Features
CHRISTIANS IN SRI LANKA:

Living in Harmony amidst Challenges after Easter Terrorist Attacks of 2019
by Prabhath de Silva
Sri Lanka has attracted the attention of ancient and modern colonial empires, foreign countries ,merchants, travelers and missionaries over the centuries owing to its strategic and prominent location at a crossroads of maritime routes traversing the Indian Ocean.
 The Portuguese were the first European colonial power to arrive in Sri Lanka in 1505. Their presence in Sri Lanka’s maritime provinces between 1505 and 1656 CE, which began as an interaction of trade and commerce, later developed into a colonial rule in the maritime provinces from 1597. The maritime provinces were ruled by the Dutch East India Company from 1656 to 1796. The British captured the maritime provinces of the Island in 1796 . When native feudal Chiefs ceded the sovereignty of the interior native Kandyan Kingdom to the British Empire by the Kandyan Convention of 1815, the whole Island came under the British rule. Sri Lanka gained independence from the British in 1948.
The Portuguese were the first European colonial power to arrive in Sri Lanka in 1505. Their presence in Sri Lanka’s maritime provinces between 1505 and 1656 CE, which began as an interaction of trade and commerce, later developed into a colonial rule in the maritime provinces from 1597. The maritime provinces were ruled by the Dutch East India Company from 1656 to 1796. The British captured the maritime provinces of the Island in 1796 . When native feudal Chiefs ceded the sovereignty of the interior native Kandyan Kingdom to the British Empire by the Kandyan Convention of 1815, the whole Island came under the British rule. Sri Lanka gained independence from the British in 1948.
The Buddhist missionaries from India during the reign of Emperor Asoka introduced Buddhism to Sri Lanka in the 3rd Century BCE, and it soon became the established religion of the ancient Sinhalese monarchy and the majority Sinhalese people. The Sinhalese majority community is predominantly Theravada Buddhist [93% of the Sinhalese population] and only a 7% of the Sinhalese population is Christian. Hinduism has been in existence since at least the 2nd century BCE The Sri Lankan Tamils are predominantly Hindu [ 85% of the Sri Lankan Tamil population]. A 15% of the Sri Lankan Tamil population is Christian. The Muslim settlers who came from the Arabian Gulf and later from South India brought Islam to the Island beginning in the 8th Century CE , converting native women upon marriage. Sri Lankan Muslims constitute 9.3 % of Sri Lankan’s population
During the presence of Portuguese in the Island (1505 to 1658), Catholic missionaries actively engaged in evangelization of natives. Thousands of native Sinhalese Buddhists and Tamil Hindus embraced the Christian Faith. The maritime provinces of Sri Lanka came under the rule of Dutch East India Company after its armies defeated the Portuguese in a series of battles between 1640 and 1658. The Dutch immediately banned Catholicism in Sri Lanka by laws. Through the brave and zealous endeavors of the Catholic missionaries from Goa, a territory of Portuguese in India, a territory of Portuguese in India, the Catholic Church in Sri Lanka which had become an outlawed underground church, survived and grew amidst persecution during the Dutch occupation. In last few decades of the Dutch rule in the maritime provinces, beginning from the 1750 s the Dutch granted religious freedom to Catholics.
From the beginning of their rule, the British granted religious freedom to all religions. The Catholic church emerged as the largest Christian church. The British permitted the Catholic Church in Sri Lanka to establish schools and charitable institutions. Catholic missionaries came from France, Belgium, Ireland, Italy, and Goa. During the British colonial rule, Anglican, Methodist, Baptist and The Salvation Army missionaries from the British Isles introduced their respective forms of Christianity to the Island in the 19th century. They established schools and charitable institutions throughout the Island. During the early British period, the American missionaries from the Congregationalist churches arrived in Sri Lanka and established churches, schools , the Island’s first western medical school in 1851, and medical missions in the Northern Province. In the early 20th century, when Sri Lanka was still a colony of the British, missionaries from the American Pentecostal churches introduced their brand of Christianity to the Island. According to the Census of 2012, a 70.2% of Sri Lankans were Theravada Buddhists, 12.6% were Hindus, 9.7% were Muslims (mainly Sunni), 7.4 Christian [Catholic 6.1%, other Christians 1.3 %] and 0.05% others.
Christians in Today’s Sri Lankan Society
In order to present a kaleidoscopic picture of today’s Christian community in Sri Lanka and the issues and challenges they face, I interviewed three pastors and four lay persons of four different Christian denominations in Sri Lanka for this article.
Voices of Pastors
 On one Sunday morning when the sun was shining bright, I stepped into the Methodist Chapel at Kalutara, a town (predominantly Buddhist) situated in the western coast of Sri Lanka 42 km south of Colombo. The Sunday worship service was in progress. Methodist Church of Sri Lanka was founded by the early British Methodist Missionaries who arrived in the Island in 1814. It was these first missionaries who had established the Methodist congregation at Kalutara through their zealous missionary endeavours in 1814. Methodist Church of Sri Lanka today has approximately 25,000 members throughout the Island. Methodist congregation of Kalutara currently has a membership of 90 people consisting of Sinhalese and a few Tamils.
On one Sunday morning when the sun was shining bright, I stepped into the Methodist Chapel at Kalutara, a town (predominantly Buddhist) situated in the western coast of Sri Lanka 42 km south of Colombo. The Sunday worship service was in progress. Methodist Church of Sri Lanka was founded by the early British Methodist Missionaries who arrived in the Island in 1814. It was these first missionaries who had established the Methodist congregation at Kalutara through their zealous missionary endeavours in 1814. Methodist Church of Sri Lanka today has approximately 25,000 members throughout the Island. Methodist congregation of Kalutara currently has a membership of 90 people consisting of Sinhalese and a few Tamils.
After the service, I spoke to the Methodist Minister in charge of this congregation, Rev. Sunil Weerasinghe (60). “Every Sunday we proclaim God’s Word and His love, and we encourage people to live in peace with their neighbors. Most people in our congregation are a low income earners. There are only a few middle class families. In the pastour church helped people find work or start their own small businesses. After all, it is better teach someone to fish than give him fish.” Rev.Weerasinghe laments: “Methodist Church of Sri Lanka nowadays have no funds for such self-employment projects.
In evening of that Sunday, I met Rev. Shirley Faber (61),President of the Christian Reformed Church of Sri Lanka (formerly known as the Dutch Reformed Church in Sri Lanka ) at his residence in Dehiwala, a suburb of Colombo. It is the oldest Protestant denomination in the Island founded by the Dutch East India Company in 1642. The Christian Reformed Church which had around 200,000 members by the end of the Dutch colonial rule in the maritime provinces of Sri Lanka in 1796, is today one of the tiniest Christian denominations today with a membership of approximately 6000 people. Speaking of ecological and social concerns, Rev. Faber said: “The mandate of the Christian Churches is not only to preach the Gospel but also to show Christian concern and love for people and the love for God’s creation. God created the world and handed over the control of His beautiful creation to the human beings. We ought to know that we are only the stewards of His creation. As stewards of His creation, we should display good stewardship. We are accountable to God as to how we utilize the resources in His creation. The Churches should show its concern for ecological and social issues. In our society, wealth and resources are unfairly distributed. During the Covid-19 crisis, our church helped both Christians and non-Christians. We should show our love for people regardless of their religion not with the motive of converting them to Christian faith’.
 As for the theological challenges, Rev. Faber is of the view that some charismatic Pentecostal churches which promote and propagate the ‘new theology of prosperity’ (health and wealth), poses a challenge in that they entice the less informed members of mainline Christian churches to join them by their controversial teachings.
As for the theological challenges, Rev. Faber is of the view that some charismatic Pentecostal churches which promote and propagate the ‘new theology of prosperity’ (health and wealth), poses a challenge in that they entice the less informed members of mainline Christian churches to join them by their controversial teachings.
Easter Sunday Attacks : Seeking Justice
On 21 April 2019, Easter Sunday, three churches (two Catholic and one Evangelical Pentecostal) and three luxury hotels in Sri Lanka, Colombo, were attacked in a series of terrorist suicide bombings launched by a local Islamic extremist terrorist group which had embraced the ideology of ISIS. A total of 267 people were killed including at least 45 foreign nationals and eight bombers, and at least 600 were injured. Among those who were killed and injured, there were many children and women. The church bombings were carried out during Easter worship services in St. Sebestian’s Church, Katuwapitiya in Negombo, St. Anthony’s Church in Colombo and Zion Pentecostal Church in Baticaloa.
Out of the 267 people killed and 600 injured, about 221 killed and an overwhelming majority of the injured were Christians attending Easter Services in the three churches. On April 21 last year, Easter Sunday, a series of suicide bomb attacks launched by a local extremist Islamic group which has embraced the ISIS ideology inside three churches and three luxury hotels in Sri Lanka. Out of the 267 people killed and 600 injured, about 221 killed and an overwhelming majority of the injured were Christians attending Easter Services in the three churches. On April 21 last year, Easter Sunday, a series of suicide bomb attacks launched by a local extremist Islamic terrorist group which has embraced the ISIS ideology inside three churches and three luxury hotels in Sri Lanka. “The impact of the attacks is still noticeable. Christians seek justice for the victims and their next of kin, “says Rev. Dr. Noel Dias, a Catholic priest, a former Senior Lecturer in Public International Law at the University of Colombo and an Attorney-at–Law, who resides at the Archbishops’ House of Colombo.
Rev. Dr. Noel Dias remarked: “The leadership of the Catholic Church played a decisive role in containing the probable escalation of retaliatory violence against the Muslim community by appealing to her faithful not to retaliate but to forgive the attackers in a true Christian spirit. The Easter terror attacks have left a lasting impact on Christians. They are still seeking justice for the victims and their families.” These concerns are echoed every day by the Christians and other people in Sri Lanka and abroad. Mr. Mike Pompeo, US State Sectary who was on an official visit to Sri Lanka on the 27th and 28th October, did not forget to place a wreath at St. Anthony’s Church in Colombo on 28 th October 2020. In his Twitter, Pompeo said: “Today, I laid a wreath at the Shrine of St. Anthony, one of the sites of the 2019 #EasterAttacks which killed and injured hundreds of innocent people. We stand with the Sri Lankan people and the world to defeat violent extremism and bring perpetrators to justice.”
 There are some questions that remain to be answered. The most important of them all is: Why didn’t the Sri Lanka’s authorities in charge of security who had repeatedly received prior foreign intelligence reports about these terror attacks and the suicide bombers during the two weeks prior to the attacks, take appropriate action to arrest the suicide bombers and prevent them? The investigations including a concluded Parliamentary Select Committee inquiry and an on-going Presidential Commission Inquiry have not yet conclusively answered these questions even after one and a half years. Suspected perpetrators have so far been indicted in the High Court for trial in connection with the Easter attacks.
There are some questions that remain to be answered. The most important of them all is: Why didn’t the Sri Lanka’s authorities in charge of security who had repeatedly received prior foreign intelligence reports about these terror attacks and the suicide bombers during the two weeks prior to the attacks, take appropriate action to arrest the suicide bombers and prevent them? The investigations including a concluded Parliamentary Select Committee inquiry and an on-going Presidential Commission Inquiry have not yet conclusively answered these questions even after one and a half years. Suspected perpetrators have so far been indicted in the High Court for trial in connection with the Easter attacks.
As for the spiritual challenges posed by the Easter Attacks, Rev. Dr. Noel Dias said: “The martyrdom is the seed of the Church. These challenges remind us of what C. S. Lewis once said: ’Pain insists upon being attended to. God whispers to us in our pleasures, speaks in our consciences, but shouts in our pains. It is his megaphone to rouse a deaf world.’
Speaking of the role of the Catholic Church in pastoral care, Rev. Dr. Dias opined: “Catholic Church is in the fore-front of organized pastoral activity, which performs very well in the educational and social service sectors. There is a great need for pastoral care in terms of building a rapport between the clergy and the laity. In terms of political involvement, Catholic Church in Sri Lanka does not get involved in party politics but raises her voice and concern when the occasion demands justice and reasonableness in the political and social context. In the perspective in theology, the church should refrain from being elitist. External pomp, over emphasis of material structures must be moderated. There is a greater need in this direction. In terms of fostering family relationships, Catholic Church is better organized than the other religious denominations. However, there is still an urgent need to address issues like pornography, drug and alcohol addiction etc.”
Voices of the Lay Christians:
Aruna Silva (50), a father of six children, who earns his livelihood as a three-wheeler taxi driver and a painter of motor vehicles said: ” I was born and bred as a Methodist. I moved to this area in 1995 and joined this congregation. There is religious freedom in the country. There were a few occasional isolated incidents of religious violence against Christian churches by a few extremist groups.” Aruna opined: “I believe that the persuasive and aggressive forms of evangelism used by some evangelical Pentecostal churches disregarding sensitivities of other religions, at times though not always, may have provoked the extremist elements to attack Christian places of worship in some rural areas”.
Naveen, a 20 year old young undergraduate student in Information Technology who is a member of this Methodist congregation at Kalutara said: “I am proud to be a Christian in Sri Lanka as it gives me a unique privilege to show my Christian testimony to non-Christian brothers and sisters by my words and deeds of love. Our good deeds would speak louder than our words. In order to help the poor people to improve their economic conditions, the church should first identify their skills and help them to earn an income in the areas they are so skilled”.
Janice Benjamin (32) is a young educated Catholic mother of five children, housewife and an active member of the Catholic movement known as “Neocatecumenal Way” founded by Kiko Argüello, a Spanish artist and Carmen Hernández in 1964. She lives in Colombo and is a member of St. Lawrence’s Church there. Janice strongly believes that “Satan is waging his final war against the family”. Says Janice, “I personally see how it is absolutely true in the context of the Church here. Many Catholics, I believe, are not given proper and adequate instructions on the Catholic Church and its history, its rich teachings, and as such it is very obvious to see the prevalence of many attacks on the family. The Neocatecumenal Way is a tiny minority within the Catholic Church. In the Neocatechumenal Way, we are given a lot of insight on the teachings of the church and the Bible particularly on marriage, family, children, contraception, abortion, and homosexuality. It is very sad to see only a minority in the church practice the official teaching of the Church on these issues. Many would go with the tide and agree with the modernist views of society. Sadly, many of my friends say that unless the Church adapts to the modern trends, it will lose its members.”
The Neocatecumenal Way of which Janice is a member, promotes the idea of having children as many as possible. Says Janice: As a young mother of five children, I would say that it is definitely a challenge for me to raise my five kids in a society which considers having more than one or two children is old fashioned and stupid. There are struggles economically, and physically and it is draining our energy and resources. But in the midst of all these I see the love of God resonates in my family of five children who are a blessing from God.”
Speaking of the most important reform needed in the Catholic Church, Janice opined: “In my opinion, the Catholic Church in Sri Lanka has to be more vocal in its teachings. The Church should do more to inculcate the rich traditions and values in her faithful, younger generations and children. The teachings of the church and the Bible should be slowly introduced to the children not in a moralistic and legalistic sense but in a way of showing them that this is how the Love of God is reflected.”
Professor Rathnajeevan Hoole (68) is a member of the Anglican Church in Sri Lanka. He belongs to the congregation of St. James’ Church in Nallur, Jaffna, his native place in the Northern province of Sri Lanka chiefly inhabited by Sri Lankan Tamils. Professor Hoole, is a former Senior Professor of Electrical Engineering at the University of Peradeniya and State University of Michigan. He is well known for his role as one of the three members of Sri Lanka’s Election Commission. Professor Hoole’s father was an Anglican clergyman. Professor Hoole has served as a member of the Diocesan Council of the Colombo Diocese of the Anglican Church in Sri Lanka for several years. A When interviewed by me, Professor Hoole expressed his concerns about the general level of education prevalent among the pastors in the Anglican Church of Sri Lanka and in other non-Catholic churches. Said Professor Hoole: “The educational standards of our protestant pastors have deteriorated over the last few decades. Pastors of non-Catholic mainline churches (except the pastors of Christian Reformed Church) are trained at Pilimatalawa Theological College where liberal theology is taught, while the pastors of evangelical free churches and Christian Reformed Church receive their theological education from evangelical/Pentecostal seminaries. The most important reform required is to groom educated Protestant pastors. Many Anglicans and other non-Catholic Christians seem against or ignorant of the creeds and Catholic side of our faith. The free churches even think the Lord’s Prayer is Roman Catholic. So unsatisfactory is our theological education. They think transference from Roman Catholicism is conversion. Most of the educated Jaffna Tamil Christians left Sri Lanka and settled down in the western countries during last six decades due to the ethnic tensions and a 30 year Civil War that ended in 2009”.
The Catholic Church in Sri Lanka and worldwide maintains very high and uniform educational standards for its clergy. In order to become a Catholic priest, a seminarian should first read for a Bachelor of Philosophy degree awarded by Gregorian University or Urban University of Rome in English medium after his General Certificate of Education (Advanced Level)-Sri Lanka’s matriculation examination. In addition to this a seminarian is required to read for a second degree of Bachelor of Theology awarded by one of these two universities. These degree are recognized by the university grants Commission of Sri Lanka and universities throughout the world.
Amidst all the challenges, the significant contributions of Christianity to the social and moral development of Sri Lankan society in some aspects remain highly significant. The most significant and prominent among such legacies is the formal educational system of primary and secondary schools in Sri Lanka. It is a lasting legacy of Christian missionaries. The missionaries of mainline Christian denominations (Catholic and non-Catholic) were responsible for introducing a formal modern educational system by establishing their respective networks of schools throughout the iIsland increasing the literacy of the people. The non-Christians were the largest beneficiaries of the Christian missionary school system. The leaders of Buddhist, Hindu and Muslim communities who had received their education from the Christian missionary schools later established Buddhist, Hindu and Muslim school networks on the lines of the Christian missionary school model in the last quarter of the 19th century and in the first half of the 20th century. The British colonial government provided financial aid to both Christian and non-Christian school networks. The Christian missionary school networks served as the models for both State and non-Christian schools. The Catholic and Protestant Churches were the pioneers in establishing Reformatories for juvenile offenders, Schools for the Blind and Deaf, children’s homes, elders’ s homes, hospitals and industrial schools for young persons etc. The concept of monogamous marriage was introduced to Sri Lanka by Christian colonial rulers and missionaries. It is now a well accepted and entrenched concept among the Buddhists and Hindus. Christian influence can also be seen in wedding ceremonies and funerals and in other moral and social aspects too.
Features
Stock market dynamics: Fundamentals, Expectations and Perceptions
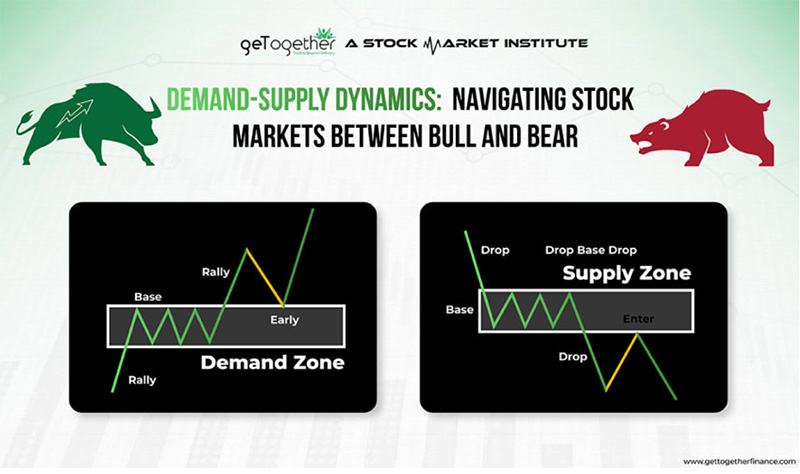
 The stock market serves as a nexus where millions of buyers and sellers converge to engage in transactions. At its core, each transaction represents an agreement between a buyer and a seller, with the central element being the price. This price is not static; it fluctuates continuously, reflecting the equilibrium between supply and demand.
The stock market serves as a nexus where millions of buyers and sellers converge to engage in transactions. At its core, each transaction represents an agreement between a buyer and a seller, with the central element being the price. This price is not static; it fluctuates continuously, reflecting the equilibrium between supply and demand.
The conventional belief posits that the interplay of supply and demand in the stock market is predominantly influenced by the fundamental factors inherent to individual companies. These factors encompass a range of critical aspects, including profitability, stability, future strategic plans, and the competency of management teams.
Consequently, share prices and index levels serve as barometers of the collective sentiment and expectations of market participants regarding the future trajectory of companies and the broader market. These prices are not mere numbers; rather, they represent a synthesis of myriad factors, including investors’ perceptions, assessments, and anticipations.
Expectations and perceptions
When buyers and sellers converge in the stock market, each transaction reflects not only the current value of a company but also the perceived future potential. As investors assess various factors, such as company performance, industry trends, economic indicators, and geopolitical events, they form expectations about how these factors will impact future earnings and growth prospects. And these perceptions often vary widely, reflecting diverse interpretations of available information and differing outlooks on the potential outcomes.
These perceptions are then manifested in the bids and asks that drive share prices and index levels. If investors anticipate robust growth and profitability for a company, they may bid up its share price, reflecting optimism and confidence in its future prospects. Conversely, perceived negative sentiment or concerns about the company’s outlook may lead to downward pressure on its share price.
Share prices and index levels, such as All Share Price Index (ASPI), serve as indicators of how investors collectively view the market. As they consider factors like the economy and global events, their expectations for future market performance are reflected in these measures. Essentially, they represent the combined opinions and outlooks of investors, incorporating both current information and future predictions. This consensus is always changing as new data emerges and sentiment shifts. Therefore, these indicators are not fixed but rather reflect ongoing discussions and reactions among market participants.
Long-term investing in the stock market entails placing perceived confidence in a company’s prospects over time. However, whether driven by past performance, societal concerns like climate change or political stability, or sheer speculative sentiment (short-term focused), buyers anticipate that share prices will increase.
However, these perceived expectations are not always realized, potentially prompting investors to become sellers. This decision, too, is often driven by the perception that anticipated prospects may not materialize as expected.
Future expectations serve as the linchpin for daily market activities, shaping the equilibrium of opinions on a company’s trajectory. Yet, share prices are not isolated from external influences; they reflect investors’ perceptions relative to the company’s performance and broader market sentiments. The pervasive fear of missing out often prompts investors to make impulsive decisions, chasing returns and disregarding rational assessments. However, smaller markets, like the Colombo Stock Exchange, have often been susceptible to manipulation by a select few prominent players, as noted by stock brokers, fund managers, and investment advisors.
When to enter the market
Interestingly, shares often rally ahead of economic upturns, creating a dissonance between market performance and day-to-day economic realities. Perception may paint a rosy picture, making investment decisions seem obvious in retrospect. However, market timing remains an arduous task, requiring foresight and conviction amid prevailing sentiments.
Learning from investment mistakes is pivotal for personal growth and financial success. Detaching ego from errors fosters introspection and prevents recurrence. Avoiding perception bias is imperative, as it distorts learnings of past decisions. Writing down experiences facilitates reflection and rational analysis, aiding in the development of effective investment strategies centered on disciplined processes.
Diversification; Risk management
Diversification, as advocated by Warren Buffett, offers protection against ignorance but remains a contentious subject. While concentrating investments in a single promising asset theoretically maximizes returns, it also heightens risks. Notably, founders or controlling shareholders wield informational advantages, contrasting with minority investors subject to regulatory disclosures. Hence, inherent risks accompany stock trading. The late Dr. Lalith Kotelawela, for instance, refrained from stock market involvement for himself and his companies, equating share trading with gambling.
Instances like Enron’s collapse underscore the multifaceted risks inherent in investing, from fraud to unforeseen macroeconomic upheavals. Diversification mitigates single-security risks, safeguarding portfolios against adverse events. However, ignoring diversification in pursuit of concentrated gains poses perilous consequences.
Overtrading, driven by short-term fixations and market noise, undermines long-term investment success. Emphasizing present circumstances overlooks the enduring impact of macroeconomic trends on market performance. Maintaining perspective and focusing on long-term fundamentals are crucial for navigating market volatilities and achieving sustainable growth.
Therefore, the stock market embodies the amalgamation of perceptions on expectations, sentiments, and uncertainties. Investors must recognize the transient nature of market dynamics, learning from past mistakes and adhering to disciplined investment strategies. While concentration may offer lucrative prospects, diversification remains a prudent risk management approach. Ultimately, maintaining a long-term perspective amidst short-term fluctuations is paramount for realizing enduring investment success.
Bear and Bull markets
The stock market, a bustling arena where investors and speculators converge, showcases a remarkable sensitivity to short-term stimuli. In pivotal market years, investors frequently succumb to timing mistakes, selling in the aftermath of bear markets and buying amid bull markets. Selling in bear markets and buying amid bull markets refers to a common behavioral pattern observed among investors.
During bear markets, characterized by declining stock prices and widespread pessimism, investors often feel compelled to sell their holdings out of fear of further losses. This behaviour is driven by a desire to mitigate losses and preserve capital. However, selling during bear markets can lead to missed opportunities for future gains, as markets often rebound after periods of decline.
Conversely, in bull markets, where stock prices are rising, investor perceptions tends to be optimistic, and confidence in the market is high. During these periods, investors are more inclined to buy stocks in anticipation of further price appreciation. This behaviour is driven by a fear of missing out on potential gains and a belief that the upward trend will continue. However, buying in bull markets can also be risky, as it may result in purchasing stocks at inflated prices.
Conclusions
Overall, the tendency to sell during bear markets and buy during bull markets can be attributed to emotional responses to market conditions, rather than rational decision-making based on fundamental analysis. As a result, investors may inadvertently buy high and sell low, thereby underperforming the market over the long term.
Furthermore, understanding the direct link between investment strategies and long-term goals is paramount. Properly defining goals enhances the alignment between assets and objectives, reinforcing the resilience of investment portfolios against short-term fluctuations.
Ultimately, gaining perspective on economic data and market movements is essential. While short-term fluctuations may induce anxiety, their significance in the grand scheme of long-term financial goals is often negligible. Just as recalling the minutiae of Central Bank actions from a decade ago holds little relevance today, current market gyrations are unlikely to alter the trajectory of well-defined investment strategies over the long term.
Finally, navigating the intricacies of the stock market demands a steadfast commitment to long-term investing principles. By transcending short-term noise and anchoring decisions on fundamental values and overarching goals, investors can weather market volatility and chart a course towards enduring financial success.
(The writer, a senior Chartered Accountant and professional banker, is Professor at SLIIT University, Malabe. He is also the author of the “Doing Social Research and Publishing Results”, a Springer publication (Singapore), and “Samaja Gaveshakaya (in Sinhala). The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the institution he works for. He can be contacted at saliya.a@slit.lk and www.researcher.com)
Features
Justice does not require a mandate

by Jehan Perera
On April 21, the country passed the fifth year anniversary of the Easter Sunday bombing that took the lives of about 300 persons and injured and maimed many more. The bombers targeted Catholic and Christian churches on Easter Day, sacred to Christians, which were filled with devotees at the time of the attacks. The bombers had emerged out of the blue as it were, there were questions whether Sri Lanka had become a site of a global battle and uncertainty that others might strike again. For two months, the capital city of Colombo almost shut down as people lived in fear. The bombing also changed the course of national politics. It paved the way for nationalist politicians whose promise was the guarantee of national security and the rightful place of the ethnic and religious majority.
Today, the memory of those events has receded from the consciousness of most people. But the impact of the bombing has been lasting. The economic setback due to foreign investors and tourists giving Sri Lanka a wide berth was to pave the way to the economic bankruptcy due to the corruption and mis-management of those who won the elections that the country is yet to overcome. Equally lasting, and perhaps more destructive has been the erosion of trust in the present and past government leaderships in the face of its unwillingness to find the truth and hold to account those who planned the attacks and those who chose not to defend against the attacks even when forewarned by foreign and local intelligence services. There is a widespread feeling in the country today that the wrongdoers are being protected.
The effort of the Catholic Church in the country to canonize those who died, to either elevate them to sainthood or martyrdom is an attempt to keep the issue of the mass killing alive both nationally and internationally. There have been international precedents for this. Examples are the Vietnamese Martyrs or the Japanese Martyrs of the 16th century which became internationalised through the Catholic Church. Cardinal Malcolm Ranjith said the Church will take the first step to collect signatures from the Catholic community countrywide to be sent for to Rome for Papal recognition. “Because once we declare them as ‘Heroes of faith’, the international community will come to recognise them more and more and it will become an international matter.” Cardinal Malcolm Ranjith has been resolute in being up there in front, voicing the sentiments of the bereaved families for justice in public protest on the road or by lobbying with national leaders and the international community.
WITHHOLDING INFORMATION
There have been several official inquiries into the trail of events that led to the Easter bombings. A couple of those who held senior positions in the security establishment even had to go to prison for a while and others have been subjected to heavy fines for their dereliction of duties. But still the sense that there has been a cover up is strong. The passage of time has brought forth more evidence of a cover up. There are objective facts that can be verified and cannot be hidden. Members of the intelligence community and the police in Sri Lanka whose investigative capacities have been seen on innumerable occasions would surely have evidence of what truly happened. It is therefore only a matter of time when the truth comes to light.
It was only two weeks ago that the Catholic Church was provided the full report of the presidential commission that investigated the bombing. The report they had previously been given, and that too after a long delay had an estimated 1500 pages removed from it. The next phase of the quest for justice will need to await a new government. The direction to ascertain the truth does not require a people’s mandate in the same way that deciding on a new economic direction might require. Justice is fundamentally concerned with the fair and equitable treatment that is not dependent upon popular opinion or electoral mandates but is grounded in universal ethical norms and legal standards. The reason that a new government is needed is when those in the government have vested interests in not disclosing the truth and not rocking the boat they are in.
Following his visit to the police Criminal Investigation Department for questioning, Fr Cyril Gamini Fernando, the spokesperson of the Archdiocese of Colombo openly said uncovering the truth behind the Easter Sunday attacks depends on a change in the political system. He mentioned that he has appeared before the CID on multiple occasions and has provided detailed statements. Despite this, there was a lack of a substantial investigation based on the information he has shared. He expressed scepticism about the government’s commitment to uncovering the masterminds behind the Easter Sunday attacks, which led to his conclusion about the need for a change in the political system.
NEW GOVERNMENT
The events of Easter 2019 are sharpest in the memory of the Christian community in Colombo and Batticaloa where the churches were bombed. At the same time, it needs to be kept in mind that the loss of life that took place that day is dwarfed by the events that took place elsewhere and at other times. If the Christians and their leadership keep on remembering and not giving up on the quest for justice, it can be imagined that those who have lost even more would also be determined to remember and not give up on their quest for justice. In May 2009, the three decade long internal war ended very bloodily on the battlefields of the north with the defeat of the LTTE and killing of its leaders in circumstances that are not fully known to most people to this day.
The events of May 2009 are not the only ones in which mass killings took place. Twenty years earlier in 1989, the JVP was defeated and its leadership was also killed. There was an orgy of violence in which tens of thousands of people were killed. As in the case of the LTTE, the decimation of the JVP took place in circumstances that were kept beneath the surface and in which the killings took place not only on one side but on multiple sides. Many novels have been written about those periods of large scale violence, about the torments of the victims and their families and the ghouls who put them to death. This is the reason why those who seek to promote the reconciliation process urge that there should be a process of transitional justice, in which truth, accountability, reparation and a political solution are brought to bear.
Last week the National NGO Secretariat organised a meeting between civil society organisations engaged in the national reconciliation process and government mechanisms. There was a spirit of positive engagement and problem solving in the discussions with the Office on Missing Persons, the Office for Reparations, the Office for National Unity and Reconciliation and the interim secretariat for the Commission on Truth, Unity and Reconciliation that is being formed. The draft of the Truth Commission law does not yet deal with issues of the JVP period and the Easter bombing which are lacunas. There is a need for a system change that the Catholic Church and Fr Fernando have openly called for, which would come through elections to get rid of the blocks to the quest for justice and the national reconciliation process.
Features
Five Hindrances in Buddhism

 by Dr. Justice Chandradasa Nanayakkara
by Dr. Justice Chandradasa Nanayakkara
Nyanaponika Thera in his Buddhist writings states: “unshakable deliverance of the mind is the highest goal in Buddha’s doctrine. Here deliverance means; the freeing of the the mind from all limitations, fetters, and bonds that tie it to the Wheel of Suffering, to the Circle of Rebirth. It means cleansing the mind of all defilements that mar its purity; removing all obstructions that impede its progress from the mundane (lokiya) to the supermundane consciousness (lokuttara citta) that is, to Arahatship.
Life’s spiritual path is paved with many hindrances and obstacles. Out of those many obstacles, Buddhism stresses five recurring hindrances (Nivaranas) that impede a person’s spiritual progress. They are (1) Sensual desires (Kamachanda) derived from gratification from the five senses of sight, sound, smell, taste, and physical sensation. (2), Ill will (Vyapada) feelings of hostility, resentment, hatred, and bitterness. (3), Sloth and Torpor (Thina Middha) halfhearted action with little or no effort or concentration (4), Restlessness and Worry (Uddachha Kukucha) inability to have a composed mind and focus one’s energy. (5), Skeptical Doubt or Indecision (vickiiccha) lack of conviction or trust in one’s abilities. These five hindrances are potent negative forces in the mind that make a person lose mindfulness, hinder his ability to see things as they are and become mentally focused and concentrated. Moreover, the five negative states of mind prevent a person from seeing clearly and making the right decisions and derail him from his spiritual path to liberation. These hindrances are forces of distraction encountered by a person engaged in meditative practice and his daily life. They prevent the development of concentration (Samadhi) which is a cornerstone of the path to liberation from suffering. It is only by constant and earnest efforts that the harmful influence of the five hindrances could be avoided. The Buddha using analogy stated that the mind with five mental hindrances is comparable to gold contaminated with five impurities such as iron, copper, tin, lead, and silver which make the gold not pliant, wieldy, or luminous but brittle and cannot be wrought well. But the mind that is free from such hindrances will be malleable wieldy, luminous, and pliant and be able to concentrate properly by eradicating mental impurities and attain wisdom. It is believed the five mental defilements (kileses) are not inherently wrong as they can provide opportunities for deeper insights into the nature of life’s suffering, compassion, and deliverance. The hindrances occur to a greater or lesser extent in every person.
The first hindrance, sensual desire is the craving derived from the gratification of our five senses: sight, sound, smell taste, and touch. It is normal for an average person to get tempted by alluring sensual objects. Lack of self-control results in the inevitable arising of passions. They arise from positive emotions associated with our senses but tend to cause us to lose track of our goals.
It is in the very nature of sensual desires that they can never be satisfied as the mind is constantly detecting objects that are coming in through our five senses. There is no end to the seeking of our enjoyment of pleasurable objects and their sensation. These sensual objects arise and disappear as do all other phenomena. Once you enjoy them you are left with the same unsatiated desires for more gratification. As soon as a person experiences one object of sensual delight rather than finding contentment and satisfaction from it, he becomes obsessed with new desires. A person who is obsessed with sensual pleasures assumes that happiness consists in submitting to the dictates of sensual desires but real happiness eludes him as craving for sensual pleasures becomes insatiable. This drives him to ceaseless pursuit of new sensual gratification. When the mind is attached to sensory experience it gives rise to too many attachments in the world and it becomes completely entangled in worldly ways and you become so trapped in delusion that you cannot see things in their true perspective. Attachments to sensual objects increase our greed, clinging and grasping, and keep us bound to the wheel of samsara. Although the five hindrances cannot be eradicated before achieving stages of Awakening they can be lessened to a great extent through mindfulness. The misconception that buddhism gives an unfair valuation to sensual pleasures, to the neglect of their positive aspects is not sustainable as the Buddha never dismissed sensual desires outright but admitted that sensuality can give a person a certain measure of happiness and satisfaction. But he declared that happiness based purely on sensuality is ephemeral and shortlived. It is the constant pursuit of sensory pleasures that bars inner peace, and mindfulness distracting us from our spiritual goals. that Buddhism does not approve of. Seeking pleasure is natural but excessive craving can tether us to the wheel of samsara preventing deeper spiritual fulfillment. When that happens the hope of reaching the end of suffering would become dismal until you overcome the sensual desires that cloud your mind.
Antidotes to sensual desires include renunciation turning away from distracting stimuli, and investing the experience of desire with mindfulness that clouds our mind and prevents us from seeing the true nature of things. Similarly, when we are overcome by sensual desires we should reflect and meditate on the true nature of our life and its ephemerality, and one day we are all going to end up as decaying corpses. This kind of reflection weakens lustful thinking as we realize the imminence of our death (Joseph Goldstein). Regarding sensual desires arising out of taste, a person is expected to indulge in moderate consumption of food solely for maintaining and sustaining the body not for enjoyment, beautifying, or adorning the body. Association and maintaining friendships with wise and noble friends also tend to mitigate sensual desires.
The second hindrance ill-will is characterised by negative emotion towards a person, object, or situation. It refers to feelings of resentment, anger, and hostility. it is an unwholesome mental state that wishes harm and misfortune on others. It clouds our judgment, prevents us from looking at situations from their true perspective, and hampers our ability to feel compassion and empathy. A specific way of dealing with ill will when it is overpowering is to generate loving thoughts, wishing happiness, and love to all beings everywhere and the specific person towards whom you direct your anger. Although, initially, you may find it difficult to cultivate those wholesome thoughts eventually anger is bound to dissipate and the mind becomes calm and collected. Another insightful way of dealing with anger and aversion is to reflect upon the law of karma and understand that we are all heirs to our actions. Kamma is an immutable law of cause and effect and we cannot avoid the consequences. The underlying intentions behind our actions determine the nature of their results.
The third hindrance is sloth and torpor are a compound word that combines both the emotional and somatic aspects of excessively low energy. It is a morbid state of the mind that refers to physical laxity, mental dullness, and callous indifference. It can manifest as sleepiness, a lack of motivation, and depression. It should not be understood as bodily drowsiness, because Arahhants who have conquered these two states, also experience bodily fatigue. (Narada). An antidote for strong sloth and torpor would be refreshing the body by giving it a rest so that our mind becomes clear-headed and focused. Engaging in walking meditation and vigorous bodily movement will also act as an antidote.
The fourth hindrance is restlessness and worry. It is another impediment to spiritual progress. Here the restless mind is likened to flustered bees in a shaken hive so that the mind cannot concentrate and focus on wholesome things. Moreover, an agitated and flustered mind prevents calmness and blocks the spiritual path. Similarly, worry is just as detrimental. People who worry over one thing and another, over things done or left undone, and over misfortunes, are unable to have peace of mind. These unwholesome states of mind prevent concentration.
The fifth and last hindrance is skeptical doubt. It refers to a loss of trust and faith in Dhamma. There are two types of doubt. An unhealthy and unwholesome doubt that undermines a person’s spiritual practice, and a healthy doubt that informs the spiritual practice. A person entertaining healthy doubt should seek intelligent clarification and investigation of Dhamma as Buddha expounded in Kalama Sutta, while a person nursing unhealthy doubt is so prejudiced and cannot be convinced by any reasoning. A person engaged in meditative practice sometimes tends to evaluate his practice pondering constantly whether any benefit would accrue to him by it. Any doubt and lack of confidence entertained by a person in this regard is bound to impede his spiritual practice. When a doubt arises in a person, it is important to recognise it as a doubt and realise that it is constantly changing. Another way to resolve a doubt concerning meditative practice is to seek clarification from a knowledgeable teacher. Any doubt entertained about any person or matter can evidence itself in a person’s behaviour and conduct, as a result of his unsettled state of mind.
In brief, to subdue the hindrances a person has to develop five psychic factors known as jhana. Sense desire is subdued by ekagatta one-pointedness or unification of the mind. Ill will by joy (piti) sloth and torpor by applied thought (vittakka) restlessness and worry by happiness (sukha) and doubt by sustained thought (vicara) Psychic factors raise a meditative person from lower to higher levels of mental purity (Piyadassi).
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoCEAT Kelani launches three new radial tyre variants in ‘Orion Brawo’ range
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoDialog-Airtel Lanka merger comes centre stage
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoCeyline Travels and MBA Alumni Association of University of Colombo sign MOU
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoSLFEA appoints JAT as a Facilitation Partner for training painters to provide overseas employment opportunities
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoHayleys Fabric celebrates triple triumph at ISPO Textrends Spring/Summer 2026
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoUrgent appeal from Sri Lankan exporters on rupee appreciation
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoHello Madras, ‘ai api kaluda?’
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoMaldivian to launch direct flights to Colombo