Foreign News
Peru’s ex-president and first lady sentenced to 15 years in jail

Peru’s former president, Ollanta Humala, has been found guilty of money laundering and sentenced to 15 years in prison.
A court in the capital, Lima, said he had accepted illegal funds from the Venezuelan president at the time, Hugo Chávez, and from the Brazilian construction company Odebrecht to bankroll his election campaigns in 2006 and 2011.
Humala’s lawyer said he would appeal against the conviction.
His wife, Nadine Heredia, was also found guilty of money laundering and sentenced to 15 years in jail. However, she has been granted safe passage to Brazil after seeking asylum in the Brazilian embassy.
Humala’s lawyer said he would appeal against the conviction.
Unlike her husband, Heredia was not present in court when Judge Nayko Coronado passed sentence – she had entered the Brazilian embassy along with the couple’s son before an arrest warrant could be executed.
Brazil offered her asylum and the Peruvian government said it would honour the 1954 asylum convention to grant both Heredia and her son safe passage.
The former president, 62, was meanwhile taken to Barbadillo prison, where two other former leaders, Alejandro Toledo and Pedro Castillo, are already being held.
Humala was the first of four Peruvian presidents to be investigated in connection with the Odebrecht scandal.
Toledo, who governed from 2001 to 2006, was sentenced last year to more than 20 years in prison for taking $35m (£26m) in bribes from the company.
Alan García, president from 1985 to 1990 and 2006 to 2011, killed himself in 2019 as he faced imminent arrest over allegations he was bribed by Odebrecht. He had denied the accusations.
Pedro Pablo Kuczynski, in office from 2016 to 2018, faced impeachment proceedings after it emerged that Odebrecht had paid him millions of dollars in his previous government role.
The investigation is ongoing. Kuczynski has always maintained the payments were not illegal.
Prosecutors said that Humala and his wife, with whom he co-founded the Nationalist Party, had accepted $3m in illegal contributions from the firm, which they used to finance his 2011 presidential campaign.
They also accused of taking $200,000 from Venezuelan leader Hugo Chávez to bankroll the 2006 campaign.
The couple have always maintained that they are the victims of political persecution.
Humala’s lawyer, Wilfredo Pedraza, also said that their 15-year sentence was “excessive”.
Prosecutors had asked for 20 years for the ex-president and 25 and a half years for Heredia.
[BBC]
Foreign News
South Korea’s former first lady sentenced to jail term in bribery case
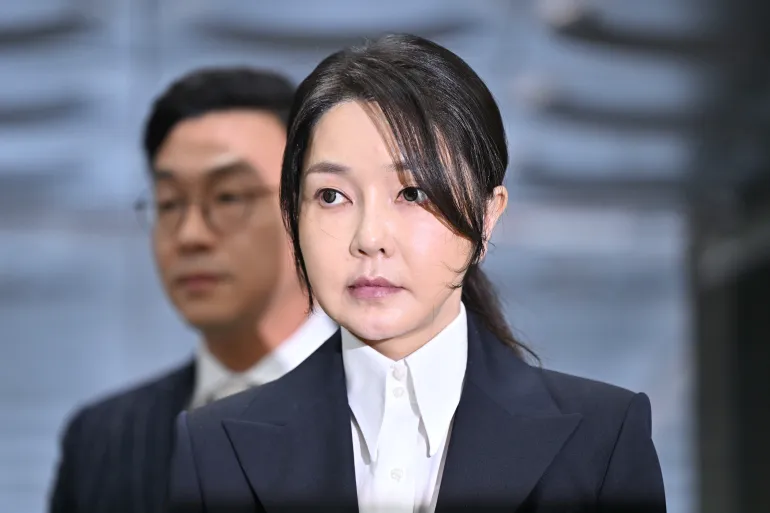

A South Korean court has sentenced former First Lady Kim Keon Hee to one year and eight months in prison after finding her guilty of accepting bribes from the Unification Church, according to South Korea’s official Yonhap news agency.
The Seoul Central District Court on Wednesday cleared Kim, the wife of disgraced ex-President Yoon Suk Yeol, of additional charges of stock price manipulation and violating the political funds act.
Kim was accused of receiving bribes and lavish gifts from businesses and politicians, as well as the Unification Church, totaling at least $200,000.
The prosecution team had also indicted Unification Church leader Han Hak-ja, now on trial, after the religious group was suspected of giving Kim valuables, including two Chanel handbags and a diamond necklace, as part of its efforts to win influence with the president’s wife.
Prosecutors in December said Kim had “stood above the law” and colluded with the religious sect to undermine “the constitutionally mandated separation of religion and state”.

Prosecutor Min Joong-ki also said South Korea’s institutions were “severely undermined by abuses of power” committed by Kim.
The former first lady had denied all the charges, claiming the allegations against her were “deeply unjust” in her final testimony last month.
But she has also apologised for “causing trouble despite being a person of no importance”.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
Plane crash kills prominent Indian politician Ajit Pawar
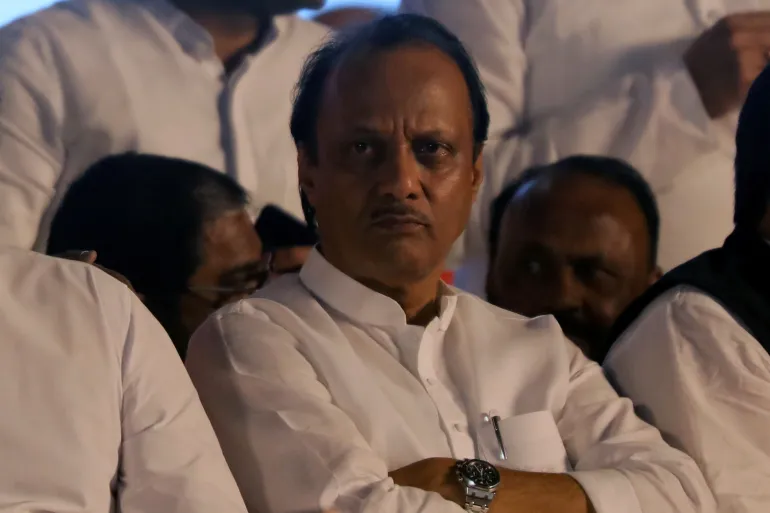

A plane crash has killed the deputy chief minister of India’s Maharashtra state, Ajit Pawar, the country’s aviation regulator has said.
The plane, which took off from the state capital, Mumbai, on Wednesday, crash-landed at the airport in Pawar’s constituency of Baramati, according to the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
Two members of the prominent politician’s staff and two crew members were also reported to have been killed.
The cause of the crash has not yet been officially confirmed.
Flightradar24, an online flight tracking service, said the aircraft was attempting a second approach to Baramati airport when it crashed.
The Times of India newspaper quoted DGCA officials as saying the aircraft, a Learjet 45 operated by a company called VSR, crashed at about 8:45am local time (03:15 GMT).
The daily said Pawar, the nephew of veteran politician Sharad Pawar, who founded the Nationalist Congress Party (NCP), was on his way to attend a public rally for the district council elections.
A witness quoted by the newspaper said the aircraft exploded moments after hitting the ground.
“When we rushed to the spot, the aircraft was on fire. There were four to five more explosions. People tried to pull the passengers out, but the fire was too intense,” said the witness.

Pawar, 66, built his political base through the grassroots cooperative movement. He was a key figure in state politics and served as the second-highest elected official in Maharashtra, as part of the larger federal governing coalition led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
He wielded considerable influence in the state’s vibrant sugar belt and was known for his ability to mobilise rural voters.
[Aljazeera]
Foreign News
Naqvi casts uncertainty on Pakistan’s participation in T20 World Cup after Bangladesh ouster

Pakistan’s participation at the upcoming Men’s T20 World Cup 2026 has been thrown into uncertainty after the PCB chairman Mohsin Naqvi said a final decision would be made after talking to Pakistan’s government. Speaking shortly after the ICC officially removed Bangladesh from the T20 World Cup owing to their refusal to play in India, Naqvi accused the ICC of “double standards” favouring India, and termed what happened to Bangladesh “an injustice”.
“Our stance on World Cup participation will be what the government of Pakistan instructs me,” he said. “The Prime Minister is not in Pakistan right now. When he returns, I’ll be able to give you our final decision. It’s the government’s decision. We obey them, not the ICC.”
Over the past week or so, Pakistan has firmly thrown its support behind Bangladesh in their dispute with the ICC demanding a venue outside of India to play their T20 World Cup matches. At an ICC meeting last week, the PCB was understood to be the only board to back the BCB in their stance. The tournament is jointly hosted by India and Sri Lanka, but Bangladesh’s games were all scheduled in India. Bangladesh, however, have said it is no longer safe for them to play in India after the BCCI, on January 3, instructed Kilkata Knight Riders to release Mustafizur Rahman rom their IPL 2026 squad.
Though no reason was stated for that directive, it came amid deteriorating relations between India and Bangladesh. On January 4, the BCB wrote to the ICC after consultation with the government that the Bangladesh team would not travel to India for its T20 World Cup matches due to security concerns, a stance it stuck to through several subsequent discussions with the ICC.
The ICC has repeatedly refused Bangladesh’s request, and earlier this week gave them an ultimatum demanding them to accept the schedule as it was, or face being removed from the tournament. On Saturday, with Bangladesh sticking to their position, the ICC formally announced Bangladesh would not be part of the T20 World Cup, and would be replaced instead by Scotland.
Naqvi was critical of the decision, calling it an injustice to Bangladesh. “I think Bangladesh has been hard done by,” he said. “You can’t have double standards. You can’t say for one country [India] they can do whatever they want and for the others to have to do the complete opposite. That’s why we’ve taken this stand, and made clear Bangladesh have had an injustice done to them. They should play in the World Cup, they are a major stakeholder in cricket.”
While there have been local, unverified reports that the PCB would refuse to participate in the World Cup in solidarity with Bangladesh should they be removed, the PCB has declined to confirm to ESPNcricinfo when approached. Naqvi’s comments to the media on Saturday was the first time anyone at the PCB has directly addressed the issue, where he repeatedly said the decision was no longer in the hands of the PCB.
“If the government of Pakistan says we mustn’t play, then maybe the ICC will bring in a 22nd team (after Scotland). It’s up to the government.”
No specific reason was given by Naqvi other than to support Bangladesh, as to why government permission would now be required for an event that starts in two weeks. Last year, both BCCI and PCB, with the approval of ICC, signed up to a hybrid model agreement by which both countries would play each other on neutral territory for all global events in the 2024-27 rights cycle.
Pakistan play all their games in Sri Lanka for this event (which already was a co-hosted event) and are scheduled to play the opening game of the tournament, against Netherlands on February 7. They are scheduled to play India on February 15 in Colombo in their group stage clash.
[Cricinfo]
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoComBank, UnionPay launch SplendorPlus Card for travelers to China
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoComBank advances ForwardTogether agenda with event on sustainable business transformation
-

 Opinion7 days ago
Opinion7 days agoRemembering Cedric, who helped neutralise LTTE terrorism
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoConference “Microfinance and Credit Regulatory Authority Bill: Neither Here, Nor There”
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoCORALL Conservation Trust Fund – a historic first for SL
-
 Opinion6 days ago
Opinion6 days agoA puppet show?
-

 Opinion3 days ago
Opinion3 days agoLuck knocks at your door every day
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days ago‘Building Blocks’ of early childhood education: Some reflections













