Melantha at 071 454 4092 or via email at thebandbrightlight@gmail.com.
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoSri Lanka’s 1st Culinary Studio opened by The Hungryislander
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoHow Sri Lanka fumbled their Champions Trophy spot
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoKiller made three overseas calls while fleeing
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoSC notices Power Minister and several others over FR petition alleging govt. set to incur loss exceeding Rs 3bn due to irregular tender
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoThe Murder of a Journalist
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoMahinda earn long awaited Tier ‘A’ promotion
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoExcellent Budget by AKD, NPP Inexperience is the Government’s Enemy
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoMobile number portability to be introduced in June