Features
Ethical drugs, unethical practices

by Geewananda Gunawardana, Ph.D.
Ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceuticals requires a high level of constant vigilance. A good example is the four deaths caused by contaminated eye drops in the USA last May despite the well-regulated and best prepared monitoring of the drug supply by the US Food and Drug Administration. Unfortunately, the consumers in places where regulations as well as their implementations fall short of ideals can fall victims much more frequently: A World health Organization (WHO) report finds that about 10% of the world’s drug supply is either subpar or fake. Global deaths among children alone due to subpar drugs is over 150 thousand annually while the economic cost is estimated to be about US $ 200 billion.
While loss of life is a tragedy, the failure to ensure the quality of medicinal products can have far reaching and long-lasting consequences of much larger magnitude. The emergence of drug resistant infections and parasitic diseases and genetic disorders due to subpar drugs will only come to light in the long run.
To get some idea about the vulnerability of pharmaceuticals, it is important to know the way the regulatory process works. Almost 90% of the new drug development takes place in North America and Europe. The rest is divided among Japan and Israel. India and China, leaders in generic drug manufacture, are only beginning to enter this field through collaboration with American and European pharmaceutical companies. When a drug is invented, the inventor obtains a patent, which is an exclusive right to market it for 20 years. However, a patent only keeps the competition away, and it does not give the authority to market the drug, which must be obtained from the regulatory agency of the respective country.
To get the marketing authority, a vast amount of data must be produced showing efficacy, safety, and manufacturability of the drug. This process takes 10 to 12 years on average and over US $ 1.5 billion in R&D costs. As the development takes up to 8 to 10 years, the actual patent life left when it goes to market is reduced to 10 to 12 years, during which time the company must recoup all the costs and make a profit. A drug marketed under patent is known as a brand name drug. These initial R&D costs make the brand name drugs expensive.
The manufacturer of the brand name drug must follow all the current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) as specified by the regulatory agency of the marketed countries. The International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) has standardised these guidelines and are followed by the major pharmaceutical manufacturing countries. Adherence to the cGMP regulations assures the identity, strength, quality, and purity of drug products by requiring that manufacturers of medications adequately control manufacturing operations.
The consequences of failing to meet guidance can be harsh. For example, the UK based Glaxo Smith Kline was fined US$ 3 billion in 2012, the highest in history for cGMP violations. The brand name drug manufacturers avoid taking any risks as the stakes are very high. There are some companies that were forced to shut down for failing to follow cGMP. A common problem with brand name drugs is the manufacture of counterfeit drugs sold in small markets despite the best efforts of the patent owner to avoid such piracy. The commitment to quality and the stringent regulatory vigilance makes brand name drugs less susceptible for quality issues.
Once the patent expires, anyone with the right capabilities can manufacture the drug and seek marketing authorisation in selected countries. These drugs are referred to as generic drugs. Since the generic manufacturers do not have to bear the billion-dollar R&D costs, they can afford to lower the price. The competition for market share also drastically reduces the cost of generic drugs, often by over 80% of the original price. The costs can be further reduced by moving the manufacturing into places where the labor and operating costs are lower and occupational safety and environmental regulations are lax or lacking altogether. The affordability and wide availability are the beneficial outcomes of generic drugs. For example, 91% of the drugs prescribed in the USA in 2022 were generic drugs. Except for a rare event, the US drug supply remains safe and reliable, mainly thanks to the diligence of the US Food and Drug Administration.
The bulk of these cost-effective generic drugs are destined for low- and middle-income countries. Unfortunately, that is where the troubles begin. The WHO has formulated international regulatory standards to ensure the safety and efficacy of the drugs in places where ICH guidance is not implemented. They also have a program for pre-qualification of drug manufacturing facilities when requested. While international organisations require WHO prequalification for drug purchases, individual governments can follow their own regulations. Knowing the presence of potential buyers who are willing to forgo cGMP requirements, some manufacturers tend to ignore the need for costly qualification or certification programms. This practice is also encouraged by the premise on the buyers’ side that testing alone can ensure the quality of drugs. However, the truth is that failing to follow cGMP can lead to unintended release of subpar drugs to markets even if the standard testing procedures are followed.
Two processes where this can happen easily are sterilisation and achieving content uniformity. Failure to ensure that every single unit of the drug, be it a pill or a vial of many thousands manufactured, is compliant could result in subpar drugs reaching the market. In the case of uneven sterilisation, microbial contamination can occur as was seen with eye drops. Failure to ensure uniformity can result in drug units containing either higher or lower doses than shown on the label.
Most of the generic drugs are manufactured in Asia. Drug manufacturing is a multistep process conducted in multiple locations under varying levels of regulatory control. A routine drug manufacture can have the following basic steps: procurement of raw materials, synthesis of starting materials and/or intermediates, synthesis of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), procurement of excipients, and formulation of the API into the drug product – capsule, tablet, syrup etc. This can vary for biologics such as vaccines and recombinant proteins etc., which make up only about 2% of all drugs used. In either case, at every step, the product must be stored in proper containers under the right conditions as determined based on its stability to prevent degradation and contamination.
Except for biologics, almost all drugs are produced by chemical synthesis. A small portion are either plant or microbial origin. The generic drug manufacturers come up with alternate synthetic routes that are cost effective. This creates a major problem: Any synthetic process generates impurities or side products in addition to the desired product. These impurities could have unknown properties, including toxicity, and must be removed or kept to a minimum using various purification steps. The processes and analytical methods used for this purpose by the brand name manufacturer are optimized to monitor and control any impurities specific to the raw materials, starting materials, and excipients they used. However, if the generic manufacturers introduce any changes, the standard quality control methods may not work, and undesired impurities will end up in the drug causing potential adverse events. Another potential problem, particularly in the warm and humid tropics, is microbial contamination, as happened with eye drops when handling and storage conditions are deviated.
With complicated supply chains, it is very difficult for the drug purchaser to track if all processes used in the manufacture of the drug were conducted under cGMP. Either they do not have the wherewithal or have no impetus altogether as happens when questionable drug procurement methods are followed. There are other ways the purity of drugs can be compromised. All drugs have a limited lifetime as specified by the expiration date. The expiration date is set assuming the storage of the drug under certain conditions and in designated containers. Any deviation, which can happen easily when transported between tropical locations, the drug can degrade reducing the potency or efficacy and introducing impurities. Without proper cGMP, it is not possible to know if such deviations have occurred.
If the drug is degraded, the desired therapeutic effect may not be achieved. In addition to that, in the case of antimicrobial and antiparasitic drugs, the administration of lower doses can lead to the development of drug resistant varieties. Infections caused by resistant organisms can be difficult, and sometimes impossible, to treat. Antimicrobial resistance is an urgent global public health threat that killed around 1.27 million people worldwide in 2019. If not controlled, this could render the current anti-infective drugs virtually useless and makes it one of the world’s most urgent public health problems.
The impurities or contaminants in drugs can have numerous undesired results including death. The deaths of 66 children in Gambia last year caused by taking contaminated cough syrup, imported from India, is just one example. A serious problem is contamination with genotoxic compounds. If not detected promptly, the consequences would not be known for many generations. The genotoxic impurities can be harmful when present in as low as parts per million amounts in the drug. The analytical techniques for detecting such low amounts require specific instruments not readily available in most laboratories. Recently, a whole family of hypertension drugs were found to contain genotoxic impurities and were withdrawn from the US markets.
These are the problems that can arise under normal operating procedures, and fortunately, the ones that can be eliminated if proper cGMP are observed. To worsen things, there are added problems that go beyond manufacture and cGMP. Unscrupulous drug companies and corrupt administrations contribute to the problem by knowingly allowing substandard drugs into healthcare systems with total disregard for life and limb. Pharmaceutical industry is notorious for its “gift” system for buying or prescribing their drugs. In one reported incident, a company sold 45 years’ worth of antibiotics to a developing country when the shelf life of the drug is only 2 years. Unloading drugs that are nearing expiration or not suitable for their own countries into low-income countries is a common practice.
The subpar drug related adverse events are predictable but also preventable. Generic drugs in general are safe and effective as international organizations have provided the means to ensure their safety and efficacy. Every step from the supply of starting materials to the dispensing of the drug to the patient must be controlled according to the guidance to receive the full benefits of drugs and avoid adversities. Sri Lanka has incorporated most of those rules and regulations to their own. However, their complete implementation remains questionable. Purchasing drugs without knowing its complete history is inviting trouble. Neglecting to do so puts future generations at risk in addition to wasting hard-earned foreign exchange.
Features
The US-China rivalry and challenges facing the South

 The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
The US-China rivalry could be said to make-up the ‘stuff and substance’ of world politics today but rarely does the international politics watcher and student of the global South in particular get the opportunity of having a balanced and comprehensive evaluation of this crucial relationship. But such a balanced assessment is vitally instrumental in making sense of current world power relations.
Thanks to the Regional Centre for Strategic Studies (RCSS), Colombo the above window of opportunity was opened on December 8th for those sections of the public zealously pursuing an understanding of current issues in global politics. The knowledge came via a forum that was conducted at the RCSS titled, ‘The US-China Rivalry and Implications for the Indo-Pacific’, where Professor Neil DeVotta of the Wake Forest University of North Carolina in the US, featured as the speaker.
A widely representative audience was present at the forum, including senior public servants, the diplomatic corps, academics, heads of civil society organizations, senior armed forces personnel and the media. The event was ably managed by the Executive Director of the RCSS, retired ambassador Ravinatha Aryasinha. Following the main presentation a lively Q&A session followed, where many a point of interest was aired and discussed.
While there is no doubt that China is fast catching up with the US with regard to particularly military, economic, scientific and technological capability, Prof. DeVotta helped to balance this standard projection of ‘China’s steady rise’ by pointing to some vital facts about China, the omission of which would amount to the observer having a somewhat uninformed perception of global political realities.
The following are some of the facts about contemporary China that were highlighted by Prof. DeVotta:
* Money is steadily moving out of China and the latter’ s economy is slowing down. In fact the country is in a ‘ Middle Income Trap’. That is, it has reached middle income status but has failed to move to upper income status since then.
* People in marked numbers are moving out of China. It is perhaps little known that some Chinese are seeking to enter the US with a view to living there. The fact is that China’s population too is on the decline.
* Although the private sector is operative in China, there has been an increase in Parastatals; that is, commercial organizations run by the state are also very much in the fore. In fact private enterprises have begun to have ruling Communist Party cells in them.
* China is at its ‘peak power’ but this fact may compel it to act ‘aggressively’ in the international sphere. For instance, it may be compelled to invade Taiwan.
* A Hard Authoritarianism could be said to characterize central power in China today, whereas the expectation in some quarters is that it would shift to a Soft Authoritarian system, as is the case in Singapore.
* China’s influence in the West is greater than it has ever been.
The speaker was equally revelatory about the US today. Just a few of these observations are:
* The US is in a ‘Unipolar Moment’. That is, it is the world’s prime power. Such positions are usually not longstanding but in the case of the US this position has been enjoyed by it for quite a while.
* China is seen by the US as a ‘Revisionist Power’ as opposed to being a ‘Status Quo Power.’ That is China is for changing the world system slowly.
* The US in its latest national security strategy is paying little attention to Soft Power as opposed to Hard Power.
* In terms of this strategy the US would not allow any single country to dominate the Asia-Pacific region.
* The overall tone of this strategy is that the US should step back and allow regional powers to play a greater role in international politics.
* The strategy also holds that the US must improve economic ties with India, but there is very little mention of China in the plan.
Given these observations on the current international situation, a matter of the foremost importance for the economically weakest countries of the South is to figure out how best they could survive materially within it. Today there is no cohesive and vibrant collective organization that could work towards the best interests of the developing world and Dr. DeVotta was more or less correct when he said that the Non-alignment Movement (NAM) has declined.
However, this columnist is of the view that rather being a spent force, NAM was allowed to die out by the South. NAM as an idea could never become extinct as long as economic and material inequalities between North and South exist. Needless to say, this situation is remaining unchanged since the eighties when NAM allowed itself to be a non-entity so to speak in world affairs.
The majority of Southern countries did not do themselves any good by uncritically embracing the ‘market economy’ as a panacea for their ills. As has been proved, this growth paradigm only aggravated the South’s development ills, except for a few states within its fold.
Considering that the US would be preferring regional powers to play a more prominent role in the international economy and given the US’ preference to be a close ally of India, the weakest of the South need to look into the possibility of tying up closely with India and giving the latter a substantive role in advocating the South’s best interests in the councils of the world.
To enable this to happen the South needs to ‘get organized’ once again. The main differences between the past and the present with regard to Southern affairs is that in the past the South had outstanding leaders, such as Jawaharlal Nehru of India, who could doughtily stand up for it. As far as this columnist could ascertain, it is the lack of exceptional leaders that in the main led to the decline of NAM and other South-centred organizations.
Accordingly, an urgent task for the South is to enable the coming into being of exceptional leaders who could work untiringly towards the realization of its just needs, such as economic equity. Meanwhile, Southern countries would do well to, indeed, follow the principles of NAM and relate cordially with all the major powers so as to realizing their best interests.
Features
Sri Lanka and Global Climate Emergency: Lessons of Cyclone Ditwah
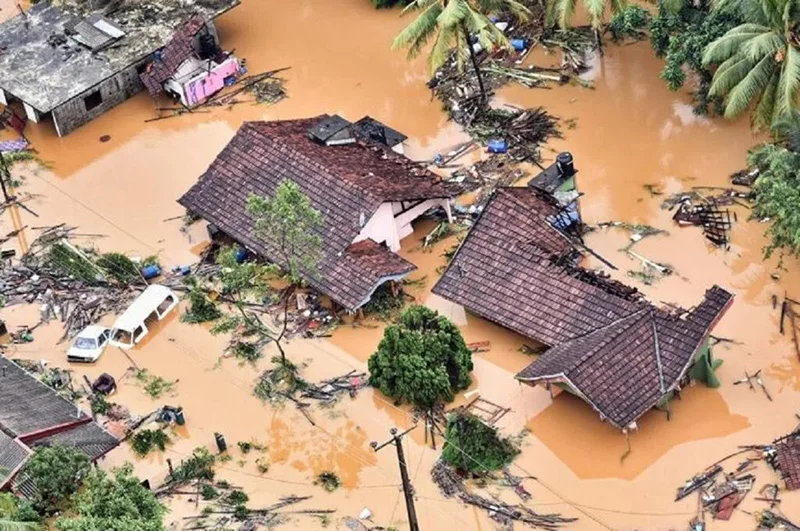

Tropical Cyclone Ditwah, which made landfall in Sri Lanka on 28 November 2025, is considered the country’s worst natural disaster since the deadly 2004 tsunami. It intensified the northeast monsoon, bringing torrential rainfall, massive flooding, and 215 severe landslides across seven districts. The cyclone left a trail of destruction, killing nearly 500 people, displacing over a million, destroying homes, roads, and railway lines, and disabling critical infrastructure including 4,000 transmission towers. Total economic losses are estimated at USD 6–7 billion—exceeding the country’s foreign reserves.
The Sri Lankan Armed Forces have led the relief efforts, aided by international partners including India and Pakistan. A Sri Lanka Air Force helicopter crashed in Wennappuwa, killing the pilot and injuring four others, while five Sri Lanka Navy personnel died in Chundikkulam in the north while widening waterways to mitigate flooding. The bravery and sacrifice of the Sri Lankan Armed Forces during this disaster—as in past disasters—continue to be held in high esteem by grateful Sri Lankans.
The Sri Lankan government, however, is facing intense criticism for its handling of Cyclone Ditwah, including failure to heed early warnings available since November 12, a slow and poorly coordinated response, and inadequate communication with the public. Systemic issues—underinvestment in disaster management, failure to activate protocols, bureaucratic neglect, and a lack of coordination among state institutions—are also blamed for avoidable deaths and destruction.
The causes of climate disasters such as Cyclone Ditwah go far beyond disaster preparedness. Faulty policymaking, mismanagement, and decades of unregulated economic development have eroded the island’s natural defenses. As climate scientist Dr. Thasun Amarasinghe notes:
“Sri Lankan wetlands—the nation’s most effective natural flood-control mechanism—have been bulldosed, filled, encroached upon, and sold. Many of these developments were approved despite warnings from environmental scientists, hydrologists, and even state institutions.”
Sri Lanka’s current vulnerabilities also stem from historical deforestation and plantation agriculture associated with colonial-era export development. Forest cover declined from 82% in 1881 to 70% in 1900, and to 54–50% by 1948, when British rule ended. It fell further to 44% in 1954 and to 16.5% by 2019.
Deforestation contributes an estimated 10–12% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Beyond removing a vital carbon sink, it damages water resources, increases runoff and erosion, and heightens flood and landslide risk. Soil-depleting monocrop agriculture further undermines traditional multi-crop systems that regenerate soil fertility, organic matter, and biodiversity.
In Sri Lanka’s Central Highlands, which were battered by Cyclone Ditwah, deforestation and unregulated construction had destabilised mountain slopes. Although high-risk zones prone to floods and landslides had long been identified, residents were not relocated, and construction and urbanisation continued unchecked.
Sri Lanka was the first country in Asia to adopt neoliberal economic policies. With the “Open Economy” reforms of 1977, a capitalist ideology equating human well-being with quantitative growth and material consumption became widespread. Development efforts were rushed, poorly supervised, and frequently approved without proper environmental assessment.
Privatisation and corporate deregulation weakened state oversight. The recent economic crisis and shrinking budgets further eroded environmental and social protections, including the maintenance of drainage networks, reservoirs, and early-warning systems. These forces have converged to make Sri Lanka a victim of a dual climate threat: gradual environmental collapse and sudden-onset disasters.
Sri Lanka: A Climate Victim
Sri Lanka’s carbon emissions remain relatively small but are rising. The impact of climate change on the island, however, is immense. Annual mean air temperature has increased significantly in recent decades (by 0.016 °C annually between 1961 and 1990). Sea-level rise has caused severe coastal erosion—0.30–0.35 meters per year—affecting nearly 55% of the shoreline. The 2004 tsunami demonstrated the extreme vulnerability of low-lying coastal plains to rising seas.
The Cyclone Ditwah catastrophe was neither wholly new nor surprising. In 2015, the Geneva-based Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC) identified Sri Lanka as the South Asian country with the highest relative risk of disaster-related displacement: “For every million inhabitants, 15,000 are at risk of being displaced every year.”
IDMC also noted that in 2017 the country experienced seven disaster events—mainly floods and landslides—resulting in 135,000 new displacements and that Sri Lanka “is also at risk for slow-onset impacts such as soil degradation, saltwater intrusion, water scarcity, and crop failure”.
Sri Lanka ranked sixth among countries most affected by extreme weather events in 2018 (Germanwatch) and second in 2019 (Global Climate Risk Index). Given these warnings, Cyclone Ditwah should not have been a surprise. Scientists have repeatedly cautioned that warmer oceans fuel stronger cyclones and warmer air holds more moisture, leading to extreme rainfall. As the Ceylon Today editorial of December 1, 2025 also observed:
“…our monsoons are no longer predictable. Cyclones form faster, hit harder, and linger longer. Rainfall becomes erratic, intense, and destructive. This is not a coincidence; it is a pattern.”
Without urgent action, even more extreme weather events will threaten Sri Lanka’s habitability and physical survival.
A Global Crisis
Extreme weather events—droughts, wildfires, cyclones, and floods—are becoming the global norm. Up to 1.2 billion people could become “climate refugees” by 2050. Global warming is disrupting weather patterns, destabilising ecosystems, and posing severe risks to life on Earth. Indonesia and Thailand were struck by the rare and devastating Tropical Cyclone Senyar in late November 2025, occurring simultaneously with Cyclone Ditwah’s landfall in Sri Lanka.
More than 75% of global greenhouse gas emissions—and nearly 90% of carbon emissions—come from burning coal, oil, and gas, which supply about 80% of the world’s energy. Countries in the Global South, like Sri Lanka, which contribute least to greenhouse gas emissions, are among the most vulnerable to climate devastation. Yet wealthy nations and multilateral institutions, including the World Bank, continue to subsidise fossil fuel exploration and production. Global climate policymaking—including COP 30 in Belém, Brazil, in 2025—has been criticised as ineffectual and dominated by fossil fuel interests.
If the climate is not stabilised, long-term planetary forces beyond human control may be unleashed. Technology and markets are not inherently the problem; rather, the issue lies in the intentions guiding them. The techno-market worldview, which promotes the belief that well-being increases through limitless growth and consumption, has contributed to severe economic inequality and more frequent extreme weather events. The climate crisis, in turn, reflects a profound mismatch between the exponential expansion of a profit-driven global economy and the far slower evolution of human consciousness needed to uphold morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom.
Sri Lanka’s 2025–26 budget, adopted on November 14, 2025—just as Cyclone Ditwah loomed—promised subsidised land and electricity for companies establishing AI data centers in the country.
President Anura Kumara Dissanayake told Parliament: “Don’t come questioning us on why we are giving land this cheap; we have to make these sacrifices.”
Yet Sri Lanka is a highly water-stressed nation, and a growing body of international research shows that AI data centers consume massive amounts of water and electricity, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
The failure of the narrow, competitive techno-market approach underscores the need for an ecological and collective framework capable of addressing the deeper roots of this existential crisis—both for Sri Lanka and the world.
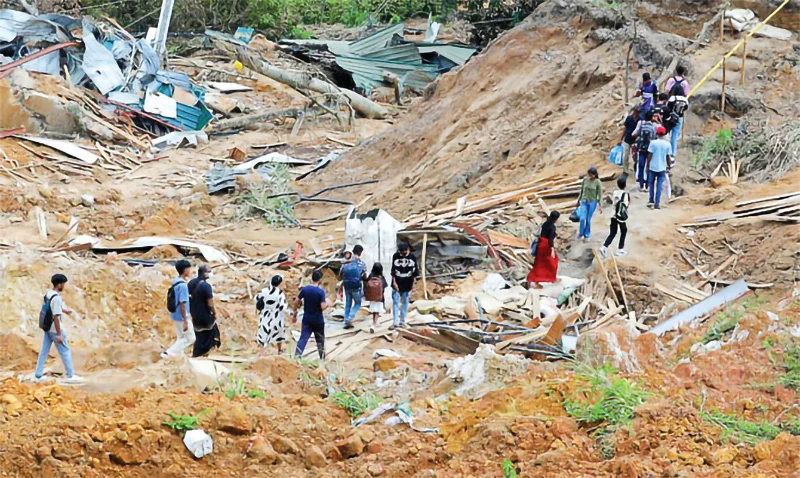

A landslide in Sri Lanka (AFP picture)
Ecological and Human Protection
Ecological consciousness demands
recognition that humanity is part of the Earth, not separate from it. Policies to address climate change must be grounded in this understanding, rather than in worldviews that prize infinite growth and technological dominance. Nature has primacy over human-created systems: the natural world does not depend on humanity, while humanity cannot survive without soil, water, air, sunlight, and the Earth’s essential life-support systems.
Although a climate victim today, Sri Lanka is also home to an ancient ecological civilization dating back to the arrival of the Buddhist monk Mahinda Thera in the 3rd century BCE. Upon meeting King Devanampiyatissa, who was out hunting in Mihintale, Mahinda Thera delivered one of the earliest recorded teachings on ecological interdependence and the duty of rulers to protect nature:
“O great King, the birds of the air and the beasts of the forest have as much right to live and move about in any part of this land as thou. The land belongs to the people and all living beings; thou art only its guardian.”
A stone inscription at Mihintale records that the king forbade the killing of animals and the destruction of trees. The Mihintale Wildlife Sanctuary is believed to be the world’s first.
Sri Lanka’s ancient dry-zone irrigation system—maintained over more than a millennium—stands as a marvel of sustainable development. Its network of interconnected reservoirs, canals, and sluices captured monsoon waters, irrigated fields, controlled floods, and even served as a defensive barrier. Floods occurred, but historical records show no disasters comparable in scale, severity, or frequency to those of today. Ancient rulers, including the legendary reservoir-builder King Parākramabāhu, and generations of rice farmers managed their environment with remarkable discipline and ecological wisdom.
The primacy of nature became especially evident when widespread power outages and the collapse of communication networks during Cyclone Ditwah forced people to rely on one another for survival. The disaster ignited spontaneous acts of compassion and solidarity across all communities—men and women, rich and poor, Buddhists, Christians, Muslims, and Hindus. Local and international efforts mobilized to rescue, shelter, feed, and emotionally support those affected. These actions demonstrated a profound human instinct for care and cooperation, often filling vacuums left by formal emergency systems.
Yet spontaneous solidarity alone is insufficient. Sri Lanka urgently needs policies on sustainable development, environmental protection, and climate resilience. These include strict, science-based regulation of construction; protection of forests and wetlands; proper maintenance of reservoirs; and climate-resilient infrastructure. Schools should teach environmental literacy that builds unity and solidarity, rather than controversial and divisive curriculum changes like the planned removal of history and introduction of contested modules on gender and sexuality.
If the IMF and international creditors—especially BlackRock, Sri Lanka’s largest sovereign bondholder, valued at USD 13 trillion—are genuinely concerned about the country’s suffering, could they not cancel at least some of Sri Lanka’s sovereign debt and support its rebuilding efforts? Addressing the climate emergency and the broader existential crisis facing Sri Lanka and the world ultimately requires an evolution in human consciousness guided by morality, compassion, generosity and wisdom. (Courtesy: IPS NEWS)
Dr Asoka Bandarage is the author of Colonialism in Sri Lanka: The Political Economy of the Kandyan Highlands, 1833-1886 (Mouton) Women, Population and Global Crisis: A Politico-Economic Analysis (Zed Books), The Separatist Conflict in Sri Lanka: Terrorism, Ethnicity, Political Economy, ( Routledge), Sustainability and Well-Being: The Middle Path to Environment, Society and the Economy (Palgrave MacMillan) Crisis in Sri Lanka and the World: Colonial and Neoliberal Origins, Ecological and Collective Alternatives (De Gruyter) and numerous other publications. She serves on the Advisory Boards of the Interfaith Moral Action on Climate and Critical Asian Studies.
Features
Cliff and Hank recreate golden era of ‘The Young Ones’

 Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin’s reunion concert at the Riverside Theatre in Perth, Australia, on 01 November, 2025, was a night to remember.
The duo, who first performed together in the 1950s as part of The Shadows, brought the house down with their classic hits and effortless chemistry.
The concert, part of Cliff’s ‘Can’t Stop Me Now’ tour, featured iconic songs like ‘Summer Holiday’, ‘The Young Ones’, ‘Bachelor Boy’, ‘Living Doll’ and a powerful rendition of ‘Mistletoe and Wine.’
Cliff, 85, and Hank, with his signature red Fender Stratocaster, proved that their music and friendship are timeless.
According to reports, the moment the lights dimmed and the first chords of ‘Move It’ rang out, the crowd knew they were in for something extraordinary.
Backed by a full band, and surrounded by dazzling visuals, Cliff strode onto the stage in immaculate form – energetic and confident – and when Hank Marvin joined him mid-set, guitar in hand, the audience erupted in applause that shook the hall.
Together they launched into ‘The Young Ones’, their timeless 1961 hit which brought the crowd to its feet, with many in attendance moved to tears.
The audience was treated to a journey through time, with vintage film clips and state-of-the-art visuals adding to the nostalgic atmosphere.
Highlights of the evening included Cliff’s powerful vocals, Hank’s distinctive guitar riffs, and their playful banter on stage.

Cliff posing for The Island photographer … February,
2007
Cliff paused between songs to reflect on their shared journey saying:
“It’s been a lifetime of songs, memories, and friendship. Hank and I started this adventure when we were just boys — and look at us now, still up here making noise!”
As the final chords of ‘Congratulations’ filled the theatre, the crowd rose for a thunderous standing ovation that lasted several minutes.
Cliff waved, Hank gave a humble bow, and, together, they left the stage, arm-in-arm, to the refrain of “We’re the young ones — and we always will be.”
Reviews of the show were glowing, with fans and critics alike praising the duo’s energy, camaraderie, and enduring talent.
Overall, the Cliff Richard and Hank Marvin reunion concert was a truly special experience, celebrating the music and friendship that has captivated audiences for decades.
When Cliff Richard visited Sri Lanka, in February, 2007, I was invited to meet him, in his suite, at a hotel, in Colombo, and I presented him with my music page, which carried his story, and he was impressed.
In return, he personally autographed a souvenir for me … that was Cliff Richard, a truly wonderful human being.
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoOver 35,000 drug offenders nabbed in 36 days
-

 Features2 days ago
Features2 days agoFinally, Mahinda Yapa sets the record straight
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoCyclone Ditwah leaves Sri Lanka’s biodiversity in ruins: Top scientist warns of unseen ecological disaster
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoLOLC Finance Factoring powers business growth
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoCPC delegation meets JVP for talks on disaster response
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoA 6th Year Accolade: The Eternal Opulence of My Fair Lady
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoRising water level in Malwathu Oya triggers alert in Thanthirimale
-

 Features5 days ago
Features5 days agoThe Catastrophic Impact of Tropical Cyclone Ditwah on Sri Lanka: