Opinion
Palm oil growers await green light for sustainable production

By Emeritus Prof. Asoka Nugawela
Palm oil is a versatile commodity. It is used in numerous products world over. The global usage in 2022/23 is estimated as 76 million metric tons. Accordingly, the average global per capita usage is in the range of 10 kg per annum. Sri Lanka too recorded similar usage during 2018/2019 period, prior to economic downturn in the country. Palm oil usage is very much higher than the usage of other vegetable oils such as coconut, soya, canola, sunflower, rape seed and olive. One major reason for the relatively high per capita usage of palm oil is the affordability to purchase and its availability. Per unit land area, the oil production is four times greater in oil palm when compared with coconut. When comparing with other crops grown for vegetable oil production it is about tenfold higher. Further, oil palm, coconut and olive are perennial crops whereas soya, sunflower, canola and rape seed are short term crops. With short term crops the capital cost component is relatively high with yearly land clearing, land preparation and planting activities to be undertaken. Oil palm with a high oil yield and having a 30-year economic life cycle has the ability to provide a relatively cheaper vegetable oil than from other crops. With perennial crops the disturbance to the soil properties and biodiversity is less than in annuals and is a positive attribute as far as sustainability is concerned.
One other reason for palm oil to be the preferred vegetable oil is because it contains both saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in almost equal proportions. Thus, it is different from coconut and other vegetable oils which contain a relatively high percentage of unsaturated fatty acids, around 90%. Palm oil with its 1:1 balance of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids is the preferred choice for many applications in the food industry.
Both the type and the number of fatty acids of fat in our diets are known to influence health and wellbeing. The present global advice is to increase the consumption of unsaturated fatty acids at the expense of saturated oils and fats. For optimal health we require a mixture of fatty acids to be present in our diet. In this context among the sources of dietary oils and fats palm oil could be viewed as a relatively better option for its ‘mixed’ fatty acid profile (saturated, mono and polyunsaturated fatty acids).
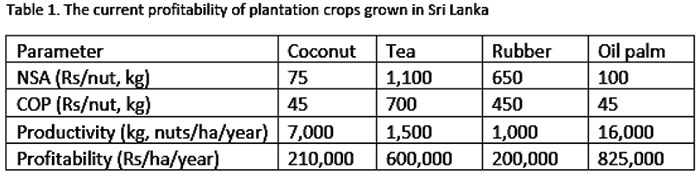 The relative advantage in the return on investment the oil palm crop is having over other plantations crops also drives the investments towards this crop. This is true for both plantation and smallholder sectors in major palm oil producing countries in the world. The profitability from different plantation crops grown in Sri Lanka under average management conditions and current agrochemical/material costs & trading conditions are summarised in Table 1. Accordingly, oil palm is by far the most profitable plantation crop in the country. (See table)
The relative advantage in the return on investment the oil palm crop is having over other plantations crops also drives the investments towards this crop. This is true for both plantation and smallholder sectors in major palm oil producing countries in the world. The profitability from different plantation crops grown in Sri Lanka under average management conditions and current agrochemical/material costs & trading conditions are summarised in Table 1. Accordingly, oil palm is by far the most profitable plantation crop in the country. (See table)
The country has a demand for palm oil as a cooking oil and also as a raw material for many other industries. The products made in these industries are essential and widely used. For vigorous growth and high yields oil palm crop should ideally be grown under tropical climatic conditions with more than 2,500 mm of rainfall per annum. The low country wet zone of the country is blessed with such climatic conditions. The return on investment is high with this crop. However, even under such a favorable business environment for this industry, the government of Sri Lanka has taken a decision to ban cultivating this crop in the country. All other palm oil producing countries in the world, i.e., more than 20, are surprised and view this as a wrong decision.
Some repercussions of this decision to ban oil palm cultivation in Sri Lanka are a). dependency on other countries to fulfill our vegetable oil need, b). loss of foreign exchange to the country by importing palm oil, c). loss of income to the potential investors, d). loss of employment opportunities and e). depriving potential smallholders, the opportunity to enhance their livelihood. Prior to the economic crisis in this country, around 200,000 MT of crude palm oil (CPO) had been imported annually. The current global market price of a metric ton of crude palm oil is around 900 US$. Thus, the foreign exchange requirement to import national crude palm oil requirement will be more than 180 million US$ per annum without freight and insurance costs.
In the past, forests have been felled to cultivate oil palm in some major palm oil producing countries. The same approach was adopted for planting other plantation crops as well in the past. Deforestation will invariably lead to further shrinking of already depleted forest cover and loss of environmental services we accrue from natural forests. Natural forests significantly contribute to depleting of greenhouses gases, to the natural water cycle and protects biodiversity, soil, catchment areas, rivers and water bodies. Due to serious negative impacts of deforestation on the environment, a worldwide lobby demanding countries to grow oil palm in a more sustainable manner was initiated. With this lobby changes are now taking place in the manner in which land is selected to grow oil palm. For most crops including oil palm, systems to certify sustainable plantation management have evolved and such certification has become a requirement for marketing of produce from plantations. Basically, issues related to cultivating oil palm had been identified, awareness created amongst parties concerned and interventions for rectification have been put in place. In Sri Lanka however, to start with there was no issue of deforestation associated with oil palm cultivation. The land for cultivating oil palm in Sri Lanka was obtained through crop diversification, a scientifically accepted approach. Even then cultivating of oil palm in Sri Lanka was suddenly banned by the government incurring the investors a loss of more than Rs. 500 million on nursery plants alone. The global lobby was against felling forests to plant oil palm. The reasons for the anti-oil palm lobby in Sri Lanka according to some environmentalists, scientists and politicians are negative impacts to the environment, loss of biodiversity, depleting soil water and threat to the existence of other plantation crops. There is no scientific basis for such allegations. But those who lobby against planting oil palm do not want to understand the difference between ecological impacts when planting oil palm subsequent to felling natural forest cover and as a crop diversification program. Various attempts made had been futile and as the Sinhala saying goes it’s like trying to wake up a person who pretends to be sleeping.
The necessity for a country to produce its own needs is more than evident now with the economic crisis the country is facing currently. With a huge disparity in outflow and inflow of foreign exchange to the country the need to produce our own requirements are very much obvious. As explained earlier in this article Sri Lanka has a conducive business environment for a successful palm oil industry. What is lacking to drive the industry forward in the country is the political will. Politicians may be fearing that a decision to lift the ban on oil palm cultivation will not be a popular decision affecting their vote base. Countries economy is currently shrinking leading significant losses in employment, falling income levels, increased inequality and government borrowings. To recover from such an economic crisis the country should not ignore viable industries that could enhance national production. A reversal to the decision to ban oil palm cultivation will lead to producing national requirement preventing the outflow of millions of dollars each year. Revenue moving out will circulate among all stakeholders of the industry helping to enhance their livelihood and strengthening the economy of the country.
Opinion
Education needed about people not feeding wildlife
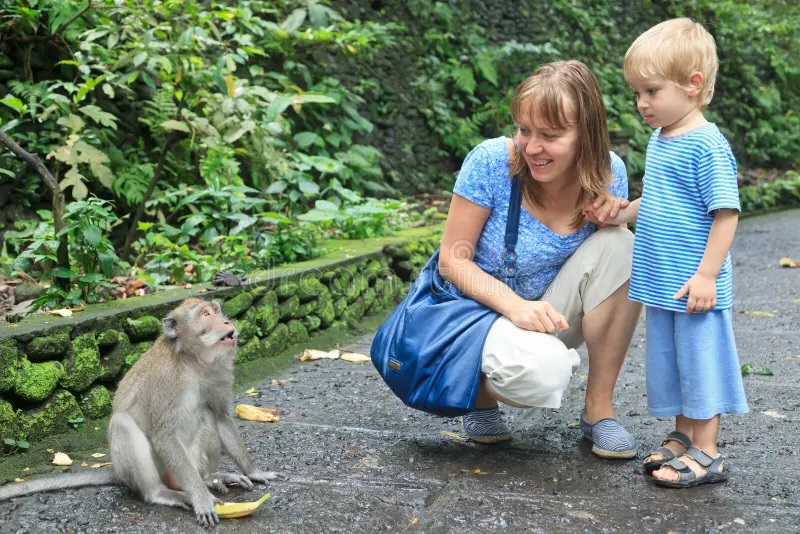

Being wildlife enthusiasts and bird watchers we took a river “safari” during a recent family trip to Bentota. We were dismayed to see that it seems to be the standard practice to feed the monkeys, I think they were the purple faced langurs, that were encountered on the river banks. Each boat that passed by stopped with boxed fruit, coconut and other odds and ends to feed them.
We managed to stop our guy from doing so but faced derision and laughter that we shouldn’t be afraid of monkeys. We tried to explain to him that this is a plague affecting Sri Lanka; elephants being fed on road sides and even in national parks, monkeys being fed from hotel balconies and apparently during river boat rides, birds being fed on hotel terraces etc.
This was met with further mockery and amused dismissal. An effort to make them understand that this was their livelihood that they were destroying it in this manner sailed over their heads. They even have a picture of a baby crocodile on the shoulders of a tourist on their billboard.
We need to consider the following:
Educate such tour operators about the importance of not interfering with the environment and the behaviour of wild animals.
Include education and training in the hotel school, and in schools in tourist resort towns about their duty and responsibility to the environment and the ecosystem on which we all depend.
If it is not already the case such operators should have licenses that should be revoked and fined if found to be engaging in such destructive acts.
Tamara Nanayakkara
Opinion
Capt. Dinham Suhood flies West
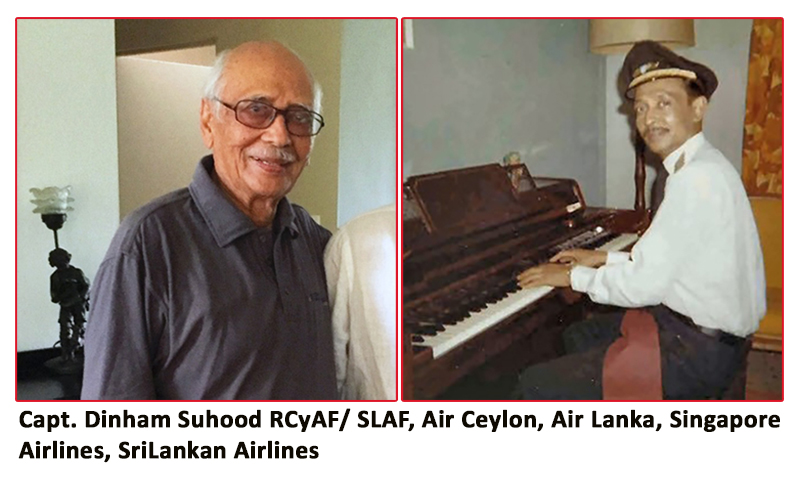

A few days ago, we heard the sad news of the passing on of Capt. Dinham Suhood. Born in 1929, he was the last surviving Air Ceylon Captain from the ‘old guard’.
He studied at St Joseph’s College, Colombo 10. He had his flying training in 1949 in Sydney, Australia and then joined Air Ceylon in late 1957. There he flew the DC3 (Dakota), HS748 (Avro), Nord 262 and the HS 121 (Trident).
I remember how he lent his large collection of ‘Airfix’ plastic aircraft models built to scale at S. Thomas’ College, exhibitions. That really inspired us schoolboys.
In 1971 he flew for a Singaporean Millionaire, a BAC One-Eleven and then later joined Air Siam where he flew Boeing B707 and the B747 before retiring and migrating to Australia in 1975.
Some of my captains had flown with him as First Officers. He was reputed to have been a true professional and always helpful to his colleagues.
He was an accomplished pianist and good dancer.
He passed on a few days short of his 97th birthday, after a brief illness.
May his soul rest in peace!
To fly west my friend is a test we must all take for a final check
Capt. Gihan A Fernando
RCyAF/ SLAF, Air Ceylon, Air Lanka, Singapore Airlines, SriLankan Airlines
Opinion
Global warming here to stay

The cause of global warming, they claim, is due to ever increasing levels of CO2. This is a by-product of burning fossil fuels like oil and gas, and of course coal. Environmentalists and other ‘green’ activists are worried about rising world atmospheric levels of CO2. Now they want to stop the whole world from burning fossil fuels, especially people who use cars powered by petrol and diesel oil, because burning petrol and oil are a major source of CO2 pollution. They are bringing forward the fateful day when oil and gas are scarce and can no longer be found and we have no choice but to travel by electricity-driven cars – or go by foot. They say we must save energy now, by walking and save the planet’s atmosphere.
THE DEMON COAL
But it is coal, above all, that is hated most by the ‘green’ lobby. It is coal that is first on their list for targeting above all the other fossil fuels. The eminently logical reason is that coal is the dirtiest polluter of all. In addition to adding CO2 to the atmosphere, it pollutes the air we breathe with fine particles of ash and poisonous chemicals which also make us ill. And some claim that coal-fired power stations produce more harmful radiation than an atomic reactor.
STOP THE COAL!
Halting the use of coal for generating electricity is a priority for them. It is an action high on the Green party list.
However, no-one talks of what we can use to fill the energy gap left by coal. Some experts publicly claim that unfortunately, energy from wind or solar panels, will not be enough and cannot satisfy our demand for instant power at all times of the day or night at a reasonable price.
THE ALTERNATIVES
It seems to be a taboo to talk about energy from nuclear power, but this is misguided. Going nuclear offers tried and tested alternatives to coal. The West has got generating energy from uranium down to a fine art, but it does involve some potentially dangerous problems, which are overcome by powerful engineering designs which then must be operated safely. But an additional factor when using URANIUM is that it produces long term radioactive waste. Relocating and storage of this waste is expensive and is a big problem.
Russia in November 2020, very kindly offered to help us with this continuous generating problem by offering standard Uranium modules for generating power. They offered to handle all aspects of the fuel cycle and its disposal. In hindsight this would have been an unbelievable bargain. It can be assumed that we could have also used Russian expertise in solving the power distribution flows throughout the grid.
THORIUM
But thankfully we are blessed with a second nuclear choice – that of the mildly radioactive THORIUM, a much cheaper and safer solution to our energy needs.
News last month (January 2026) told us of how China has built a container ship that can run on Thorium for ten years without refuelling. They must have solved the corrosion problem of the main fluoride mixing container walls. China has rare earths and can use AI computers to solve their metallurgical problems – fast!
Nevertheless, Russia can equally offer Sri Lanka Thorium- powered generating stations. Here the benefits are even more obviously evident. Thorium can be a quite cheap source of energy using locally mined material plus, so importantly, the radioactive waste remains dangerous for only a few hundred years, unlike uranium waste.
Because they are relatively small, only the size of a semi-detached house, such thorium generating stations can be located near the point of use, reducing the need for UNSIGHTLY towers and power grid distribution lines.
The design and supply of standard Thorium reactor machines may be more expensive but can be obtained from Russia itself, or China – our friends in our time of need.
Priyantha Hettige
-

 Life style21 hours ago
Life style21 hours agoMarriot new GM Suranga
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoAutodoc 360 relocates to reinforce commitment to premium auto care
-

 Midweek Review5 days ago
Midweek Review5 days agoA question of national pride
-

 Opinion4 days ago
Opinion4 days agoWill computers ever be intelligent?
-

 Features21 hours ago
Features21 hours agoThe Rise of Takaichi
-

 Features21 hours ago
Features21 hours agoWetlands of Sri Lanka:
-

 Midweek Review5 days ago
Midweek Review5 days agoTheatre and Anthropocentrism in the age of Climate Emergency
-

 Editorial7 days ago
Editorial7 days agoThe JRJ syndrome













