Business
Can Overseas Sri Lankans finally have their say?

Voting Beyond Borders:
 Dr Bilesha Weeraratne is a Research Fellow and Head of Migration and Urbanisation Research at IPS. Prior to re-joining IPS in 2014, she was a Postdoctoral Research Associate at Princeton University, New Jersey, USA. Her research interests include internal and international migration, climate mobility, urbanisation, the economics of education, labour economics, economic development, econometrics and economic modeling. She holds an MA in Economics from Rutgers University, USA and an MPhil and PhD in Economics from the City University of New York, USA.
Dr Bilesha Weeraratne is a Research Fellow and Head of Migration and Urbanisation Research at IPS. Prior to re-joining IPS in 2014, she was a Postdoctoral Research Associate at Princeton University, New Jersey, USA. Her research interests include internal and international migration, climate mobility, urbanisation, the economics of education, labour economics, economic development, econometrics and economic modeling. She holds an MA in Economics from Rutgers University, USA and an MPhil and PhD in Economics from the City University of New York, USA.
By Dr Bilesha Weeraratne
The recent presidential election in Sri Lanka marked a series of “firsts,” setting it apart from previous elections. It saw a record-low number of 350,516 valid voters per candidate, implementation of the Regulation of Election Expenditure Act of 2023, and a second count of votes. Notably, there was also greater engagement from Overseas Sri Lankans (OSLs) in the country’s electoral process than at any time previously.
Indeed President Anura Kumara Dissanayaka actively engaged with Sri Lankan expatriates during his campaign, visiting countries including South Korea, Australia, the USA, Canada, Sweden, the UK and Japan. Continuing a trend from the previous presidential election in 2019, there was evidence of Sri Lankans returning to vote. However, despite this enthusiasm, the long-standing debate over granting OSLs the right to vote from abroad remains unresolved. Of the OSLs, it also means 1.5 million Sri Lankan workers abroad could not vote in the recent election according to the SLBFE.
Voting with Their Wallets
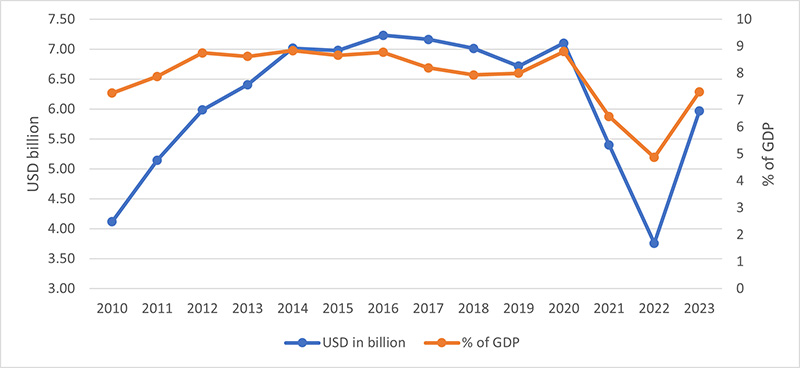
While OSLs may not have voting rights yet, those who regularly remit earnings back to Sri Lanka have already demonstrated their influence—by voting with their wallets. In the run-up to the 2022 economic crisis, government efforts to attract more formal remittances by offering higher interest rates failed to convince OSLs, as the formal foreign exchange rate offered was far below the informal rate. As a result, in 2022, remittances to Sri Lanka declined by a record 42%. Compared to the steady 10-year average USD 6.4 billion inflow (from 2010 to 2020), the decline to USD 3.7 billion was the final nail in the coffin that sparked the 2022 sovereign debt default.
Remittance and Voting Rights
The literature identifies three mechanisms for linking the receipt of remittances with political participation.
1) Income Channel: those with greater resources are able to devote more resources (both in terms of material support and time) to political activities;
2) Independence Channel: remittances reduce the dependence of recipients on the government for material prosperity; and
3) Insurance Channel -remittances promote feelings of economic security in recipients that allow them to pay more attention to non-material concerns.
While these mechanisms are for all voters in households receiving remittances, OSLs prefer a say in how the macroeconomy back in Sri Lanka is managed by elected officials, i.e. how does the government spend the foreign exchange OSLs regularly send as remittances? what are the interest rates on their savings? how is inflation feeding into the purchasing power of their remittances? how is the foreign exchange rate affecting the disposable income of their remittances? how are savings and investments of their remittances taxed? and what are the public services available to their families left behind? to name a few. The answers to such questions are linked to election promises and how governments actually perform when in office. Voting rights would allow OSLs a voice in economic policies that impact their remittances and financial interests in Sri Lanka.
Overseas Absentee Voting:
A Long-Awaited Promise
Providing voting rights or Overseas Absentee Voting (OAV) has been in discussion for many years, with various candidates, including the current president, promising to make it a reality. Sri Lanka has also ratified the United Nations Convention on the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of their Families, which calls for migrant workers’ voting rights (Article 41). Many previous governments, though keen, have not been successful on this front. Previous efforts include a Parliamentary Select Committee for Electoral Reforms recommending voting rights for OSLs in 2021, and a Special Presidential Commission in 2023 (among other issues) being required to make recommendations on a mechanism for OSL voting rights. In 2023, the Election Commission developed a beta version of an online method for registering OSLs for voting. However, according to the Commissioner General of Elections their hands are tied “until the Parliament passes a law to enable migrant workers to vote from their destination states.”
How to Make Overseas Absentee Voting a Reality
There are many possible and sophisticated ways to implement OAV, including advanced in-person (similar to postal voting in Sri Lanka), voting by mail, facsimile, or internet, as well as proxy voting (where a duly authorised representative or a proxy vote on behalf of the absent voter). Some countries such as the Philippines, for instance, use a combination of in-person and postal voting.
For Sri Lanka, keeping things simple would be one important mindset in transitioning from an eternal election promise to making overseas absentee voting a reality. A manageable starting point could be advanced in-person in-embassy voting, which would function analogous to Sri Lanka’s postal voting system. Embassies could serve as analogous to postal voting centers for expatriates, and OLSs to postal voters.
Hence, learning from the Philippines, a few key steps in the process of allowing in-person in-embassy voting are:
Enshrine in the Constitution the right of qualified OSLs to vote
Enact an Act related to OAV
Define a system and the mechanism for exercising such rights, covering aspects of
Defining qualifications for OAV
Identifying a registration procedure for eligible OSL
Identifying voting and vote counting mechanisms.
Not an Easy Road
Implementing OAV will not be without challenges. For Sri Lankans residing in countries without a local embassy, registration and voting might require travel to the nearest consular post. While critics would highlight that time and financial cost would “deter the diaspora from proactively partaking in voting”, employees such as female domestic workers would have the added challenge of seeking “approval of their masters and traveling a long distance to both register and vote”. Mail voting or assigning longer voting periods, including weekends, could alleviate some of these concerns.
Other concerns of out-of-country voting include potential vote buying and exploitation. Activists also raise concerns about whether politically appointed staff in diplomatic missions would influence, especially the unskilled and voiceless OSLs. Therefore, there is a need for a “mechanism with checks and balances” to “prevent the integrity of the electoral result from being questioned”.
While criticisms of each optional OAV method will likely emerge, it is important to start taking initial steps toward one feasible and practical option. The issues can be ironed out with time, and more sophisticated options can be pursued.
Finally, it is important to realise that achieving this goal in time for the upcoming Parliamentary election on 14 November or the pending provincial or local government elections in 2025 is not easy. Yet, initial steps towards this change are much needed and the time is right for it.
Business
Sri Lanka betting its tourism future on cold, hard numbers

National Airport Exit Survey tells quite a story
Australia’s role here is strategic, not charitable
In a quiet but significant shift, Sri Lanka’s tourism sector is moving beyond traditional destination marketing and instinct-based planning. The recent launch of the “From Data to Decisions” initiative jointly backed by Australia’s Market Development Facility and the Sri Lanka Tourism Development Authority, sent an unambiguous message: sentiment is out, statistics are in.
The initiative is anchored by a 12-month National Airport Exit Survey, a trove of data covering 16,000 travellers. The findings sketch a new traveller profile: nearly half are young (20–35), independent, and book online. Galle, Ella, and Sigiriya are the hotspots; women travellers outnumber men; and a promising 45% plan to return. This isn’t just trivia. It’s a strategic blueprint. If Sri Lanka Tourism listens, it can tailor everything from infrastructure to marketing, moving from guesswork to precision.
The keynote speaker, Deputy Minister Prof. Ruwan Ranasinghe called data “a vital pillar of tourism transformation.” Yet the unspoken truth is that Sri Lanka has long relied on generic appeals -beaches, heritage, smiles. In today’s crowded market, that’s no longer enough. As SLTDA Chairman Buddhika Hewawasam noted, this partnership is about “elevating how we collect, analyse, and use data.”
Australia’s role here is strategic, not charitable. By funding research and advocating for a Tourism Satellite Account, it is helping Sri Lanka build a tourism sector that is both sustainable and measurable. Australian High Commissioner Matthew Duckworth linked this support to “global standards of environmental protection” – a clear nod to the growing demand for green travel. This isn’t just aid; it’s influence through insight.
“The real test lies ahead,” a tourism expert told The Island. “Data is only as good as the decisions it drives. Will these insights overcome bureaucratic inertia? Will marketing budgets actually follow the evidence toward younger, independent, female travellers?,” he asked.
“The comprehensive report promised for early 2026 must move swiftly from recommendation to action. In an era where destinations are discovered on Instagram and planned with algorithms, intuition alone is a high-stakes gamble. This forum made one thing clear: Sri Lanka is finally building its future on what visitors actually do – not just what we hope they’ll do. The numbers are in. Now, the industry must dare to follow them,” he said.
By Sanath Nanayakkare
Business
New ATA Chair champions Asia’s small tea farmers, unveils ambitious agenda

In his inaugural address as the new Chairman of the Asia Tea Alliance (ATA), Nimal Udugampola placed the region’s millions of smallholders at the core of the global tea industry’s future, asserting they are the “indispensable engine” of a sector that produces over 90% of the world’s tea.
Udugampola, who is also Chairman of Sri Lanka’s Tea Smallholdings Development Authority, used his speech at the 6th ATA Summit held in Colombo on Nov. 27 to declare that the prosperity of Asian tea is “entirely contingent” on the resilience of its small-scale farmers, who have historically been overlooked by premium global markets.
“In Sri Lanka, smallholders account for over 75% of our national production. Across Asia, millions of families maintain the quality and character of our regional teas,” he stated, accepting the chairmanship for the 2025-2027 term.
To empower this vital community, Udugampola unveiled a vision focused on Sustainability, Equity, and Digital Transformation. The strategic agenda includes:
Climate Resilience: Promoting climate-smart agriculture and regenerative farming to protect smallholdings from environmental disruption.
Digital Equity: Leveraging technology like blockchain to create farm-to-cup traceability, connecting smallholders directly with premium consumers and ensuring fair value.
Market Expansion: Driving innovation in tea products and marketing to attract younger consumers and enter non-traditional markets.
Standard Harmonization: Establishing common regional quality and sustainability standards to protect the “Asian Tea” brand and push for stable, fair pricing.
Linking the alliance’s goals to national ambition, Udugampola highlighted Sri Lanka’s target of producing 400 million kilograms of tea by 2030. He presented the country’s “Pivithuru Tea Initiative” as a model for other ATA nations, designed to achieve this through smallholder empowerment, digitalization, and aligned policy objectives.
By Sanath Nanayakkare
Business
Brandix recognised as Green Brand of Year at SLIM Awards 2025
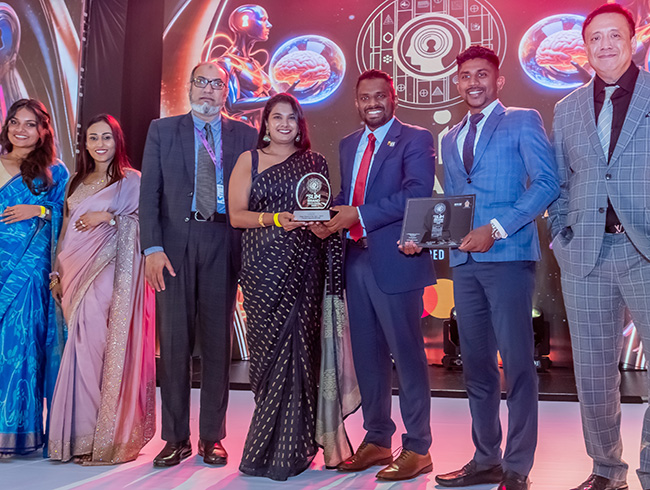

Brandix Apparel Solutions was recognised as the Green Brand of the Year at the Sri Lanka Institute of Marketing (SLIM) Brand Excellence Awards 2025, taking home Silver, the highest award presented in the category this year.
The ‘Green Brand of the Year’ recognises the brand that drives measurable environmental impact through sustainable practices, climate-aligned goals and long-term commitment to protecting natural resources.
A pioneer in responsible apparel manufacturing for over two decades, Brandix has championed best practices in the sphere of sustainable manufacturing covering environmental, social, and governance aspects. The company built the world’s first Net Zero Carbon-certified apparel manufacturing facility (across Scope 1 and Scope 2) and meets over 60% of its energy requirement in Sri Lanka via renewable sources.
Head of ESG at Brandix, Nirmal Perera, said: “Being recognised as Green Brand of the Year is an encouraging milestone for our teams working across sustainability.”
-
News5 days ago
Lunuwila tragedy not caused by those videoing Bell 212: SLAF
-

 News10 hours ago
News10 hours agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-
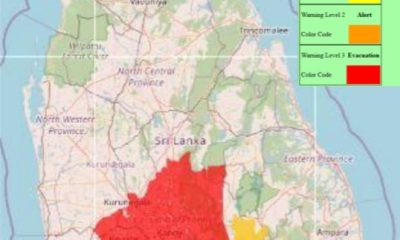
 News4 days ago
News4 days agoLevel III landslide early warning continue to be in force in the districts of Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala and Matale
-
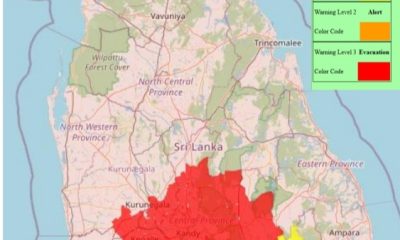
 Latest News7 days ago
Latest News7 days agoLevel III landslide early warnings issued to the districts of Badulla, Kandy, Kegalle, Kurunegala, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoDitwah: An unusual cyclone
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady














