Opinion
Five Years on with garbage, myths and lies

Sri Lanka – Singapore Free Trade Agreement
By Gomi Senadhira
This month the highly controversial Sri Lanka – Singapore Free Trade Agreement (SLSFTA), which was signed in January 2018 and enforced in May 2018, completes five years in operation. Given the high level of concern among domestic stakeholders regarding the agreement. President Maithripala Sirisena appointed an independent committee of experts, in August 2018, to study the agreement and the committee handed over its report to the President in December 2018. The committee had identified a number of pitfalls in the agreement and President Maithripala Sirisena had directed that the agreement be amended as per the recommendations of the expert group. In May 2021, it was revealed that the National Negotiation Committee had reviewed the SLSFTA and identified 18 amendments to be made to the agreement. Hence, as the SLSFTA marks five years of implementation, it is appropriate for relevant government agencies to provide an overview of the significant trade and economic effects of the FTA during the period, and any efforts undertaken by the government to revise the articles in the agreement which are unfavourable to Sri Lanka. This is particularly important in trade policy because Sri Lanka is currently engaged in FTA negotiations with a number of other countries, including China, India, and Thailand. A careful analysis of the SLSFTA, at this stage, would help to avoid repeating similar mistakes in these negotiations as well. Furthermore, the way our trade negotiators and “experts” reacted to some of these public concerns on the agreement also reveals the limits of their expertise on trade agreements and negotiations, and their understanding of the commitments they had extended to Singapore! Some of their comments are so absurd that it appears that they do not even comprehend the very basics of trade negotiations!
One of the most controversial issues in the SLSFTA was the commitments undertaken by Sri Lanka to open up import and process waste/garbage from Singapore. I was the first to raise this issue in August 2018 (SL chosen as garbage dump by Singapore after China, etc. shut their doors, The Island 18th August 2018). Last year, in a study undertaken by Anushka Wijesinha, who was an advisor to the Ministry of Development Strategies and International Trade, and Janaka Wijayasiri state, “At times, the concern morphed into undue fears and propelled misleading views and myths…Another concern that arose quite surprisingly was that the SLFTA – and the tariff liberalisation offered – would permit harmful products such as garbage, clinical waste, nuclear waste, chemical waste etc. to be imported to Sri Lanka. The argument by those individuals and groups that raised this issue was that since waste products are included in the TLP, such items can be dumped into the country under the agreement… To be clear, the reduction or elimination of tariffs does not grant automatic entry of a product into a country – all applicable domestic regulations and mechanisms would still apply, including any applicable import licensing requirements, standards, and other regulatory approvals. The SLSFTA does not take away Sri Lanka’s rights under International Environmental Protection Treaties to which Sri Lanka is a signatory and therefore, relevant environmental laws and regulations would apply to such imported products with no exception for those imports from Singapore under the SLSFTA.” (Sri Lanka – Singapore FTA Four Years On: Policy Context, Key Issues, and Future Prospects – August 2022)
When I exposed the commitments undertaken in the agreement to allow waste, particularly plastic waste, imports from Singapore it was not done based simply on tariff liberalisation. It was done after analysing the global trade of plastic waste, the challenges Singapore was facing in exporting plastic waste, Sri Lanka’s import of plastic waste, and Sri Lanka’s commitments in the agreement under the TLP, rules of origin, and services.
The Global situation
The developed countries lawfully or unlawfully export garbage as “recyclable waste” overseas for recycling. That is because recycling is a labour-intensive and dirty industry. For example, a PET bottle would have to be washed, its cap, and the label taken off before it can be recycled. So, it is a labour- intensive process. Very often large quantities of toxic or hazardous wastes also are mixed with “clean” waste. Then it also becomes a hazardous industry. During the cleaning process toxic waste is released into local environs and workers get exposed to them. So, developed countries prefer to do this “recycling” in developing countries. To do their dirty work these global garbage traders particularly target developing countries with corrupt officials and shady businessmen where import licensing requirements, standards, and other regulatory approvals can be bent and corrupt officials would facilitate the clearing of even toxic garbage containers without any examination. In these countries, the bulk of the imported garbage ends up in the local garbage dumps.
China was the world’s largest importer of garbage and imported almost 60% of the world’s plastic waste. However, there was a growing public outcry, over many years, against the import of “foreign garbage.” in general and import of plastic waste in particular. This intensified after the release of the documentary film “Plastic China” in 2016 depicting the lives of two families who make their living recycling plastic waste imported from developed countries. In 2017 China decided to ban imports of 24 types of rubbish and notified the WTO accordingly. “We found that large amounts of dirty wastes or even hazardous wastes are mixed in the solid waste that can be used as raw materials. This seriously polluted China’s environment. To protect China’s environmental interests and people’s health, we urgently adjust the imported solid wastes list, and forbid the import of solid wastes that are highly polluted. Protection of human health or safety; Protection of animal or plant life or health; Protection of the environment,” stated China’s WTO notification.
Normally, in international trade when the import of a product is banned in one country, it will be redirected to other countries. After the Chinese ban. Increased volumes of plastic waste started to move into other traditional importers of waste for reprocessing (Thailand, Vietnam, and other countries in the region) and these countries too started to restrict the imports of waste products. So, where will the world’s waste exports end up, if not in China or South East Asia? By late 2016, the Chinese plastic waste processing industry was looking for places in South Asia and Africa to relocate this billion-dollar industry.
 Situation in Singapore
Situation in Singapore
Singapore is one of the world’s largest, per capita, plastic waste generators. From 2012 to 2017 the total volume of plastic waste generated in Singapore averaged around 800 thousand tons per year. In 2013 Singapore exported over 90,000 tons of plastic waste. Out of it over 57,000 Tons went to China. After China’s ban on the import of plastic waste, Singapore’s exports fell to around 30, 000 tons by 2021. In Singapore, plastic waste is either exported or incinerated. Ash from incineration is shipped to a man-made island and that landfill is also fast filling up. Furthermore, the incineration of plastic waste even under controlled conditions leads to environmental degradation. Singapore is very keen on maintaining its air quality and incineration is not a preferred option. But recycling in Singapore is expensive. So, recycling companies in Singapore used to undertake that in Malaysia, China, or other countries in the region. After the Chinese ban exports to China have stopped totally and other importers also were contemplating import restrictions. Hence, it was no secret, when the SLSFTA was negotiated Singapore was exploring new overseas locations to establish recycling operations, or dumping grounds. In 2021 Singapore generated 982 thousand tons of plastic waste and only around six percent of the plastic waste generated was recycled. (See Table I)
The situation in Sri Lanka
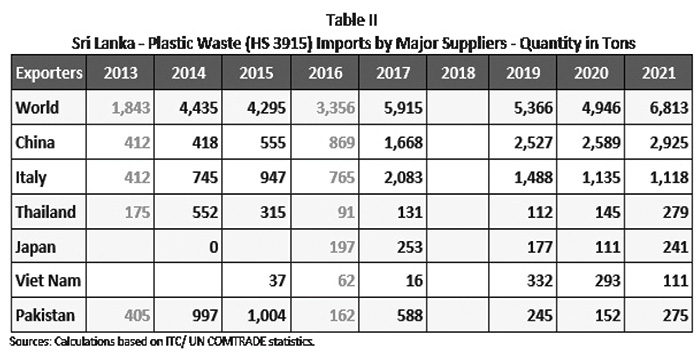
 When the SLSFTA was under negotiation Sri Lanka had already commenced importing plastic waste. The surge in imports between 2013 and 2017 shown in the Table II, clearly indicated the presence of a small but growing plastic waste “recycling” industry in Sri Lanka. My comments in 2018 was partly based on this analysis. (See Table II)
When the SLSFTA was under negotiation Sri Lanka had already commenced importing plastic waste. The surge in imports between 2013 and 2017 shown in the Table II, clearly indicated the presence of a small but growing plastic waste “recycling” industry in Sri Lanka. My comments in 2018 was partly based on this analysis. (See Table II)
Though trade flows indicated a possible presence of global waste “recycling” mafia in Sri Lanka, I didn’t know, at that stage, garbage “recycling” or “resource recovery industries” had already commenced thriving operations within the BOI, under the Commercial Hub Regulation Act.
That was revealed only after the media exposure in 2019, of a huge waste dump inside the BOI. At that time, a representative from the “resource recovery industry” operated in the Katunayake FTZ, brazenly claimed at a press conference that this was the world’s “fastest-growing and most admired industry”. However, the investigation revealed that this clandestine waste dump inside the BOI contained toxic waste. Then came the discovery of over 200 stinking garbage containers in the Colombo port! Again, with toxic waste! These were discovered only because dirty fluids started to ooze out these smelly containers. It was reported that the environmental and customs officials even refused to open these containers as it was unsafe to do so. It was also reported that the garbage consignments moved from the port to the BOI were not physically checked by the Customs and other regulatory agencies, and these agencies did not conduct any entry processing or check on documents, due to BOI regulations! Though the Finance Minister promised the Parliament, in July 2019, that he would conduct a comprehensive investigation into the matter and would take legal action against the culprits nothing much had happened even after four years. It is also noteworthy that these garbage containers were discovered only after the collapse of Meethotamulla Garbage Dump in 2017. If Meethotamulla had not imploded, at least some of the waste may have ended up there.
Sri Lanka – Singapore FTA
 The SLSFTA was negotiated at a time when the global crisis in the garbage trade was at its peak. So, how did Sri Lankan negotiators react to the crisis? Did they see it as a threat or an opportunity? Trade negotiators are expected to analyse trade statistics before making any commitment on any tariff line. Didn’t they know that Sri Lanka was already importing plastic waste? The representatives from the BOI were involved in the negotiations. Didn’t they know Sri Lanka had established these “resource recovery industries” within the BOI? How Singaporean negotiators approached this issue. Did they request any commitments from Sri Lanka in the area of import and processing of waste? Did we provide these commitments without any requests? And finally, didn’t they even know that Sri Lanka made these commitments?
The SLSFTA was negotiated at a time when the global crisis in the garbage trade was at its peak. So, how did Sri Lankan negotiators react to the crisis? Did they see it as a threat or an opportunity? Trade negotiators are expected to analyse trade statistics before making any commitment on any tariff line. Didn’t they know that Sri Lanka was already importing plastic waste? The representatives from the BOI were involved in the negotiations. Didn’t they know Sri Lanka had established these “resource recovery industries” within the BOI? How Singaporean negotiators approached this issue. Did they request any commitments from Sri Lanka in the area of import and processing of waste? Did we provide these commitments without any requests? And finally, didn’t they even know that Sri Lanka made these commitments?
When I warned that plastic and asbestos waste will be imported for processing and recycling, the Ministry of Development Strategies and International Trade responded by stating “… in order for products manufactured in Singapore using non-originating raw materials (imported raw materials) to become eligible for Customs duty concessions under SLSFTA, origin criteria listed below should be complied with: I. Sufficient working or processing + comply with value addition of 35% of FOB or II. Sufficient working or processing + comply with CTH (change of tariff no at 4- digit level between the finished product and imported inputs) or… Sufficient working or processing + comply with Product Specific Rules”),” (“Garbage in, Garbage out’- Malik’s response,” The Island, October 9, 2018).
Unfortunately, our trade negotiators and advisers are not even aware that under the SLSFTA Rules of Origin, waste and scrap for recycling qualify as wholly obtained products, like plants … grown and harvested, or live animals born, raised and slaughtered in Singapore. The relevant sections are Article 4 k, l, and m, which state” … (k) used articles collected there fit only for the recovery of raw materials; (l) wastes and scrap resulting from manufacturing operations conducted there; (m) waste and scrap derived from used goods collected in the exporting Party, provided that those goods are fit only for the recovery of raw materials.“ Under these sub- articles plastic waste, asbestos waste and similar products, can be imported for the recovery of raw materials by the “resource recovery industry” which had a highly lucrative operation in the BOI zones when the agreement was signed.
The agreement clearly categorises waste collected in Singapore as a wholly obtained product under Article 4, the Ministry of DS& IT claimed waste cannot be imported under Article 5. Didn’t our International Trade Ministry and other trade “experts” understand waste collected in Singapore is covered under Article 4 and hence the limitations in Article 5 do not apply? Or was it a deliberate attempt to hoodwink the public?
Then there are a few specific rules of origin that would facilitate the dumping of dangerous products in Sri Lanka. For example, crocidolite asbestos (HS 6812) also known as blue asbestos, is considered the most hazardous type of asbestos. Sri Lanka prohibited the use of crocidolite asbestos in 1987. Singapore banned the use of all types of Asbestos in 1989. However, a significant amount of the material remains in the buildings and elsewhere in Singapore and there are strict laws governing the demolishing and removal of these materials. Shockingly this item is not only included in Sri Lanka’s TLP but our negotiators have spent time and money on formulating very simple specific rules of origin to facilitate its imports. If a product containing Crocidolite, simply changes its tariff subheading then it qualifies as a product of Singaporean origin.
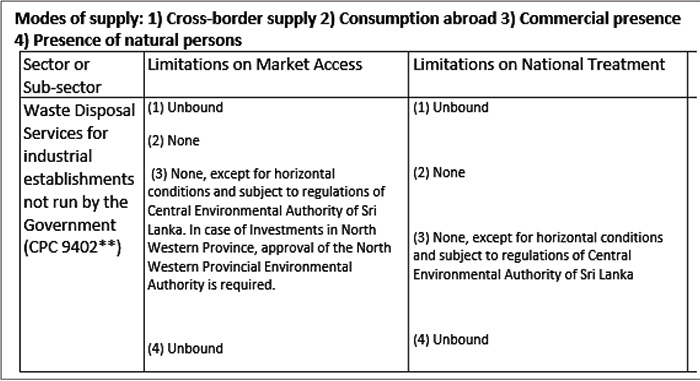
Then in the Services Chapter Sri Lanka has undertaken a specific commitment on Waste Disposal Services which is reproduced below (see Table 3):
The CPC 9402 refers to “refuse collection and disposal services’ and it includes collection services of garbage, trash, rubbish and waste, whether from households or from industrial and commercial establishments, transport services and disposal services by incineration or by other means. The use of “**” against the CPC code indicates that the specific commitment for that code shall not extend to the total range of services covered under that code. Sri Lanka’s commitment clearly limits its scope to waste collected from industrial establishments not run by the Government, but no other areas are excluded.
Under these commitments, services can be provided through four modes of supply. For “Waste Disposal Services” Sri Lanka has opened up only two modes of supply, namely, Mode 2) Consumption abroad and Mode 3) Commercial presence. The term “None” under this commitment means that the country is committing itself to provide full liberalization without any limitations on market access or national treatment for the service sector and modes of supply for which commitments are written.
By opening up Mode 2 without any restrictions, Sri Lanka permits the other party to the agreement to process its solid waste in Sri Lanka. If the intention of Sri Lankan negotiators, as the government claims, was to limit this to waste collected in Sri Lanka, then mode 2 should have been left unbound. By opening up of Mode 3 Sri Lanka has allowed Singaporean Waste Disposal Services to establish a subsidiary in Sri Lanka, subject to regulations of the Central Environmental Authority of Sri Lanka. Therefore, under this commitment waste can be imported from Singapore not only to recover raw materials but also to dispose of.
Before the SLSFTA entered into force in May 2018, if a Singaporean, Chinese or any other national wanted to recycle imported waste in Sri Lanka, it was possible to do so under BOI regulations. After May 2018, any Singaporean company can establish refuse disposal services in Sri Lanka, under the commitments undertaken by Sri Lanka in the services chapter of the SLSFTA, to recycle and/or process waste!
After I raised this issue it was widely discussed. I believe the Presidential Commission also recommended that the articles which permit waste import and recycling should be amended. My article “SL chosen as garbage dump by Singapore after China etc. shut their doors,” published in the Island in 2018, was tabled in the parliament by Shehan Semasinghe. Later, in April 2022, he became the Minister of Trade and since September 2022 he is the Minister of State for Finance. In spite of all that the government had not taken any action to protect Sri Lanka from becoming a garbage dump for developed countries other than calling my claim, “… a despicable attempt … to deceive the public” and in turn releasing few press releases with incorrect information to mislead the public. Even when the government imposed a ban on imports of hundreds of products, waste items like plastic waste were not included in that list and every year Sri Lanka continues to import thousands of tons of plastic waste!
In 2019, the Philippines, in a major diplomatic row with Canada, reshipped 2,400 tonnes of Canadian toxic waste which was imported labelled as plastic waste for recycling. Other countries in the region also had taken similar action. But we in Sri Lanka are not like that. Last year alone Sri Lanka imported over 6000 tons of plastic waste! Most of it came from China, a country that banned the import of plastic waste to protect environmental interests and people’s health and safety.
(The writer can be contacted via senadhiragomi@gmail.com.)
Opinion
We do not want to be press-ganged

Reference ,the Indian High Commissioner’s recent comments ( The Island, 9th Jan. ) on strong India-Sri Lanka relationship and the assistance granted on recovering from the financial collapse of Sri Lanka and yet again for cyclone recovery., Sri Lankans should express their thanks to India for standing up as a friendly neighbour.
On the Defence Cooperation agreement, the Indian High Commissioner’s assertion was that there was nothing beyond that which had been included in the text. But, dear High Commissioner, we Sri Lankans have burnt our fingers when we signed agreements with the European nations who invaded our country; they took our leaders around the Mulberry bush and made our nation pay a very high price by controlling our destiny for hundreds of years. When the Opposition parties in the Parliament requested the Sri Lankan government to reveal the contents of the Defence agreements signed with India as per the prevalent common practice, the government’s strange response was that India did not want them disclosed.
Even the terms of the one-sided infamous Indo-Sri Lanka agreement, signed in 1987, were disclosed to the public.
Mr. High Commissioner, we are not satisfied with your reply as we are weak, economically, and unable to clearly understand your “India’s Neighbourhood First and Mahasagar policies” . We need the details of the defence agreements signed with our government, early.
RANJITH SOYSA
Opinion
When will we learn?

At every election—general or presidential—we do not truly vote, we simply outvote. We push out the incumbent and bring in another, whether recycled from the past or presented as “fresh.” The last time, we chose a newcomer who had spent years criticising others, conveniently ignoring the centuries of damage they inflicted during successive governments. Only now do we realise that governing is far more difficult than criticising.
There is a saying: “Even with elephants, you cannot bring back the wisdom that has passed.” But are we learning? Among our legislators, there have been individuals accused of murder, fraud, and countless illegal acts. True, the courts did not punish them—but are we so blind as to remain naive in the face of such allegations? These fraudsters and criminals, and any sane citizen living in this decade, cannot deny those realities.
Meanwhile, many of our compatriots abroad, living comfortably with their families, ignore these past crimes with blind devotion and campaign for different parties. For most of us, the wish during an election is not the welfare of the country, but simply to send our personal favourite to the council. The clearest example was the election of a teledrama actress—someone who did not even understand the Constitution—over experienced and honest politicians.
It is time to stop this bogus hero worship. Vote not for personalities, but for the country. Vote for integrity, for competence, and for the future we deserve.
Deshapriya Rajapaksha
Opinion
Chlorophyll –The Life-giver is in peril
Chlorophyll is the green pigment found in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. It is essential for photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy to sustain life on Earth. As it is green it reflects Green of the sunlight spectrum and absorbs its Red and Blue ranges. The energy in these rays are used to produce carbohydrates utilising water and carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen in the process. Thus, it performs, in this reaction, three functions essential for life on earth; it produces food and oxygen and removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to maintain equilibrium in our environment. It is one of the wonders of nature that are in peril today. It is essential for life on earth, at least for the present, as there are no suitable alternatives. While chlorophyll can be produced in a lab, it cannot be produced using simple, everyday chemicals in a straightforward process. The total synthesis of chlorophyll is an extremely complex multi-step organic chemistry process that requires specialized knowledge, advanced laboratory equipment, and numerous complex intermediary compounds and catalysts.
Chlorophyll probably evolved inside bacteria in water and migrated to land with plants that preceded animals who also evolved in water. Plants had to come on land first to oxygenate the atmosphere and make it possible for animals to follow. There was very little oxygen in the ocean or on the surface before chlorophyll carrying bacteria and algae started photosynthesis. Now 70% of our atmospheric oxygen is produced by sea phytoplankton and algae, hence the importance of the sea as a source of oxygen.
Chemically, chlorophyll is a porphyrin compound with a central magnesium (Mg²⁺) ion. Factors that affect its production and function are light intensity, availability of nutrients, especially nitrogen and magnesium, water supply and temperature. Availability of nutrients and temperature could be adversely affected due to sea pollution and global warming respectively.
Temperature range for optimum chlorophyll function is 25 – 35 C depending on the types of plants. Plants in temperate climates are adopted to function at lower temperatures and those in tropical regions prefer higher temperatures. Chlorophyll in most plants work most efficiently at 30 C. At lower temperatures it could slow down and become dormant. At temperatures above 40 C chlorophyll enzymes begin to denature and protein complexes can be damaged. Photosynthesis would decline sharply at these high temperatures.
Global warming therefore could affect chlorophyll function and threaten its very existence. Already there is a qualitative as well as quantitative decline of chlorophyll particularly in the sea. The last decade has been the hottest ten years and 2024 the hottest year since recording had started. The ocean absorbs 90% of the excess heat that reaches the Earth due to the greenhouse effect. Global warming has caused sea surface temperatures to rise significantly, leading to record-breaking temperatures in recent years (like 2023-2024), a faster warming rate (four times faster than 40 years ago), and more frequent, intense marine heatwaves, disrupting marine life and weather patterns. The ocean’s surface is heating up much faster, about four times quicker than in the late 1980s, with the last decade being the warmest on record. 2023 and 2024 saw unprecedented high sea surface temperatures, with some periods exceeding previous records by large margins, potentially becoming the new normal.
Half of the global sea surface has gradually changed in colour indicating chlorophyll decline (Frankie Adkins, 2024, Z Hong, 2025). Sea is blue in colour due to the absorption of Red of the sunlight spectrum by water and reflecting Blue. When the green chlorophyll of the phytoplankton is decreased the sea becomes bluer. Researchers from MIT and Georgia Tech found these color changes are global, affecting over half the ocean’s surface in the last two decades, and are consistent with climate model predictions. Sea phytoplankton and algae produce more than 70% of the atmospheric oxygen, replenishing what is consumed by animals. Danger to the life of these animals including humans due to decline of sea chlorophyll is obvious. Unless this trend is reversed there would be irreparable damage and irreversible changes in the ecosystems that involve chlorophyll function as a vital component.
The balance 30% of oxygen is supplied mainly by terrestrial plants which are lost due mainly to human action, either by felling and clearing or due to global warming. Since 2000, approximately 100 million hectares of forest area was lost globally by 2018 due to permanent deforestation. More recent estimates from the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) indicate that an estimated 420 million hectares of forest have been lost through deforestation since 1990, with a net loss of approximately 4.7 million hectares per year between 2010 and 2020 (accounting for forest gains by reforestation). From 2001 to 2024, there had been a total of 520 million hectares of tree cover loss globally. This figure includes both temporary loss (e.g., due to fires or logging where forests regrow) and permanent deforestation. Roughly 37% of tree cover loss since 2000 was likely permanent deforestation, resulting in conversion to non-forest land uses such as agriculture, mining, or urban development. Tropical forests account for the vast majority (nearly 94%) of permanent deforestation, largely driven by agricultural expansion. Limiting warming to 1.5°C significantly reduces risks, but without strong action, widespread plant loss and biodiversity decline are projected, making climate change a dominant threat to nature, notes the World Economic Forum. Tropical trees are Earth’s climate regulators—they cool the planet, store massive amounts of carbon, control rainfall, and stabilize global climate systems. Losing them would make climate change faster, hotter, and harder to reverse.
Another vital function of chlorophyll is carbon fixing. Carbon fixation by plants is crucial because it converts atmospheric carbon dioxide into organic compounds, forming the base of the food web, providing energy/building blocks for life, regulating Earth’s climate by removing greenhouse gases, and driving the global carbon cycle, making life as we know it possible. Plants use carbon fixation (photosynthesis) to create their own food (sugars), providing energy and organic matter that sustains all other life forms. By absorbing vast amounts of CO2 (a greenhouse gas) from the atmosphere, plants help control its concentration, mitigating global warming. Chlorophyll drives the Carbon Cycle, it’s the primary natural mechanism for moving inorganic carbon into the biosphere, making it available for all living organisms.
In essence, carbon fixation turns the air we breathe out (carbon dioxide) into the food we eat and the air we breathe in (oxygen), sustaining ecosystems and regulating our planet’s climate.
While land plants store much more total carbon in their biomass, marine plants (like phytoplankton) and algae fix nearly the same amount of carbon annually as all terrestrial plants combined, making the ocean a massive and highly efficient carbon sink, especially coastal ecosystems that sequester carbon far faster than forests. Coastal marine plants (mangroves, salt marshes, seagrasses) are extremely efficient carbon sequesters, absorbing carbon at rates up to 50 times faster than terrestrial forests.
If Chlorophyll decline, which is mainly due to human action driven by uncontrolled greed, is not arrested as soon as possible life on Earth would not be possible.
(Some information was obtained from Wikipedia)
by N. A. de S. Amaratunga ✍️
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoSajith: Ashoka Chakra replaces Dharmachakra in Buddhism textbook
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoDialog and UnionPay International Join Forces to Elevate Sri Lanka’s Digital Payment Landscape
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoThe Paradox of Trump Power: Contested Authoritarian at Home, Uncontested Bully Abroad
-

 Features3 days ago
Features3 days agoSubject:Whatever happened to (my) three million dollars?
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoLevel I landslide early warnings issued to the Districts of Badulla, Kandy, Matale and Nuwara-Eliya extended
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoNational Communication Programme for Child Health Promotion (SBCC) has been launched. – PM
-

 News3 days ago
News3 days ago65 withdrawn cases re-filed by Govt, PM tells Parliament
-

 Opinion5 days ago
Opinion5 days agoThe minstrel monk and Rafiki, the old mandrill in The Lion King – II





















