Features
Nexus between money, exchange rate, money printing and inflation

 Money, exchange rates, and money printing are crucial components of a nation’s monetary policy framework, wielding significant influence over economic and financial stability. This intricate relationship between these fundamental factors directly affects financial and economic dynamics. I am going to examine the nexus between these factors, clarifying their roles in the financial system and the implications of their interactions. The relationship between money supply and money printing is symbiotic, with the latter directly influencing the former.
Money, exchange rates, and money printing are crucial components of a nation’s monetary policy framework, wielding significant influence over economic and financial stability. This intricate relationship between these fundamental factors directly affects financial and economic dynamics. I am going to examine the nexus between these factors, clarifying their roles in the financial system and the implications of their interactions. The relationship between money supply and money printing is symbiotic, with the latter directly influencing the former.
Money
Recently, Emeritus Professor of Economics, Sirimal Abeyratne, explained the meanings of some economic concepts about money and inflation. He emphasised that in economics, money transcends mere physical notes and coins circulating in the system. Similarly, he clarified that money printing does not entail the simplistic act of “multiplying sacks of coins or bundles of notes”, akin to minting physical currency.
Money supply, often referred to as the money stock, encompasses the total quantity of money circulating within an economy at a given time. It includes various forms of money such as currency, demand deposits, and other liquid instruments. Money supply acts as the lifeblood of economic transactions, facilitating exchange, investment, and consumption activities. Central to the concept of money supply are its determinants, including central bank policies, commercial bank lending practices, and public demand for money. Changes in these determinants can influence the quantity of money in circulation, impacting economic activity and price levels.
Reverse causal relationships
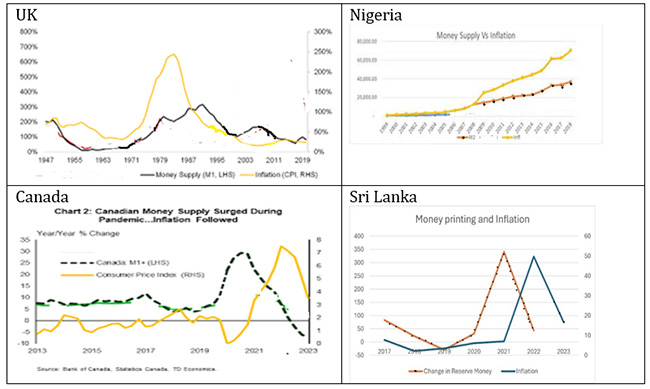
Crucially, Professor Abeyratne highlighted the concept of reverse causation between the stock of money, which is determined (a multiplier) by reserve money, and inflation through the mechanism of increased aggregate demand. It suggests that money supply, can impact aggregate demand, subsequently influencing inflationary pressures within the economy. Therefore by understanding the complexities inherent in concepts like money supply, money printing, and their implications for inflation and aggregate demand, policymakers and economists can formulate more informed and effective monetary policy strategies to foster economic stability and growth.
Money printing
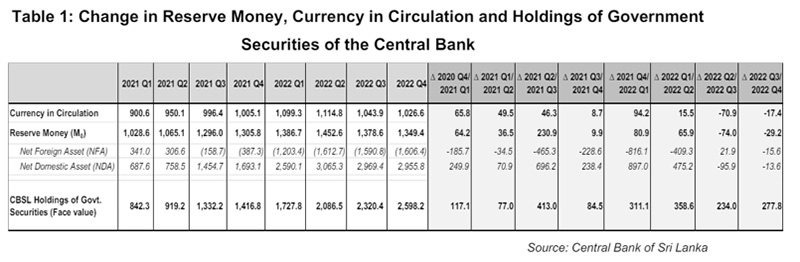
According to Dr. Nandalal Weerasinghe, the Governor of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL), money printing can be defined as the change in reserve money, denoted as M0, which represents the injection of fresh money into the economy. Reserves consist of the stock of cash and funds, including statutory reserves, deposited by commercial banks with the CBSL. In 2020 and 2021, the increase in M0 (money printing) was LKR 372 billion, while the money stock (M2 broad) rose by LKR 3,024 billion.
CBSL further explains (Janaka Edirisinghe Deputy Director Economic Research Department) that in economic terms, the Central Bank has two primary methods for issuing new money into the economy. Firstly, when the Central Bank extends credit to licensed commercial banks or the government, it effectively creates new money, termed as the accumulation of domestic assets. Secondly, when the Central Bank acquires foreign exchange from the domestic foreign exchange market or government inflows, it generates new money, known as the accumulation of foreign assets. The combined value of these two assets is referred to as reserve money. Therefore, the main way to measure money printing is by looking at the change in Reserve Money. Table 1 shows this indicator along with other measures used to evaluate money printing. (See Table 01)
Money and Economic Growth
Money printing, also known as quantitative easing (QE) when conducted by central banks, involves the electronic creation of new money to purchase financial assets like government bonds or mortgage-backed securities. Central banks employ money printing as a monetary policy tool to achieve specific objectives such as lowering interest rates, boosting aggregate demand, and achieving target levels of inflation.
When central banks engage in money printing through QE programs, they inject newly created money into the financial system, thereby increasing the overall money supply. This liquidity infusion aims to lower interest rates, stimulate borrowing and spending, and ultimately expand the money supply to support economic activity especially during economic downturns or deflationary periods. However, the effectiveness of money printing in achieving these goals is debated due to potential unintended consequences like asset price inflation and currency depreciation.
Conversely, a contractionary monetary policy, such as reducing the pace of money printing or tightening monetary conditions, can lead to a decrease in the growth rate of the money supply or even a contraction. This reduction in money supply growth can dampen economic activity, increase borrowing costs, and potentially contribute to deflationary pressures.
Nexus of financial factors
From a financial perspective, we may have to go beyond analysing the bi-directional relationship between reserve money and inflation, via mediation of aggregate demand. Deeper study is necessary to explore the multi-directional and mutually co-integrated nature of relationships among the most prominent variables in financial market dynamics. While central banks employ money printing to achieve objectives like lowering interest rates and boosting aggregate demand, its effectiveness and potential drawbacks, such as asset price inflation and currency depreciation, remain subjects of debate.
The nexus between money supply, money printing, aggregate demand, inflation, exchange rate and stock market performance are complex and mutually influential. When central banks engage in money printing, they aim to bolster aggregate demand by injecting liquidity into the financial system. This liquidity expansion can lead to increased consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity. Conversely, a contractionary monetary policy, such as reducing the pace of money printing, can dampen aggregate demand by limiting liquidity and tightening financial conditions.
Aggregate Demand
Incorporating aggregate demand into the nexus provides a holistic view of monetary policy’s impact on economic outcomes. Changes in money supply and money printing influence aggregate demand, which in turn affects consumption, investment, and overall economic growth. Moreover, fluctuations in aggregate demand can feedback into monetary policy decisions, shaping central banks’ strategies to achieve macroeconomic objectives.
Foreign Reserves and Exchange Rate
Incorporating the value of money against the US dollar into the nexus reveals another dimension. Changes in money supply and money printing can influence the value of the currency against the US dollar, which in turn affects various aspects of the economy such as trade competitiveness and foreign exchange reserves.
Sri Lanka receives foreign exchange from exports, remittances, tourism, investments, loans, and other sources. Commercial banks handle most inflows for their clients, while the Central Bank manages government transactions. When the government needs foreign currency but lacks it, the Central Bank steps in, reducing its foreign assets. To cover this, the government exchanges Sri Lankan rupees with the Central Bank, possibly reducing the money supply unless it borrows more. Once all foreign exchange needs are met, the Central Bank can buy foreign currency from banks, increasing its assets and injecting new money into the economy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the nexus between money, money printing, aggregate demand, inflation, exchange rate and stock market performance underscores the intricate relationship between monetary policy actions and economic and financial dynamics. While money printing can influence money supply dynamics, its effectiveness and implications depend on various factors such as economic conditions, policy implementation, and market expectations.
Sri Lanka receives foreign exchange from various sources. When the government requires foreign currency, the Central Bank of Sri Lanka (CBSL) uses its foreign assets to exchange Sri Lankan rupees, potentially reducing the money supply unless the government borrows more. After meeting all requirements, the CBSL purchases foreign currency from banks, increasing its assets and injecting new money into the economy.
Hence, it’s crucial to craft policy tools meticulously, navigating these dynamics to meet the country’s goals of stable prices, sustainable economic growth, and financial stability.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT University, Malabe. He is also the author of the “Doing Social Research and Publishing Results”, a Springer publication (Singapore), and “Samaja Gaveshakaya (in Sinhala). The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the institution he works for. He can be contacted at saliya.a@slit.lk and www.researcher.com)
Features
The Truth will set us free – I

Sri Lanka becoming a Macbethian sick state?
The traditional ritual of anointing medicinal oil (or ‘hisa thel gaema’ in Sinhalese, literally, applying oil to the head) is unique to the Sinhala Aluth Avurudda observances. This year, the ritual was performed at the auspicious moment of 9:04 a.m. (Sri Lanka time) on Wednesday April 16. It was observed at appointed venues across the country at the same time. The anointing was done, as usual, mostly by Buddhist monks in their monasteries.
Where they were not available for the purpose, a senior citizen would do the needful. The oil anointing ceremony was held to invoke blessings of good health on all the individuals who subjected themselves to the ritual. Prime Minister Harini Amarasuriya was shown participating in the oil anointing ceremony at the historic Kolonnawa Raja Maha Viharaya. There were many social media videos showing similar oil anointing scenes that included even elephants and hippos in a zoo receiving the compassionate treatment; this is not seen as going too far with traditions, for extending loving-kindness even to animals is taken for granted in the majority Buddhist Sri Lanka. Watching this ritual (that used to be so familiar for me in my childhood and youth) from abroad I couldn’t help my eyes filling with tears, feeling kind of homesick, in spite of me having spent more than forty-three years of my adult life living and working away from my Mother Country Sri Lanka.
Though usually Buddhist monks do the anointing, it is not considered a religious practice by the ordinary Buddhists. It is only a part of the completely secular Sinhala Aluth Avurudda festival. The most important annual religious festival for the Sinhalese (especially Sinhala Buddhists) is Vesak, which will be held next month. However, the oil anointing ceremony impresses on the Avurudu celebrants the great importance of maintaining their physical and mental health throughout the coming year, reflecting the high level of attention that our traditional culture pays to that objective.
However, the actual discrepancy that is noticed between the ideal and the reality in the mundane world, as in other countries, is a different matter. Shining beacons like ideals of a long-evolved culture are important for what they are; their importance doesn’t go away because those ideals are only imperfectly realised by the people of that culture. But the values endure.
The news of this happy occasion and my awareness of a deepening political and cultural malaise in my beloved Motherland back home reminded me of a book I read during the Covid-19 lockdown period of 2020-2022: OUR MALADY by American historian and public intellectual, the Yale University professor Timothy D. Snyder published in 2020. The book, whose subtitle is ‘Liberty and Solidarity’, is about the weakness of the American healthcare system that he himself got a taste of, privately.
Professor Snyder came to know first-hand how America failed its citizens in the public healthcare sphere as an inmate of a hospital ward, where he was admitted to the emergency room at midnight on December 29, 2019. He was complaining of a condition of severe bodily ‘malaise’. Doctors later told him that he had an abscess the size of a baseball in his liver. The emergency operation to remove the abscess was done after seventeen hours of his having had to wait confined to a hospital bed!
‘Rage’ is the word he repeatedly uses to describe how he felt during his hospitalisation. He was not raging against God or any particular person or a group or the bacteria that caused his illness. ‘I raged against a world where I was not’, Snyder writes in the Prologue to the book (implying how much he was angry about there not being a healthy enough healthcare system to look after Americans who fell ill like himself. The book grew out of entries he made in a diary that he maintained while recuperating in hospital. Proficient in a number of European languages including English, French and Polish, he adopts a sort of poetic idiom to deal with his naturally dull subject.
He imagined he was not suffering in solitude, though. He thought about other Americans in his situation, and empathised with them. The absence of a sound healthcare system is America’s malady according to Snyder. Probably, the current situation in America is different, having changed for the better. We must remember that the time he is talking about was the last year of the first term (January 20, 2017-January 20, 2021) of the 45th US president Donald Trump of the Republican Party.
Currently, Trump is serving as the 47th US president. The ideas that professor Snyder develops in the book have global topical relevance, I think. They are organised into four Chapters or ‘Lessons’ as he dubs them, which in my opinion, have implications that could be utilised even by the citizens of the Macbethian ‘sick state’ that Sri Lanka has become today, complete with a Macbeth (though a muppet) and a shadowy but more determined Lady Macbeth.
Timothy Snyder offers the four Lessons for his fellow Americans, and by extension, to fellow humans around the world including us, Sri Lankans. Perhaps these are uniquely American issues, with little direct relevance to a small country like Sri Lanka with no stake in the international pharmaceutical industry. But then no country can escape from the implications of the following facts (taken from Wikipedia): In 2023, the global pharmaceutical industry earned revenues of US $ 1.48 trillion, whereas the top 10 arms manufacturing companies earned only US $ 632 billion. In the same year, the global life and health insurance carriers industry, which is the biggest industry in the world in terms of revenue, earned US $ 4.3 trillion.
Our own late medical professor Senake Bibile (1920-1977), a pharmacology expert and a rare philanthropist and compassionate social activist of the Trotskyite Sama Samaja party persuasion who always had the welfare of the suffering poor at heart, met his death allegedly in mysterious circumstances in Guyana where he was attending a UN conference, promoting the domestic drug policy that he had developed for Sri Lanka, as a model for use in other countries and by the World Health Organization (WHO), United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), and the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) for developing policies for ‘rational pharmaceutical use’.
It goes without saying that Sri Lankans are also highly vulnerable to the deleterious effects of the inhuman excesses of the purely profit oriented international Big Pharma; these harmful consequences get transferred to the innocent citizens magnified several times through the unholy alliance between the local corporate drugs mafiosi and corrupt politicians. Be that as it may, Snyder adds another three equally important related points, covering all four, each in a Lesson that must receive the utmost attention of all adult Sri Lankans: health care for children and children’s education, truth in politics, and the supremacy of the doctors’ role in a malady situation. We will look at these briefly, intermittently taking our eyes off America to reflect on our own country Sri Lanka.
 Lesson 1 is ‘Health care is a human right’.
Lesson 1 is ‘Health care is a human right’.
Despite its wealth, professor Snyder complains, America is a sick nation; life expectancy is falling for Americans. Moody’s Analytics suggests that US millennials will die younger than their parents or grandparents, though there is no lack of money spent. What is causing this decline in life expectancy? Snyder’s unsettling answer is that the American healthcare system prioritises profit over people’s lives. America still lacks a universal healthcare system, in spite of being a supporter of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and this leads to unequal access to health care, as Snyder asserts.
Exorbitantly priced commercial medicine has a devastating effect on the protection of the health-care rights of the people. It has robbed the American citizens of their health, in Snyder’s view. The American health-care system’s profit-focussed approach and lack of investment in protective equipment for medical professionals jeopardised their safety during the Covid-19 pandemic. In America, 20 million people lost their jobs and over 150,000 died from pandemic. Health insurance became too expensive, and health care unaffordable. Without a diagnosis, many became dangerously ill or unknowingly infected others with the virus.
Though poor, Sri Lanka beats America in respect of looking after public health. It has a better record in providing satisfactory health care for the citizens. The state runs an almost 100% free medicare service for all the citizens. There is a (kind of) parallel paid private hospital system as well, that caters to the better off segment of the population that can resort to it if they prefer to do so. This potentially eases the burden on the free state medical services, which can then focus more on attending to the needs of the economically weaker section of the population.
The maintenance by the state of such a public welfare-based healthcare system is desired and supported by our dominant socio-cultural background that strongly resonates with the humanistic spirit of the Aluth Avurudda that prioritises health over all forms of wealth. This is embodied in the principle Arogya parama labha ‘Good health is the greatest wealth’, the antithesis of the American attitude towards citizens’ health.
Sri Lanka was among the handful of countries that contained the Covid-19 pandemic most efficiently, minimizing deaths, whereas in America, according to Snyder, flaws in the healthcare system were aggravated by the contagion. This led to more deaths in America than in other wealthy nations like Japan and Germany. But the not so well-to-do Sri Lanka escaped with a minimum number of Covid-caused fatalities amidst obstacles mounted by antinationalist ill-wishers as I saw it at the time. That is Professor Snyder’s Lesson 1, which is about the human right of easily accessible health care. Sri Lanka is actually ahead of America in this respect in spite of relative poverty.
by Rohana R. Wasala
(To be concluded.)
Features
Four-day work week; too much rigidity; respectful farewell

 I received a video that announced Japan was considering changing to a four-day work week. Suspicious of such news in my cell phone, I googled and found that certain countries had already opted for work weeks of four days and thus three-day weekends. This change too is a consequence of closedowns of work due to the Covid pandemic.
I received a video that announced Japan was considering changing to a four-day work week. Suspicious of such news in my cell phone, I googled and found that certain countries had already opted for work weeks of four days and thus three-day weekends. This change too is a consequence of closedowns of work due to the Covid pandemic.
“Several countries are experimenting with or have implemented four-day work weeks, including Belgium, Iceland, Spain, the United Kingdom and Portugal. Other countries like Germany, Australia, Canada, the Netherlands and the US have also shown interest in, or have tested the four-day work week model.”
The video I got was about Japan changing its government work week to four days from mid-April with many projected objectives. One is to improve government employees’ work-life balance and to address the country’s declining birth rate. Also, the hours of the work day are to be reduced so parents can spend more time caring for their kids termed: ‘Childcare partial leave’. Flexible work hours for women to be implemented so choosing between careers and family will not be necessary.
In Germany experimental trials were carried out in 2023-24 involving 43 companies; 73% plan to continue with the new work structure. Noted for productivity and efficiency, Germany has in addition to one day less working, on average only 34 hours per week. A five-day week of 9 to 5 has 40 work hours per week. Fewer hours at work has been found to promote smarter and more focussed effort with employees happier and more engaged.
Long ago in the 1970s Cassandra shifted from employment in the private sector to a semi government job. She was shocked at the laissez faire attitude of her co-workers in an information centre. Most came to work at around 9.00 am: discussed the bus journey and home; had breakfast; read the morning newspapers; did a bit of work and were ready to have lunch by 12.00 noon. Two hours for this and half for a small snooze. Work till 3.30 pm or so when books/files were closed and grooming selves commenced, to depart at 4.30 pm sharp.
The work ethic in a remote government school and a private school in a city were as opposed to each other as the proverbial chalk to cheese. Do minimum against teaching; don’t care attitude to dedication and commitment; take leave to maximum vs hardly taking leave in consideration of the fact parents of students pay fees; non disciplining principals to dedicated pedagogues who set an example.
Cassandra supposes, and correctly, that with the change of government and a system change, even though many offices are overstaffed, employees put in a solid day’s work. The public is better served, most definitely.
Hence how would it be for Sri Lanka to lop off one work day a week? There will certainly be benefits, but aren’t many of us complaining about the presence of too many public holidays; we enjoy 24 to 30 a year including every full moon Poya Day. A travesty!
The utter mayhem of Poya weekends
Those who lived through the period when the calendar in this overzealous Buddhist country went lunar (sic) and made the four Poya Days of a month and half the pre-Poya Day as the country’s weekend. It was a total mess since many a week had more than five week days in it till the moon changed from one phase to another. Ceylon was completely out of sync with the rest of the world. That was in 1966 with Dudley Senanayake as Prime Minister. Mercifully, in 1970, the Saturday Sunday weekend was reverted to, and sanity regained.
Conclusion is that making our week of four days’ work and weekend three days has to be carefully considered, tested and implemented, or kept as it is. Better it would be if government offices were pruned of excess staff recruited on politicians’ orders and genuinely legitimate officers made to work efficiently.
VVIP Mother in queue
A photograph made the rounds on social media of a frail looking, white haired lady in a queue in Kandy moving slowly to pay homage to the Sacred Tooth Relic. It was said to be President AKD’s mother who was hospitalised just a couple of months ago. Admired is her devotion as well as the fact she came incognito; not informing her son of her intended travel.
But Cass is censorious. Here was a genuine case of needing a bit of stretching of points and helping her to fulfil her desire to pay homage with ease. After all, he is working hard and very probably long hours to get this country on an even keel. He needs appreciation and if he refuses advantages, let a less able person benefit.
A truly honourable Pope
Roman Catholics across the globe mourn the death of the 266th Pope on the Monday after the Easter weekend; and the world respects and reveres him. People comment he must have willed himself to live through Easter, even presenting himself to crowds gathered in the huge grounds of St Peter’s Basilica.
Pope Francis was born Jorge Bergoglio on December 17, 1936, in Buenos Aires, Argentina. He was inspired to join the Society of Jesus or Jesuits in 1958 after a serious illness. Ordained a Catholic priest in 1969, he was the Jesuit provincial superior in Argentina from 1973 to 79. He became the Archbishop of Buenos Aires in 1998 and was created a cardinal in 2001 by Pope John Paul II. He was elected in the papal conclave following the resignation of Pope Benedict XVI as head of the Catholic Church and Sovereign of the Vatican City State in 1913, claiming many firsts: a Jesuit becoming Pope; first from America, from the Southern Hemisphere. He chose his papal name in honour of Saint Francis of Assisi, kind to all living beings. “Throughout his public life, Francis was noted for his humility, emphasis on God’s mercy, international visibility as pope, concern for the poor and commitment to interreligious dialogue. He was known for having a less formal approach to the papacy than his predecessors.”
We remember his visit to Sri Lanka from January 13 to 15, 2015, when he travelled to the Shrine of Our Lady of Madhu and canonized Sri Lanka’s first saint, Joseph Vaz. He conducted a Mass and bestowed blessings to the multitude at Galle Face Green. As he entered and left the Green, he placed his hands on the heads of infants, children, the very poor, the old and infirm; never mind oil and dirt on heads. A truly great and good person.
Features
Kashmir terror attack underscores need for South Asian stability and amity

 The most urgent need for the South Asian region right now, in the wake of the cold-blooded killing by gunmen of nearly 30 local tourists in Indian-administered Kashmir two days back, is the initiation of measures that could ensure regional stability and peace. The state actors that matter most in this situation are India and Pakistan and it would be in the best interests of the region for both countries to stringently refrain from succumbing to knee-jerk reactions in the face of any perceived provocations arising from the bloodshed.
The most urgent need for the South Asian region right now, in the wake of the cold-blooded killing by gunmen of nearly 30 local tourists in Indian-administered Kashmir two days back, is the initiation of measures that could ensure regional stability and peace. The state actors that matter most in this situation are India and Pakistan and it would be in the best interests of the region for both countries to stringently refrain from succumbing to knee-jerk reactions in the face of any perceived provocations arising from the bloodshed.
The consequences for the countries concerned and the region could be grave if the terror incident leads to stepped-up friction and hostility between India and Pakistan. Some hardline elements in India, for instance, are on record in the international media as calling on the Indian state to initiate tough military action against Pakistan for the Kashmiri terror in question and a positive response to such urgings could even lead to a new India-Pakistan war.
Those wishing South Asia well are likely to advocate maximum restraint by both states and call for negotiations by them to avert any military stand-offs and conflicts that could prove counter-productive for all quarters concerned. This columnist lends his pen to such advocacy.
Right now in Sri Lanka, nationalistic elements in the country’s South in particular are splitting hairs over an MoU relating to security cooperation Sri Lanka has signed with India. Essentially, the main line of speculation among these sections is that Sri Lanka is coming under the suzerainty of India, so to speak, in the security sphere and would be under its dictates in the handling of its security interests. In the process, these nationalistic sections are giving fresh life to the deep-seated anti-India phobia among sections of the Sri Lankan public. The eventual result will be heightened, irrational hostility towards India among vulnerable, unenlightened Sri Lankans.
Nothing new will be said if the point is made that such irrational fears with respect to India are particularly marked among India’s smaller neighbouring states and their publics. Needless to say, collective fears of this kind only lead to perpetually strained relations between India and her neighbours, resulting in regional disunity, which, of course would not be in South Asia’s best interests.
SAARC is seen as ‘dead’ by some sections in South Asia and its present dysfunctional nature seems to give credence to this belief. Continued friction between India and Pakistan is seen as playing a major role in such inner paralysis and this is, no doubt, the main causative factor in SARRC’s current seeming ineffectiveness.
However, the widespread anti-India phobia referred to needs to be factored in as playing a role in SAARC’s lack of dynamism and ‘life’ as well. If democratic governments go some distance in exorcising such anti-Indianism from their people’s psyches, some progress could be made in restoring SAARC to ‘life’ and the latter could then play a constructive role in defusing India-Pakistan tensions.
It does not follow that if SAARC was ‘alive and well’, security related incidents of the kind that were witnessed in India-administered Kashmir recently would not occur. This is far from being the case, but if SAARC was fully operational, the states concerned would be in possession of the means and channels of resolving the issues that flow from such crises with greater amicability and mutual accommodation.
Accordingly, the South Asian Eight would be acting in their interests by seeking to restore SAARC back to ‘life’. An essential task in this process is the elimination of mutual fear and suspicion among the Eight and the states concerned need to do all that they could to eliminate any fixations and phobias that the countries have in relation to each other.
It does not follow from the foregoing that the SAARC Eight should not broad base their relations and pull back from fostering beneficial ties with extra-regional countries and groupings that have a bearing on their best interests. On the contrary, each SAARC country’s ties need to be wide-ranging and based on the principle that each such state would be a friend to all countries and an enemy of none as long as the latter are well-meaning.
The foregoing sharp focus on SAARC and its fortunes is necessitated by the consideration that the developmental issues in particular facing the region are best resolved by the region itself on the basis of its multiple material and intellectual resources. The grouping should not only be revived but a revisit should also be made to its past programs; particularly those which related to intra-regional conflict resolution. Thus, talking to each other under a new visionary commitment to SAARC collective wellbeing is crucially needed.
On the question of ties with India, it should be perceived by the latter’s smaller neighbours that there is no getting away from the need to foster increasingly closer relations with India, today a number one global power.
This should not amount to these smaller neighbours surrendering their rights and sovereignty to India. Far from it. On the contrary these smaller states should seek to craft mutually beneficial ties with India. It is a question of these small states following a truly Non-aligned foreign policy and using their best diplomatic and political skills to structure their ties with India in a way that would be mutually beneficial. It is up to these neighbours to cultivate the skills needed to meet these major challenges.
Going ahead, it will be in South Asia’s best interests to get SAARC back on its feet once again. If this aim is pursued with visionary zeal and if SAARC amity is sealed once and for all intra-regional friction and enmities could be put to rest. What smaller states should avoid scrupulously is the pitting of extra-regional powers against India and Pakistan in their squabbles with either of the latter. This practice has been pivotal in bringing strife and contention into South Asia and in dividing the region against itself.
Accordingly, the principal challenge facing South Asia is to be imbued once again with the SAARC spirit. The latter spirit’s healing powers need to be made real and enduring. Thus will we have a region truly united in brotherhood and peace.
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoDIMO pioneers major fleet expansion with Tata SIGNA Prime Movers for ILM
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoFamily discovers rare species thought to be extinct for over a century in home garden
-

 Features4 days ago
Features4 days agoRuGoesWild: Taking science into the wild — and into the hearts of Sri Lankans
-

 Foreign News6 days ago
Foreign News6 days agoChina races robots against humans in Beijing half marathon
-

 Editorial7 days ago
Editorial7 days agoSelective use of PTA
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoOrders under the provisions of the Prevention of Corruptions Act No. 9 of 2023 for concurrence of parliament
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoNew species of Bronzeback snake, discovered in Sri Lanka
-

 Features6 days ago
Features6 days agoThe ironies of history














