Features
Why are SL universities’ positions low in world ranking indices?

 Arespected law firm in New Zealand, when advertising positions for apprentice lawyers, tends to overlook applications from graduates who have not attended top-ranked institutions. Hence, it becomes crucial for universities to achieve international high rankings. Beyond scenarios like job searches, there are several reasons why a higher ranking holds significance for a university:
Arespected law firm in New Zealand, when advertising positions for apprentice lawyers, tends to overlook applications from graduates who have not attended top-ranked institutions. Hence, it becomes crucial for universities to achieve international high rankings. Beyond scenarios like job searches, there are several reasons why a higher ranking holds significance for a university:
https://www.adscientificindex.com/university-ranking/?funding=All+Universities&country_code=lk
Source: https://www.topuniversities.com/world-university-rankings
Prestige, Reputation and Research
A higher rank enhances the prestige and reputation of a university both nationally and internationally. It signifies academic excellence, research prowess, and overall institutional quality, attracting top students, faculty, and researchers. A higher rank provides global recognition and visibility to the university, positioning it as a leader in higher education and research. This recognition opens doors to international collaborations, partnerships, and exchange programmes, enriching the academic and cultural experiences of students and faculty.
Higher-ranked universities tend to have greater research impact and influence. They attract top researchers, secure more research funding, and produce groundbreaking discoveries and innovations that address societal challenges and drive economic growth.
Competitiveness and Attracting Talents
A higher rank increases the competitiveness of the university in attracting funding, grants, and partnerships. Funding agencies, philanthropic organisations, and industry partners are more likely to collaborate with highly ranked universities, leading to increased opportunities for research, innovation, and economic development.
Universities with higher ranks are more attractive to talented students, faculty, and researchers. Top-ranked universities can recruit and retain the best minds in academia, fostering a vibrant intellectual community and facilitating knowledge creation and dissemination.
Higher-ranked universities typically experience higher student enrollment and retention rates. Students are drawn to universities with strong academic reputations, diverse programme offerings, and attractive campus environments, enhancing the university’s revenue and sustainability.
The reputation and network of a higher-ranked university can positively impact the career prospects and success of its alumni. Graduates from prestigious universities often have access to better job opportunities, higher salaries, and influential professional networks, contributing to their long-term success and the reputation of the university.
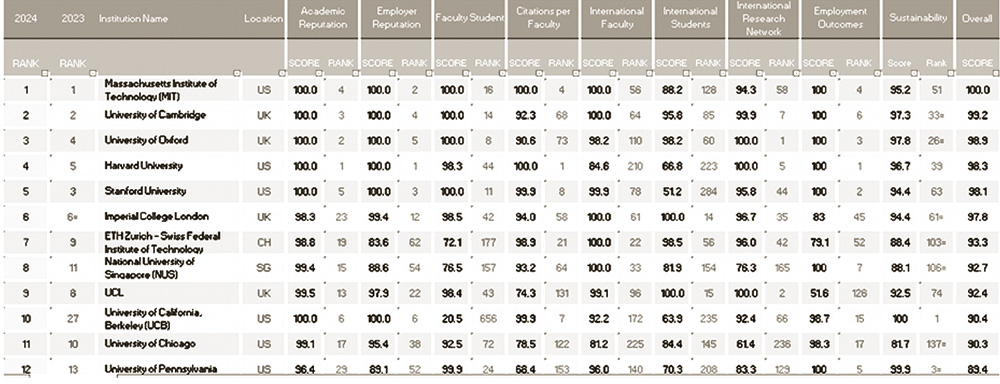
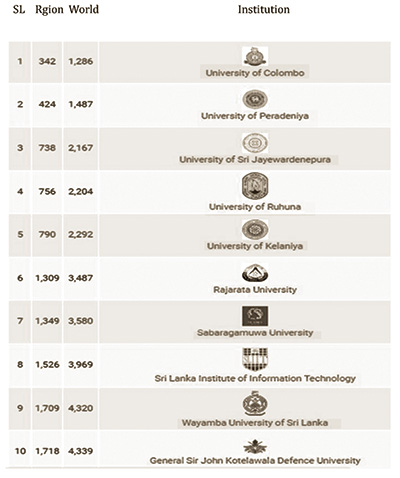 Overall, a higher rank serves as a symbol of excellence, attracting talent, resources, and opportunities that contribute to the continued success and advancement of the university. The tables provide global rankings of universities, as well as rankings specific to the South Asian region and Sri Lanka.
Overall, a higher rank serves as a symbol of excellence, attracting talent, resources, and opportunities that contribute to the continued success and advancement of the university. The tables provide global rankings of universities, as well as rankings specific to the South Asian region and Sri Lanka.
Several factors contribute to Sri Lankan universities being ranked low:
Quality of Education and Research: Some Sri Lankan universities struggle to maintain high standards of education and research due to factors such as outdated curricula, inadequate teaching resources, and limited access to modern technologies and learning materials.
Low levels of research output and innovation contribute to the low rankings of Sri Lankan universities. Factors such as limited research funding, inadequate research infrastructure, and a lack of incentives for faculty to engage in research can hinder the production of high-quality research outputs.
Faculty Quality and funding: The quality and professional development of faculty members play a significant role in the rankings of universities. Challenges such as brain drain, where talented academics seek opportunities abroad due to better prospects, and limited opportunities for faculty development and training can impact the quality of teaching and research. Issues related to governance and management, including bureaucratic inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and political interference, can affect the overall functioning and performance of universities.
Sri Lankan universities often face challenges due to limited funding and investment in higher education. Insufficient financial resources can impact infrastructure development, research facilities, faculty recruitment, and student support services. Inadequate infrastructure and facilities, including outdated laboratories, libraries, and IT infrastructure, can hinder the ability of universities to provide quality education and conduct impactful research.
International Collaboration and Recognition: Limited international collaboration and recognition can also contribute to the low rankings of Sri Lankan universities. Engaging in partnerships with international institutions, participating in global research networks, and obtaining accreditation from reputable international organizations can enhance the visibility and reputation of universities.
The role of university administration
The factor of governance and management plays a significant role in influencing the encouragement or discouragement of research publication in quality journals indexed in databases like Scopus or Web of Science.
However, there seems to be a prevailing trend of publishing solely for the sake of meeting publication quotas in local journals that lack indexing, primarily to accumulate points for career advancement purposes.
Bureaucratic Inefficiencies: Inefficient bureaucratic processes within universities can create barriers and delays in the research publication process. For instance, complex administrative procedures for obtaining approvals such as ethical approval, funding, or accessing resources can discourage faculty members from pursuing research or submitting their work to quality indexed international journals. The time and effort required to navigate bureaucratic red tape may outweigh the benefits of publishing prestigious journals.
Lack of Transparency: Universities that lack transparency in their governance and decision-making processes may create an environment where researchers feel uncertain or insecure about the publication process. Without clear guidelines, criteria, and expectations for research publication, faculty members may hesitate to invest time and resources in producing high-quality research or submitting it to reputable journals. Additionally, concerns about favoritism, bias, or arbitrary decision-making in the publication process can undermine trust and confidence among researchers.
Political Interference: Political interference in university governance can have detrimental effects on research culture and academic freedom. When political agendas influence decision-making related to research priorities, funding allocation, or editorial policies, it may compromise the integrity and independence of academic research. Researchers may feel pressured to align their work with political interests or avoid controversial topics that could jeopardize their careers or funding opportunities. In such environments, there may be a tendency to prioritize quantity over quality in research output, with less emphasis on publishing in prestigious journals indexed in databases like Scopus or Web of Science.
Role of the Ministry of Education and the University Grant Commission
The University Grants Commission (UGC) serves as the governing authority for the university system in Sri Lanka, guided by nicely crafted vision, mission, and goals as per their website; https://www.ugc.ac.lk/
The absence of goals focused on “high impact research,” as outlined in the mission statement, highlights a potential gap in the UGC’s initiatives. This oversight may contribute to the lack of emphasis on promoting research publication in high-quality international journals, which is crucial for achieving higher ranks in ranking indices.
Further, in the promotion process for academics to the positions of Associate Professors and Professors, the University Grants Commission (UGC) has issued circulars outlining a point system; UGC Circular No. 723 of 12 December 1997, 869 of 30 November 2005, and 916 of 30 September 2009.
According to these circulars, a senior lecturer in the university system must accumulate 105 points to qualify for the Professor position, with a minimum of 55 points required from Research and Creative work. However, the conditions for claiming these points are relatively lax, requiring only that publications appear in numbered volumes and pass peer review. While there are no restrictions on maximum points, a critical issue remains: there is no minimum requirement for points articles published in globally recognized indexed journals.
Consequently, some faculties of certain universities resort to publishing their own “journals” and organizing “international conferences” to claim points without conducting rigorous research or publishing them in internationally reputed indexed databases.
Crucially, there should be a cap on the maximum points awarded for local publications, even if they are published by “recognized publishers,” a term not clearly defined in the circular. Publishers like Sarasavi, Vijitha, and Gunasena are well-known, yet citations from their publications are not acknowledged by WoS, Scopus or Google, thus not factored into rankings by agencies.
The Way out.
To boost Sri Lankan universities in global rankings, the UGC and Ministry of Education should revise their missions and goals to include more research and internationally recognized indexed publications for universities and ensure clear communication to prospective university staff.
Staff should receive more than just recognition for publications, with rewards such as cash incentives and public appreciation. Making research projects compulsory for undergraduates, postgraduates, and masters, and incentivizing manuscript submissions with marks or cash rewards, could further motivate students.
Conclusions
Overall, addressing issues related to governance and management is essential for fostering a conducive environment for research publication in quality indexed journals. Universities need to streamline administrative processes, enhance transparency in decision-making, and safeguard academic freedom from political interference. By promoting a culture of excellence, integrity, and meritocracy, universities can encourage faculty members to actively engage in research and contribute to knowledge dissemination through publications in reputable indexed journals.
Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts from various stakeholders, including government authorities, university administrations, faculty members, students, and funding agencies. To elevate Sri Lankan universities in global rankings, the UGC and Ministry of Education should update their missions to prioritize research and internationally recognized publications. Additionally, staff should be rewarded beyond recognition, with incentives like cash rewards and public appreciation. Implementing compulsory research projects and incentivizing manuscript submissions can enhance student motivation at all academic levels.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT University, Malabe. He is also the author of the “Doing Social Research and Publishing Results”, a Springer publication (Singapore), and “Samaja Gaveshakaya (in Sinhala). The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the institution he works for. He can be contacted at saliya.a@slit.lk and www.researcher.com)
Features
Rebuilding the country requires consultation

A positive feature of the government that is emerging is its responsiveness to public opinion. The manner in which it has been responding to the furore over the Grade 6 English Reader, in which a weblink to a gay dating site was inserted, has been constructive. Government leaders have taken pains to explain the mishap and reassure everyone concerned that it was not meant to be there and would be removed. They have been meeting religious prelates, educationists and community leaders. In a context where public trust in institutions has been badly eroded over many years, such responsiveness matters. It signals that the government sees itself as accountable to society, including to parents, teachers, and those concerned about the values transmitted through the school system.
This incident also appears to have strengthened unity within the government. The attempt by some opposition politicians and gender misogynists to pin responsibility for this lapse on Prime Minister Dr Harini Amarasuriya, who is also the Minister of Education, has prompted other senior members of the government to come to her defence. This is contrary to speculation that the powerful JVP component of the government is unhappy with the prime minister. More importantly, it demonstrates an understanding within the government that individual ministers should not be scapegoated for systemic shortcomings. Effective governance depends on collective responsibility and solidarity within the leadership, especially during moments of public controversy.
The continuing important role of the prime minister in the government is evident in her meetings with international dignitaries and also in addressing the general public. Last week she chaired the inaugural meeting of the Presidential Task Force to Rebuild Sri Lanka in the aftermath of Cyclone Ditwah. The composition of the task force once again reflects the responsiveness of the government to public opinion. Unlike previous mechanisms set up by governments, which were either all male or without ethnic minority representation, this one includes both, and also includes civil society representation. Decision-making bodies in which there is diversity are more likely to command public legitimacy.
Task Force
The Presidential Task Force to Rebuild Sri Lanka overlooks eight committees to manage different aspects of the recovery, each headed by a sector minister. These committees will focus on Needs Assessment, Restoration of Public Infrastructure, Housing, Local Economies and Livelihoods, Social Infrastructure, Finance and Funding, Data and Information Systems, and Public Communication. This structure appears comprehensive and well designed. However, experience from post-disaster reconstruction in countries such as Indonesia and Sri Lanka after the 2004 tsunami suggests that institutional design alone does not guarantee success. What matters equally is how far these committees engage with those on the ground and remain open to feedback that may complicate, slow down, or even challenge initial plans.
An option that the task force might wish to consider is to develop a linkage with civil society groups with expertise in the areas that the task force is expected to work. The CSO Collective for Emergency Relief has set up several committees that could be linked to the committees supervised by the task force. Such linkages would not weaken the government’s authority but strengthen it by grounding policy in lived realities. Recent findings emphasise the idea of “co-production”, where state and society jointly shape solutions in which sustainable outcomes often emerge when communities are treated not as passive beneficiaries but as partners in problem-solving.
Cyclone Ditwah destroyed more than physical infrastructure. It also destroyed communities. Some were swallowed by landslides and floods, while many others will need to be moved from their homes as they live in areas vulnerable to future disasters. The trauma of displacement is not merely material but social and psychological. Moving communities to new locations requires careful planning. It is not simply a matter of providing people with houses. They need to be relocated to locations and in a manner that permits communities to live together and to have livelihoods. This will require consultation with those who are displaced. Post-disaster evaluations have acknowledged that relocation schemes imposed without community consent often fail, leading to abandonment of new settlements or the emergence of new forms of marginalisation. Even today, abandoned tsunami housing is to be seen in various places that were affected by the 2004 tsunami.
Malaiyaha Tamils
The large-scale reconstruction that needs to take place in parts of the country most severely affected by Cyclone Ditwah also brings an opportunity to deal with the special problems of the Malaiyaha Tamil population. These are people of recent Indian origin who were unjustly treated at the time of Independence and denied rights of citizenship such as land ownership and the vote. This has been a festering problem and a blot on the conscience of the country. The need to resettle people living in those parts of the hill country which are vulnerable to landslides is an opportunity to do justice by the Malaiyaha Tamil community. Technocratic solutions such as high-rise apartments or English-style townhouses that have or are being contemplated may be cost-effective, but may also be culturally inappropriate and socially disruptive. The task is not simply to build houses but to rebuild communities.
The resettlement of people who have lost their homes and communities requires consultation with them. In the same manner, the education reform programme, of which the textbook controversy is only a small part, too needs to be discussed with concerned stakeholders including school teachers and university faculty. Opening up for discussion does not mean giving up one’s own position or values. Rather, it means recognising that better solutions emerge when different perspectives are heard and negotiated. Consultation takes time and can be frustrating, particularly in contexts of crisis where pressure for quick results is intense. However, solutions developed with stakeholder participation are more resilient and less costly in the long run.
Rebuilding after Cyclone Ditwah, addressing historical injustices faced by the Malaiyaha Tamil community, advancing education reform, changing the electoral system to hold provincial elections without further delay and other challenges facing the government, including national reconciliation, all require dialogue across differences and patience with disagreement. Opening up for discussion is not to give up on one’s own position or values, but to listen, to learn, and to arrive at solutions that have wider acceptance. Consultation needs to be treated as an investment in sustainability and legitimacy and not as an obstacle to rapid decisionmaking. Addressing the problems together, especially engagement with affected parties and those who work with them, offers the best chance of rebuilding not only physical infrastructure but also trust between the government and people in the year ahead.
by Jehan Perera
Features
PSTA: Terrorism without terror continues

 When the government appointed a committee, led by Rienzie Arsekularatne, Senior President’s Counsel, to draft a new law to replace the Prevention of Terrorism Act (PTA), as promised by the ruling NPP, the writer, in an article published in this journal in July 2025, expressed optimism that, given Arsekularatne’s experience in criminal justice, he would be able to address issues from the perspectives of the State, criminal justice, human rights, suspects, accused, activists, and victims. The draft Protection of the State from Terrorism Act (PSTA), produced by the Committee, has been sharply criticised by individuals and organisations who expected a better outcome that aligns with modern criminal justice and human rights principles.
When the government appointed a committee, led by Rienzie Arsekularatne, Senior President’s Counsel, to draft a new law to replace the Prevention of Terrorism Act (PTA), as promised by the ruling NPP, the writer, in an article published in this journal in July 2025, expressed optimism that, given Arsekularatne’s experience in criminal justice, he would be able to address issues from the perspectives of the State, criminal justice, human rights, suspects, accused, activists, and victims. The draft Protection of the State from Terrorism Act (PSTA), produced by the Committee, has been sharply criticised by individuals and organisations who expected a better outcome that aligns with modern criminal justice and human rights principles.
This article is limited to a discussion of the definition of terrorism. As the writer explained previously, the dangers of an overly broad definition go beyond conviction and increased punishment. Special laws on terrorism allow deviations from standard laws in areas such as preventive detention, arrest, administrative detention, restrictions on judicial decisions regarding bail, lengthy pre-trial detention, the use of confessions, superadded punishments, such as confiscation of property and cancellation of professional licences, banning organisations, and restrictions on publications, among others. The misuse of such laws is not uncommon. Drastic legislation, such as the PTA and emergency regulations, although intended to be used to curb intense violence and deal with emergencies, has been exploited to suppress political opposition.
International Standards
The writer’s basic premise is that, for an act to come within the definition of terrorism, it must either involve “terror” or a “state of intense or overwhelming fear” or be committed to achieve an objective of an individual or organisation that uses “terror” or a “state of intense or overwhelming fear” to realise its aims. The UN General Assembly has accepted that the threshold for a possible general offence of terrorism is the provocation of “a state of terror” (Resolution 60/43). The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe has taken a similar view, using the phrase “to create a climate of terror.”
In his 2023 report on the implementation of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy, the Secretary-General warned that vague and overly broad definitions of terrorism in domestic law, often lacking adequate safeguards, violate the principle of legality under international human rights law. He noted that such laws lead to heavy-handed, ineffective, and counterproductive counter-terrorism practices and are frequently misused to target civil society actors and human rights defenders by labelling them as terrorists to obstruct their work.
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) has stressed in its Handbook on Criminal Justice Responses to Terrorism that definitions of terrorist acts must use precise and unambiguous language, narrowly define punishable conduct and clearly distinguish it from non-punishable behaviour or offences subject to other penalties. The handbook was developed over several months by a team of international experts, including the writer, and was finalised at a workshop in Vienna.
Anti-Terrorism Bill, 2023
A five-member Bench of the Supreme Court that examined the Anti-Terrorism Bill, 2023, agreed with the petitioners that the definition of terrorism in the Bill was too broad and infringed Article 12(1) of the Constitution, and recommended that an exemption (“carve out”) similar to that used in New Zealand under which “the fact that a person engages in any protest, advocacy, or dissent, or engages in any strike, lockout, or other industrial action, is not, by itself, a sufficient basis for inferring that the person” committed the wrongful acts that would otherwise constitute terrorism.
While recognising the Court’s finding that the definition was too broad, the writer argued, in his previous article, that the political, administrative, and law enforcement cultures of the country concerned are crucial factors to consider. Countries such as New Zealand are well ahead of developing nations, where the risk of misuse is higher, and, therefore, definitions should be narrower, with broader and more precise exemptions. How such a “carve out” would play out in practice is uncertain.
In the Supreme Court, it was submitted that for an act to constitute an offence, under a special law on terrorism, there must be terror unleashed in the commission of the act, or it must be carried out in pursuance of the object of an organisation that uses terror to achieve its objectives. In general, only acts that aim at creating “terror” or a “state of intense or overwhelming fear” should come under the definition of terrorism. There can be terrorism-related acts without violence, for example, when a member of an extremist organisation remotely sabotages an electronic, automated or computerised system in pursuance of the organisation’s goal. But when the same act is committed by, say, a whizz-kid without such a connection, that would be illegal and should be punished, but not under a special law on terrorism. In its determination of the Bill, the Court did not address this submission.
PSTA Proposal
Proposed section 3(1) of the PSTA reads:
Any person who, intentionally or knowingly, commits any act which causes a consequence specified in subsection (2), for the purpose of-
(a) provoking a state of terror;
(b) intimidating the public or any section of the public;
(c) compelling the Government of Sri Lanka, or any other Government, or an international organisation, to do or to abstain from doing any act; or
(d) propagating war, or violating territorial integrity or infringing the sovereignty of Sri Lanka or any other sovereign country, commits the offence of terrorism.
The consequences listed in sub-section (2) include: death; hurt; hostage-taking; abduction or kidnapping; serious damage to any place of public use, any public property, any public or private transportation system or any infrastructure facility or environment; robbery, extortion or theft of public or private property; serious risk to the health and safety of the public or a section of the public; serious obstruction or damage to, or interference with, any electronic or automated or computerised system or network or cyber environment of domains assigned to, or websites registered with such domains assigned to Sri Lanka; destruction of, or serious damage to, religious or cultural property; serious obstruction or damage to, or interference with any electronic, analogue, digital or other wire-linked or wireless transmission system, including signal transmission and any other frequency-based transmission system; without lawful authority, importing, exporting, manufacturing, collecting, obtaining, supplying, trafficking, possessing or using firearms, offensive weapons, ammunition, explosives, articles or things used in the manufacture of explosives or combustible or corrosive substances and biological, chemical, electric, electronic or nuclear weapons, other nuclear explosive devices, nuclear material, radioactive substances, or radiation-emitting devices.
Under section 3(5), “any person who commits an act which constitutes an offence under the nine international treaties on terrorism, ratified by Sri Lanka, also commits the offence of terrorism.” No one would contest that.
The New Zealand “carve-out” is found in sub-section (4): “The fact that a person engages in any protest, advocacy or dissent or engages in any strike, lockout or other industrial action, is not by itself a sufficient basis for inferring that such person (a) commits or attempts, abets, conspires, or prepares to commit the act with the intention or knowledge specified in subsection (1); or (b) is intending to cause or knowingly causes an outcome specified in subsection (2).”
While the Arsekularatne Committee has proposed, including the New Zealand “carve out”, it has ignored a crucial qualification in section 5(2) of that country’s Terrorism Suppression Act, that for an act to be considered a terrorist act, it must be carried out for one or more purposes that are or include advancing “an ideological, political, or religious cause”, with the intention of either intimidating a population or coercing or forcing a government or an international organisation to do or abstain from doing any act.
When the Committee was appointed, the Human Rights Commission of Sri Lanka opined that any new offence with respect to “terrorism” should contain a specific and narrow definition of terrorism, such as the following: “Any person who by the use of force or violence unlawfully targets the civilian population or a segment of the civilian population with the intent to spread fear among such population or segment thereof in furtherance of a political, ideological, or religious cause commits the offence of terrorism”.
The writer submits that, rather than bringing in the requirement of “a political, ideological, or religious cause”, it would be prudent to qualify proposed section 3(1) by the requirement that only acts that aim at creating “terror” or a “state of intense or overwhelming fear” or are carried out to achieve a goal of an individual or organisation that employs “terror” or a “state of intense or overwhelming fear” to attain its objectives should come under the definition of terrorism. Such a threshold is recognised internationally; no “carve out” is then needed, and the concerns of the Human Rights Commission would also be addressed.
by Dr. Jayampathy Wickramaratne
President’s Counsel
Features
ROCK meets REGGAE 2026

 We generally have in our midst the famous JAYASRI twins, Rohitha and Rohan, who are based in Austria but make it a point to entertain their fans in Sri Lanka on a regular basis.
We generally have in our midst the famous JAYASRI twins, Rohitha and Rohan, who are based in Austria but make it a point to entertain their fans in Sri Lanka on a regular basis.
Well, rock and reggae fans get ready for a major happening on 28th February (Oops, a special day where I’m concerned!) as the much-awaited ROCK meets REGGAE event booms into action at the Nelum Pokuna outdoor theatre.
It was seven years ago, in 2019, that the last ROCK meets REGGAE concert was held in Colombo, and then the Covid scene cropped up.

Chitral Somapala with BLACK MAJESTY
This year’s event will feature our rock star Chitral Somapala with the Australian Rock+Metal band BLACK MAJESTY, and the reggae twins Rohitha and Rohan Jayalath with the original JAYASRI – the full band, with seven members from Vienna, Austria.
According to Rohitha, the JAYASRI outfit is enthusiastically looking forward to entertaining music lovers here with their brand of music.
Their playlist for 28th February will consist of the songs they do at festivals in Europe, as well as originals, and also English and Sinhala hits, and selected covers.
Says Rohitha: “We have put up a great team, here in Sri Lanka, to give this event an international setting and maintain high standards, and this will be a great experience for our Sri Lankan music lovers … not only for Rock and Reggae fans. Yes, there will be some opening acts, and many surprises, as well.”

Rohitha, Chitral and Rohan: Big scene at ROCK meets REGGAE
Rohitha and Rohan also conveyed their love and festive blessings to everyone in Sri Lanka, stating “This Christmas was different as our country faced a catastrophic situation and, indeed, it’s a great time to help and share the real love of Jesus Christ by helping the poor, the needy and the homeless people. Let’s RISE UP as a great nation in 2026.”
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoSajith: Ashoka Chakra replaces Dharmachakra in Buddhism textbook
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoDialog and UnionPay International Join Forces to Elevate Sri Lanka’s Digital Payment Landscape
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoThe Paradox of Trump Power: Contested Authoritarian at Home, Uncontested Bully Abroad
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoSubject:Whatever happened to (my) three million dollars?
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoLevel I landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Badulla, Kandy, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya extended
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoNational Communication Programme for Child Health Promotion (SBCC) has been launched. – PM
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days ago65 withdrawn cases re-filed by Govt, PM tells Parliament
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoThe minstrel monk and Rafiki, the old mandrill in The Lion King – II