Business
Plastic Pandemic: The ecological fallout of COVID-19 and policy options for Sri Lanka
by Ruwan Samaraweera
 The lockdowns introduced in 2020 to curb the spread of COVID-19 saw the narrative “nature is healing” gain prominence. However, the notion that nature, in the absence of people, was healing fizzled out fairly quickly with the emergence of fresh environmental challenges, most notably, the resurgence of single-use plastics. In fact, in the months following the lockdowns, reliance on plastics grew exponentially, with the scale of the negative environmental impacts far outweighing initial gains such as reduced air and noise pollution. This blog examines the ecological fallout of the pandemic and suggests policy options for Sri Lanka to avert the looming environmental disaster.
The lockdowns introduced in 2020 to curb the spread of COVID-19 saw the narrative “nature is healing” gain prominence. However, the notion that nature, in the absence of people, was healing fizzled out fairly quickly with the emergence of fresh environmental challenges, most notably, the resurgence of single-use plastics. In fact, in the months following the lockdowns, reliance on plastics grew exponentially, with the scale of the negative environmental impacts far outweighing initial gains such as reduced air and noise pollution. This blog examines the ecological fallout of the pandemic and suggests policy options for Sri Lanka to avert the looming environmental disaster.
The Plastic Pandemic
Plastics have several applications and offer undeniable benefits to consumers and producers due to specific, inherent properties. They are hygienic, lightweight, flexible and anti-corrosive. As such, plastics are among the most extensively-produced material globally with 359 million tonnes of plastics produced in 2018 alone. However, plastics have become a severe environmental concern due to haphazard disposal. Plastics include consumables like plastic bags, straws, cups, bottles etc., which are thrown away after being used just once, referred to as single-use plastics. Worldwide consumption of plastic bags ranges from 1 to 5 trillion annually, and almost 160,000 plastic bags are consumed per second globally.
Without even being a large consumer of plastics globally, Sri Lanka generates more than 5 million kilograms of plastic waste per day, where the per capita daily contribution is nearly 0.5 kg. Sri Lanka is already struggling to cope with the amount of plastic waste generated each year. Unless concrete measures are taken to alter the current manufacturing methods and consumption patterns of plastics, the situation could result in irreversible damage to the environment. The global threat of the COVID-19 pandemic makes the problem (ex: Styrofoam, aluminium cans, polystyrene etc.) even more challenging.
An Ugly Resurgence
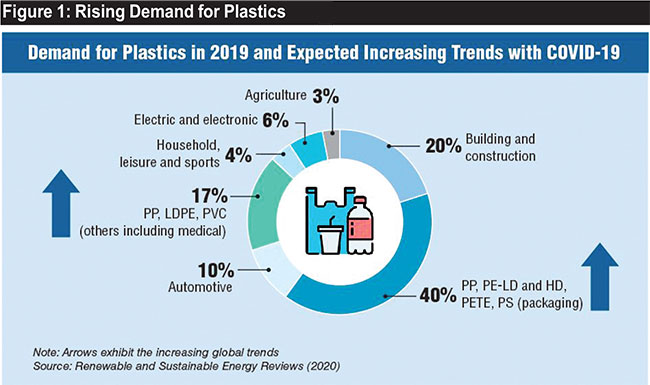
The demand for plastic by medical and packaging sectors is increasing sharply compared to pre-pandemic conditions (Figure 1). For instance, an estimated 89 million medical masks, 76 million gloves and 1.6 million goggles are required monthly in the battle against the pandemic, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). As a result, researchers expect a 53.4% market growth for disposable facemasks over 2020-2027. The disposable facemasks are produced using polymers such as polypropylene (PP), polyurethane, polyacrylonitrile, polystyrene, polycarbonate, polyethylene (LDPE), or polyester, which are potential sources of microplastics.
Estimates illustrate that the demand for disposable syringes and plastic containers that store vaccines will be increased with nationwide vaccination efforts against COVID-19. As a result, the global market will experience a 7% compound annual growth rate and reach a value of USD 14.4 billion by 2030. Moreover, the demand for other personal protective equipment like face shields made from PP, LDPE gowns, vinyl gloves made from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) will increase sharply along with the plastic packaging material. Thus, the production and consumption of PP, LDPE and PVC material will exhibit an increasing trend.
Lockdowns and resulting online shopping and home delivery can escalate the demand for plastic, which is reflected by the accumulation of plastic wastes, especially from food packaging. In Thailand, plastic waste rose by 15% during the pandemic, primarily due to food packaging waste, resulting from tripled food delivery demand. During the pandemic, many governments worldwide banned the use of reusable cups and food utensils due to safety reasons since reusable commodities could be contagious. Scholars also predict a drastic increase in medical waste that includes single-use plastic and other environmentally problematic material.
For instance, in Hubei province, China, medical waste generation increased sharply, and by 9 March 2020, the country collected 468.9 tonnes of medical waste related to the pandemic. A more significant proportion of that waste is comprised of single-use plastics. Wuhan’s medical waste exceeded the maximum incineration capacity of 46 tonnes/day due to a dramatic rise in waste accumulation up to 240 tonnes/day. Hence, despite their detrimental impacts, managing the pandemic is linked with single-use plastics and other environmentally-harmful material.
Addressing environmental, economic, health, and socio-cultural issues related to single-use plastics and other damaging material requires identifying the most problematic single-use plastic and other material, evaluating the scale of the problem, identifying significant sources of pollution and potential impacts of mismanagement on the environment, human and animal health, and the economy. Various methods can reduce the harmful effects of single-use plastics and other environmentally problematic materials. However, the availability of alternatives is crucial to cut down the use effectively.
Voluntary reduction strategies
One of the key instruments for single-use plastic is voluntary reduction strategies. Those are based on consumption patterns, consumer and producer choices upon an increased understanding.
Awareness creation
Voluntary adjustments are facilitated by awareness creation among stakeholder groups which are a gradual and transformational process that changes consumer and producer behaviour.
Policy instruments
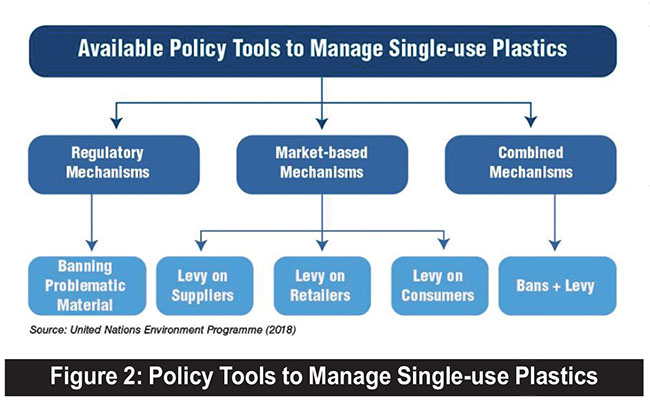
Policy instruments can be classified as regulatory and economic (market-based and a combination of regulatory and financial) instruments.
The principal legislation governing plastic pollution in Sri Lanka is the National Environmental Act No 47 of 1980, where Section 32 comprises the manufacture, sale and use of plastic and polythene. As previously mentioned, several amendments were made to the act to address the challenges in managing plastic waste. Lobbying from local industry and pressures from major exporting countries, and availability of alternatives remain significant challenges in implementing bans. However, as discussed earlier, single-use plastics have the lowest recyclability and highest disposable rates. Therefore, implementing a combined approach of levies, bans, and extended producer responsibility (EPR) wherever necessary would enhance the positive impacts.
Link to blog: https://www.ips.lk/talkingeconomics/2021/12/07/plastic-pandemic-the-ecological-fallout-of-covid-19-and-policy-options-for-sri-lanka/
Ruwan Samaraweera is a Research Officer at IPS, with a background in entrepreneurial agriculture. He holds a Bachelor’s in Export Agriculture from Uva Wellassa University of Sri Lanka. His research interests are in environmental economics, agricultural economics, macro-economic policy and planning, labour and migration, and poverty and development policy. (Talk to Ruwan – ruwan@ips.lk)
Business
‘Port City Colombo makes progress in attracting key investments’

Port City Colombo, a multi-service Special Economic Zone (SEZ) and a regional financial centre and business hub, has made significant progress in capturing key investments, as the project gears up for a tenacious drive to attract prospective land development and business set-up investors from the South Asian, APAC, and Middle Eastern regions before the end of 2024, a Port City Colombo press release said.
The release added: ‘With a strong emphasis on capturing high-value Foreign Direct Investments, Port City Colombo has on-boarded approximately forty-one companies registered as Authorised Persons (AP’s), as approved by the Colombo Port City Economic Commission. Fifty-two percent (52%) of the project’s Marina District, which includes South Asia’s first-ever luxury yacht marina and 5-star hotel, has further already attracted investment. Reputed international and local corporate entities, including Asiri Port City Hospital (Private) Limited, TIQRI, CODEGEN INNOVATIONS, 99x Technology AS, IVIVA PTE Ltd, Echelon Trade (Pvt) Ltd, and Port City BPO (Pvt) Ltd, have been additionally designated as Businesses of Strategic Importance.
‘Approximately more than twenty prospective investors are presently in the pipeline to register as Authorised Persons, demonstrating strengthened confidence in Port City Colombo’s positive outlook as a competitive regional investment hotspot.
‘Positioned within the Colombo Port City Special Economic Zone, Port City Colombo presents a low-risk financial environment that enhances the ease of doing business for global investors in Sri Lanka, whilst being economically ring-fenced against domestic macroeconomic challenges. This visionary FDI investment destination also showcases a thriving commercial ecosystem and liveable master-planned city, enabling a diversity of businesses to set up operations against the backdrop of transactions in 16 different international currencies with no capital or exchange controls, 100% foreign ownership, and fiscal incentives for 25 plus years.
‘Port City Colombo provides investors two primary options of investment: land development investments, which include residential and commercial property development, and business set-up and investments, which encompass a variety of opportunities in IT/ITes, financial services, hospitality/tourism, logistics, and so forth. Commercial entities, who are interested in investing or setting up business operations, are required to become qualified as an Authorised Person, which is defined as any individual or entity permitted by the Colombo Port City Economic Commission (CPCEC) to conduct business within the vicinity and from the area of authority of the Colombo Port City Special Economic Zone.
‘As Port City Colombo progresses forward with its vigorous AP and BSI drive, the project aims to fulfil the ambition of transforming Sri Lanka into an attractive global investment destination, whilst emulating the successful international economic models of Dubai and Singapore. For more information about our investment opportunities, please visit www.portcitycolombo.lk. ‘
Business
Rainbow Pages Champions League: 28 leading companies battling for victory

A six-a-side soft ball corporate cricket tournament was successfully held at the G H Buddhadasa Ground in Battaramulla recently with the participation of 28 teams representing leading companies in the island. The tournament was organized by the Rainbow Pages Welfare Society. Rainbow Pages is the National Business Directory in Sri Lanka managed by SLT-MOBITEL group.
The teams in the semi-finals were Winners Global, Sonasu Connect, GM Garments, and Salota International. Winners Global won the championship, while GM Garments and Salota International were both named co-runners-up in the Champions League corporate cricket tournament.
Business
LOLC and Hayleys dominate share market trading; turnover touches Rs. 2.5 billion

By Hiran H.Senewiratne
CSE activities were positive yesterday due to LOLC Group counters dominating the market. But there was an acute increase in Hayleys shares as well due to the company being one of six companies that tendered bids for the Sri Lanka Airlines divestiture, market analysts said.
Both indices moved upwards. The All Share Price Index went up by 77.50 points while S and P SL20 rose by 11.1 points. Turnover stood at Rs 2.5 billion with one crossing. The crossing was reported in Colombo Fort Lands, which crossed 1 million shares to the tune of Rs 30 million; its shares traded at Rs 30.
In the retail market top seven companies that mainly contributed to the turnover were; Browns Investments Rs 400 million (66 million shares traded), LOLC Finance Rs 318 million (44 million shares traded), Capital Alliance Rs 150 million (2.4 million shares traded), CIC Holdings Rs 97.9 million (1.3 million shares traded), Central Industries Rs 93.1 million (716,000 shares traded), Agsta Rs 92.9 million (11 million shares traded) and Dolphin Hotel Rs 91.3 million (2.2 million shares traded). During the day 207 million share volumes changed hands in 26000 transactions.
Yesterday the rupee opened stronger at Rs 300.00/40 to the US dollar in the spot market after closing at Rs 300.50/301.00 on Monday, dealers said. The rupee closed at 302.00/50 to the US dollar on Friday.
Bond yields were flat as buyers awaited the next development in sovereign bond re-structuring, market participants said. There were both positive and negative sentiments among bond investors, dealers said. Meanwhile, a bond maturing on 15.12.2026 was quoted at 11.32/40 percent from 11.30/40 percent on Monday. A bond maturing on 15.09.2027 was quoted at 11.92/12.00 percent, down from 11.95/05 percent. A bond maturing on 15.12.2028 was quoted flat at 12.15/25 percent.
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoCEAT Kelani launches three new radial tyre variants in ‘Orion Brawo’ range
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog-Airtel Lanka merger comes centre stage
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCeyline Travels and MBA Alumni Association of University of Colombo sign MOU
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoSLFEA appoints JAT as a Facilitation Partner for training painters to provide overseas employment opportunities
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHayleys Fabric celebrates triple triumph at ISPO Textrends Spring/Summer 2026
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoUrgent appeal from Sri Lankan exporters on rupee appreciation
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoMaldivian to launch direct flights to Colombo
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoHello Madras, ‘ai api kaluda?’